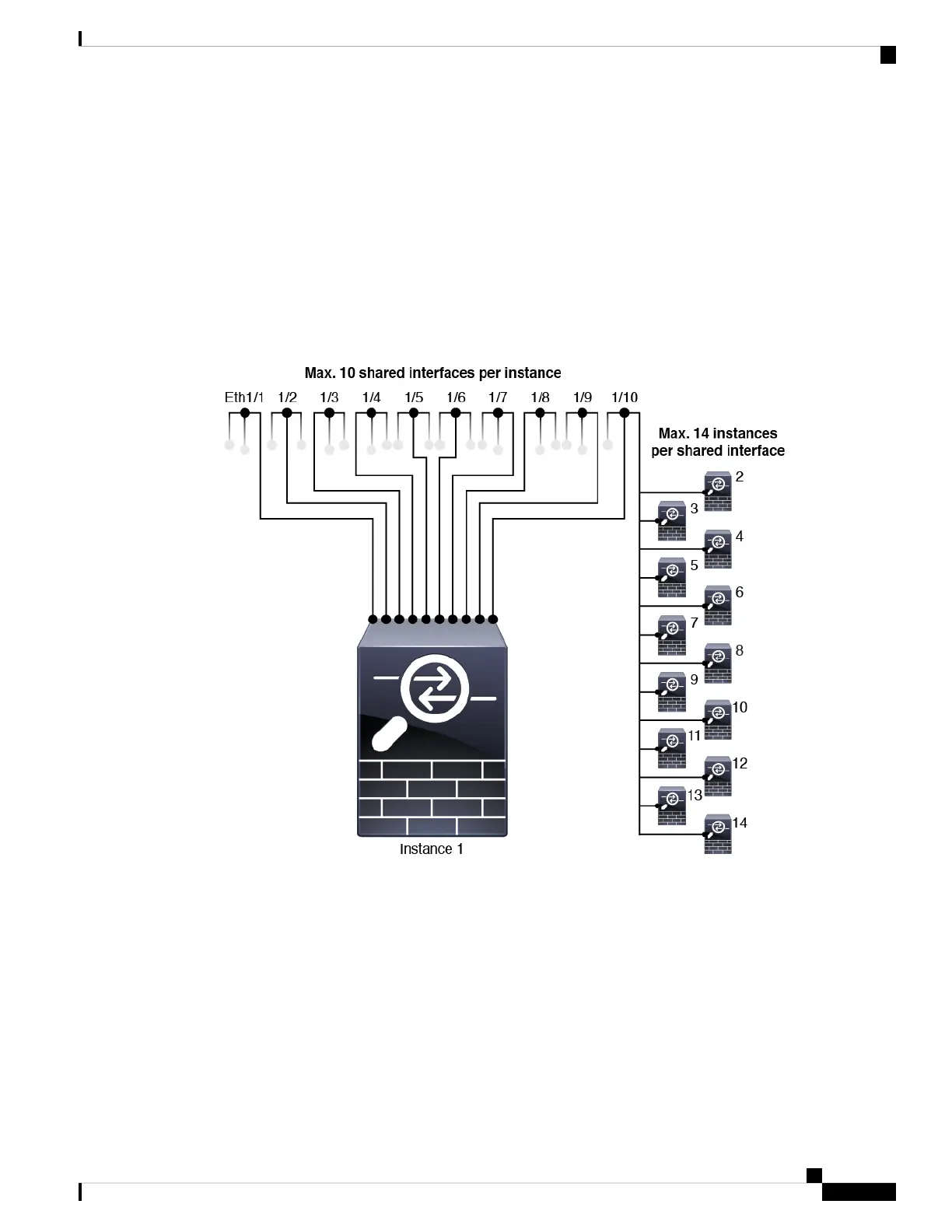
Shared Interface Scalability
Instances can share data-sharing type interfaces. This capability lets you conserve physical interface usage as
well as support flexible networking deployments. When you share an interface, the chassis uses unique MAC
addresses to forward traffic to the correct instance. However, shared interfaces can cause the forwarding table
to grow large due to the need for a full mesh topology within the chassis (every instance must be able to
communicate with every other instance that is sharing the same interface). Therefore, there are limits to how
many interfaces you can share.
In addition to the forwarding table, the chassis maintains a VLAN group table for VLAN subinterface
forwarding. You can create up to 500 VLAN subinterfaces.
See the following limits for shared interface allocation:
Shared Interface Best Practices
For optimal scalability of the forwarding table, share as few interfaces as possible. Instead, you can create up
to 500 VLAN subinterfaces on one or more physical interfaces and then divide the VLANs among the container
instances.
When sharing interfaces, follow these practices in the order of most scalable to least scalable:
1. Best—Share subinterfaces under a single parent, and use the same set of subinterfaces with the same
group of instances.
For example, create a large EtherChannel to bundle all of your like-kind interfaces together, and then
share subinterfaces of that EtherChannel: Port-Channel1.2, 3, and 4 instead of Port-Channel2,
Multi-Instance Mode for the Secure Firewall 3100
5
Multi-Instance Mode for the Secure Firewall 3100
Shared Interface Scalability
 Loading...
Loading...











