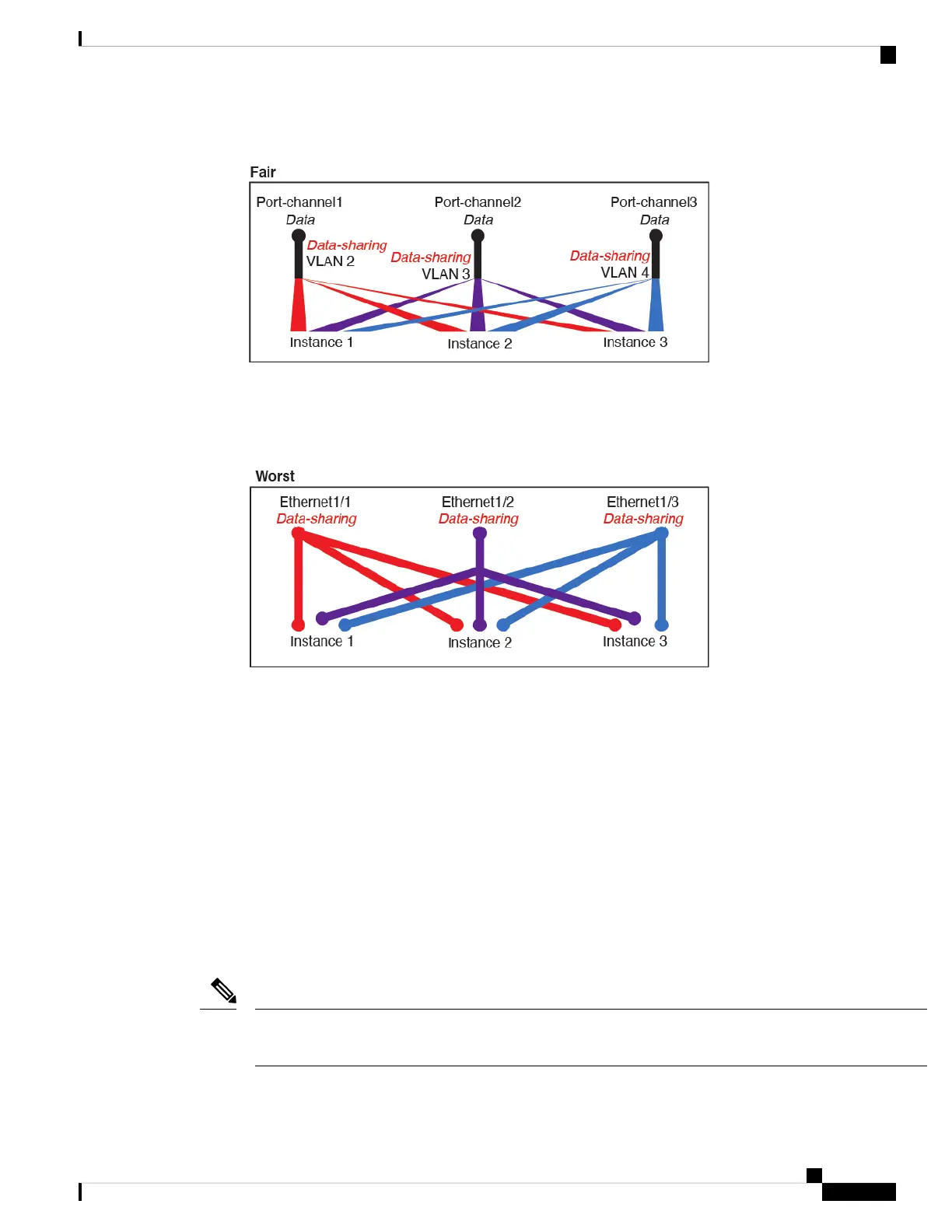
Figure 4: Fair: Shared Subinterfaces on Separate Parents
3. Worst—Share individual parent interfaces (physical or EtherChannel).
This method uses the most forwarding table entries.
Figure 5: Worst: Shared Parent Interfaces
How the Chassis Classifies Packets
Each packet that enters the chassis must be classified, so that the chassis can determine to which instance to
send a packet.
• Unique Interfaces—If only one instance is associated with the ingress interface, the chassis classifies the
packet into that instance. For bridge group member interfaces (in transparent mode or routed mode),
inline sets, or passive interfaces, this method is used to classify packets at all times.
• Unique MAC Addresses—The chassis automatically generates unique MAC addresses for all interfaces,
including shared interfaces. If multiple instances share an interface, then the classifier uses unique MAC
addresses assigned to the interface in each instance. An upstream router cannot route directly to an
instance without unique MAC addresses. You can also set the MAC addresses manually when you
configure each interface within the application.
If the destination MAC address is a multicast or broadcast MAC address, the packet is duplicated and delivered
to each instance.
Note
Multi-Instance Mode for the Secure Firewall 3100
7
Multi-Instance Mode for the Secure Firewall 3100
How the Chassis Classifies Packets

 Loading...
Loading...











