SM-A20758-A/3 7. References
63 2020-10-06
◼ EVD-3000
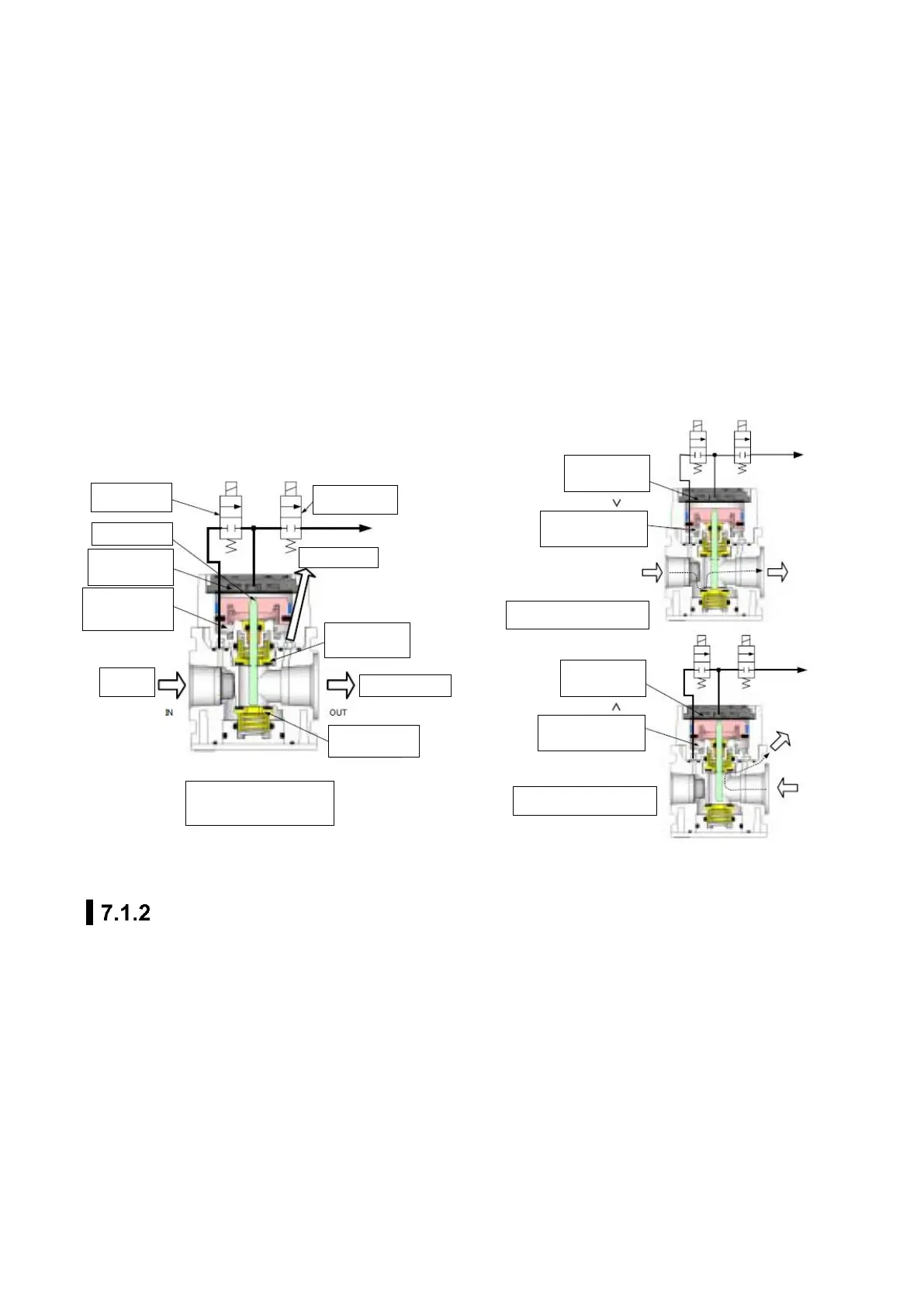
The EVD-3000 series includes the pilot control section described above and a booster section for
improving flow characteristics. The booster section includes an air supply valve (top valve), an exhaust
valve (bottom valve), and a piston assembly to open and close them. The exhaust valve is connected to
the piston assembly.
The lower chamber of the piston assembly has the same pressure as the controlled pressure. The upper
chamber controls the pilot pressure by PWM-driving the solenoid valve. This difference in pressure
moves the piston assembly up and down to open and close the valve.
The EVD-3000 series senses the controlled pressure with a pressure sensor to constantly adjust the
pilot pressure as follows for high-precision pressure control:
When the controlled pressure is lower than the set pressure, that is, the controlled pressure is to be
boosted, the pilot pressure is controlled to achieve the following state:
Upper chamber pressure (pilot pressure) > Lower chamber pressure (controlled pressure)
When the controlled pressure is higher than the set pressure, that is, the controlled pressure is to be
reduced, the pilot pressure is controlled to achieve the following state:
Upper chamber pressure (pilot pressure) < Lower chamber pressure (controlled pressure)
About overactive state
Definition of overactive state: The overactive state is defined as a state in which the solenoid valve
continues to turn ON and OFF repeatedly like the patterns B and C as shown in "・Pressure control
diagram" above.
A continuous ON time like the pattern A or an extremely short ON time like the pattern D will not cause
the overactive state.
If this overactive state continues for a long time, the life of the solenoid valve will be greatly affected.

 Loading...
Loading...