39
Appendix B
First in Chain Applications
The repeater contains a three-pin header next to the Repeater ID DIP switch that can enable a
repeater with an ID other than A to become the first repeater in a chain if two or more repeater
chains are required in a given network.
First in Chain Description
In most of the examples shown of repeater networks (See “Repeater Architecture” on page 6
for more information), the examples rely on the principle that the installation is linear, with a
station or group of stations near the first repeater and a receiver near the last repeater. In some
applications, the receiver may be at the center of a group of stations, with one or more stations
requiring the use of a repeater or chain of repeaters. In those instances, the stations may not be
able to share the same repeater chain. The first in chain functionality allows you to create
multiple chains.
All repeaters require a unique ID and are still limited to a combination of eight stations and
eight repeaters, but the first in chain application lets a repeater with a repeater ID other than A
(B, for example) assume first in chain role of repeater A would have while still having a unique
ID.
First in Chain Configurations
Use a first in chain configuration as part of a multiple station/single receiver setup when the
stations are located at a distance so great that they cannot share a repeater or chain of repeaters
and require separate repeaters or chains or repeaters.
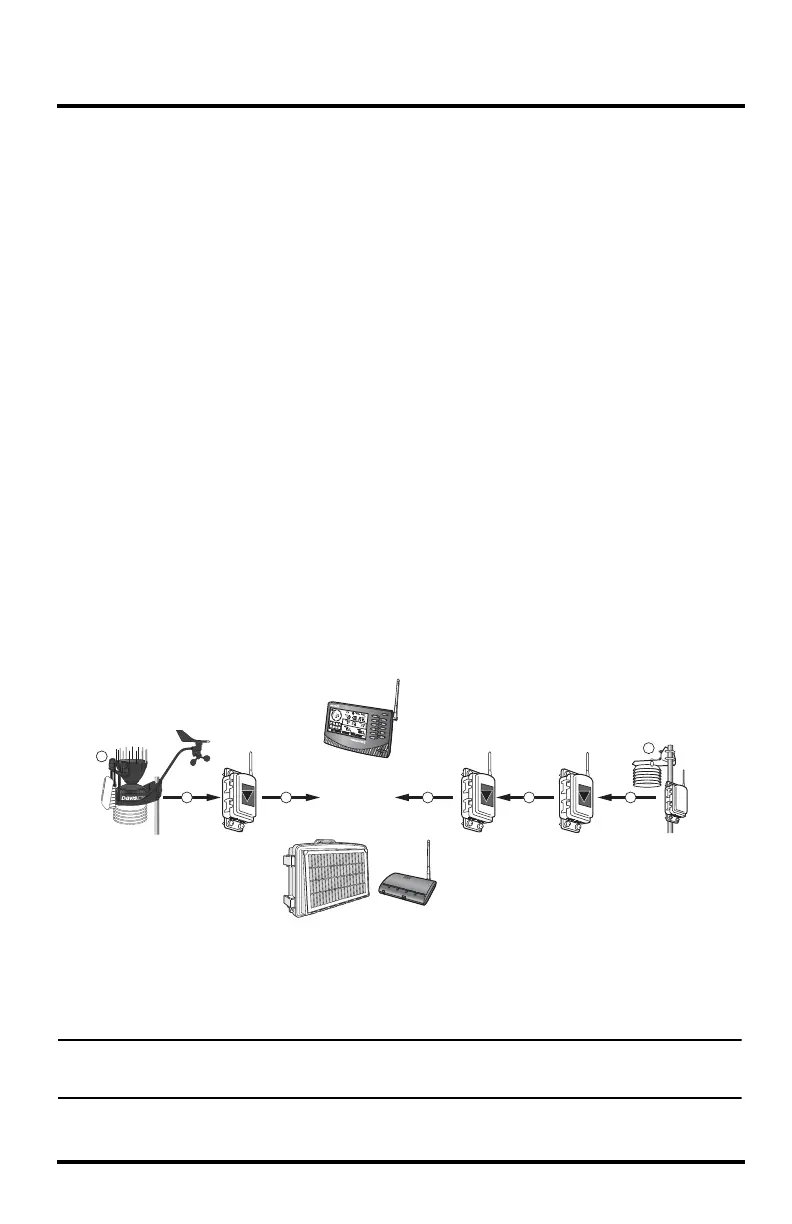
The diagram below shows an example first in chain/multiple repeater configuration:
In this example a receiver is in the middle of two station chains, with a transmitting station on
either end of the receiver.
The two repeaters used to repeat the second station’s signal are still alphanumerically ordered,
but repeater B assumes first in chain duties and does not look for and try to acquire repeater A.
Note: Despite the use of first in chain jumpers for one or multiple repeaters, all repeaters still require a
sequential ordering. For example, in the above diagram there are three repeaters in a network. Even
though there are two separate chains, those three repeaters should still have IDs A through C.
1
B
A
1 1
2
2 2
2
Any Vantage Pro2
Station
Repeater
Vantage Pro2
Console
or Envoy
or Vantage Connect
Repeater
First In Chain
Repeater
Temperature
Humidity
Station
C
™

 Loading...
Loading...















