137
K000000000EJ 023826A0 100714
ANNEX B
Coefficients of the fuels and Formulas
The following chart, derived from standard UNI 10389-1, lists the coefficients of the memorized fuels, used for
calculating losses and efficiencies.
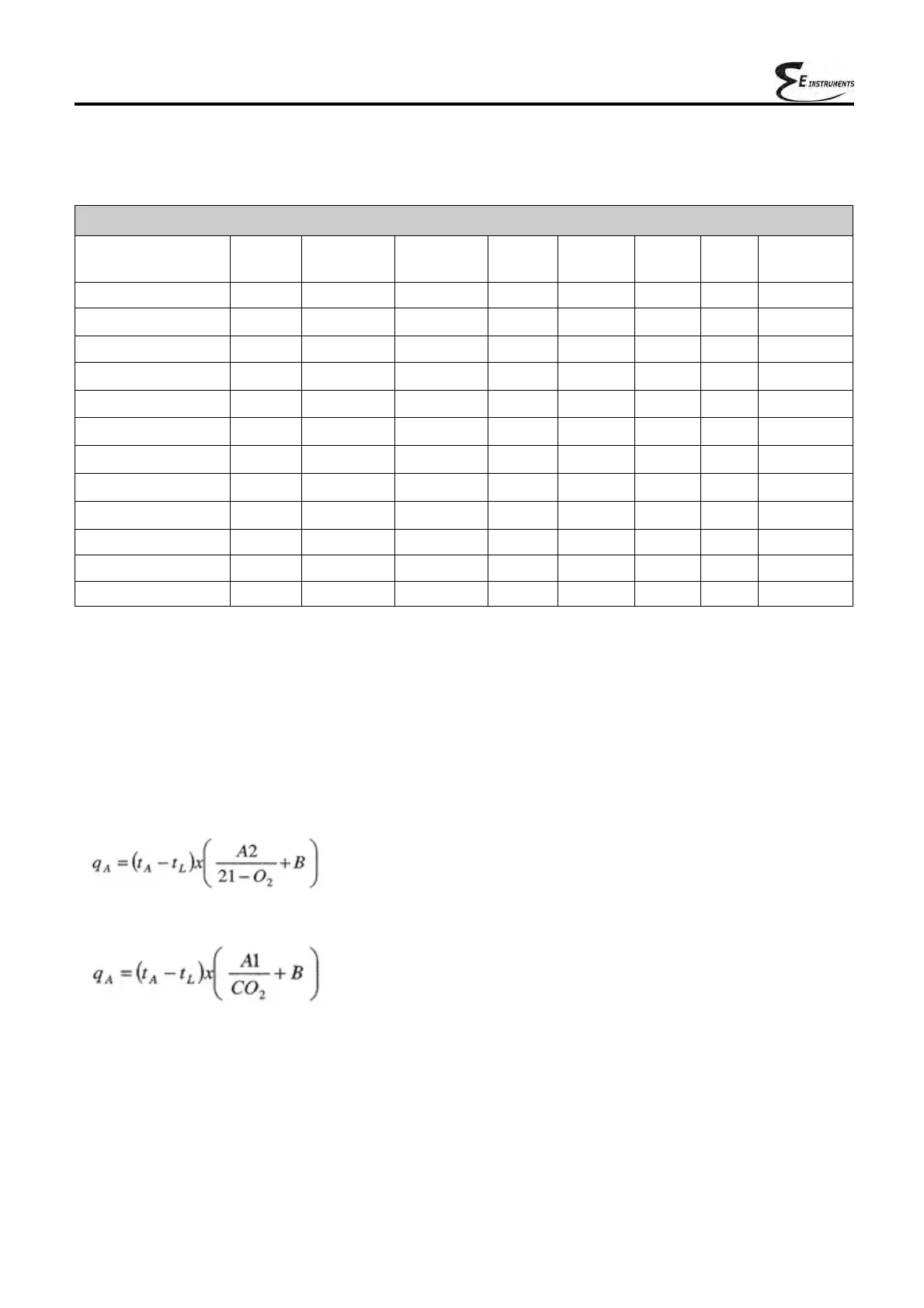
Coefficients for calculating combustion efficiency
Fuel A1 B CO2t
(%)
PCI
(KJ/Kg)
PCS
(KJ/Kg)
M aria
(Kg/Kg)
M H
2
O
(Kg/Kg)
V gas dry
(m
3
/Kg)
Natural gas 0.660 0.0100 11.70 50050 55550 17.17 2.250 11.94
Propane 0.630 0.0080 13.90 45950 49950 15.61 1.638 11.11
L.P.G. 0.630 0.0080 13.90 45730 49650 15.52 1.602 11.03
Butane 0.630 0.0080 13.90 45360 49150 15.38 1.548 10.99
Diesel oil 0.680 0.0070 15.10 42700 45500 14.22 1.143 10.34
Fuel oil 0.680 0.0070 15.70 41300 43720 13.73 0.990 10.06
Propane air 0.682 0.0069 13.76 28250 30700 9.13 0.999 6.77
Biogas 0.719 0.0086 16.81 19200 21250 6.38 0.840 5.82
Pellets 8% 0.740 0.0071 19.01 18150 19750 6.02 0.660 4.58
Wood 20% 0.761 0.0089 18.93 15450 17170 5.27 0.700 4.01
Chipped wood 0.8020 0.0108 20.56 11950 13565 4.20 0.660 3.25
Coal 0.7620 0.0023 19.06 31400 32300 10.70 0.370 8.14
Details of the coefficients of the fuels:
• CO2 t: The value of CO2 generated by combustion in stoichiometric condition, i.e. without excess Oxygen
and therefore maximum.
• A1, A2, B: Also please have a look at the Siegert formulas from the European standard EN50379-1 (in the
following).
A1 is the parameter in the Siegert Formula when the CO2 measurement is available.
A2 is used when the O2 measurement is available.
Note: Please also consider that in the U.S. usually the A1 parameter is the same as the 'european'
A1 BUT divided by 21.
Flue gas heat losses are calculated from measured oxygen content according to the relationship:
Flue gas heat losses are calculated from measured carbon dioxide content according to the relationship:
• CO conv: Conversion coefficient from ppm to mg/KWh. It can be expressed as a function of the gas density
(CO in this case) and the volume of the dry smoke.
• NO conv: Same as CO conv, but for NO.
• NOx conv: Same as CO conv, but for NO.
• SO2 conv: Same as CO conv, but for NO.
• PCI: Calorific Value. Italian for LHV (Lower Heating Value).
• PCS: Calorific Value. Italian for HHV (Higher Heating Value).
• m H2O: Mass of the air produced (per each Kg of fuel) in the combustion in stoichiometric condition.
• m Air: Mass of the air needed for combustion in stoichiometric condition.
• V g.d.: Volume of dry smokes produced in the combustion.
 Loading...
Loading...