Setup & Operation 4. Setting of End Effectors
42 VT Rev.1
The moment M (Nm) and inertia moment I (kgm
2
) when the volume of the load (end
effector + work piece) is small can be obtained by the following formula.
: Eccentric quantity of load (m)
: Gravitational acceleration (m/s
2
)
The figure below shows distribution of the center of gravity when the volume of the load
(end effector + work piece) is small.
Design the end effector so that the center of gravity is within the allowable moment.
If the volume of the load is large, calculate the moment and inertia moment by referring to
Setup & Operation 4.3.2 INERTIA setting - Calculating the Inertia Moment.
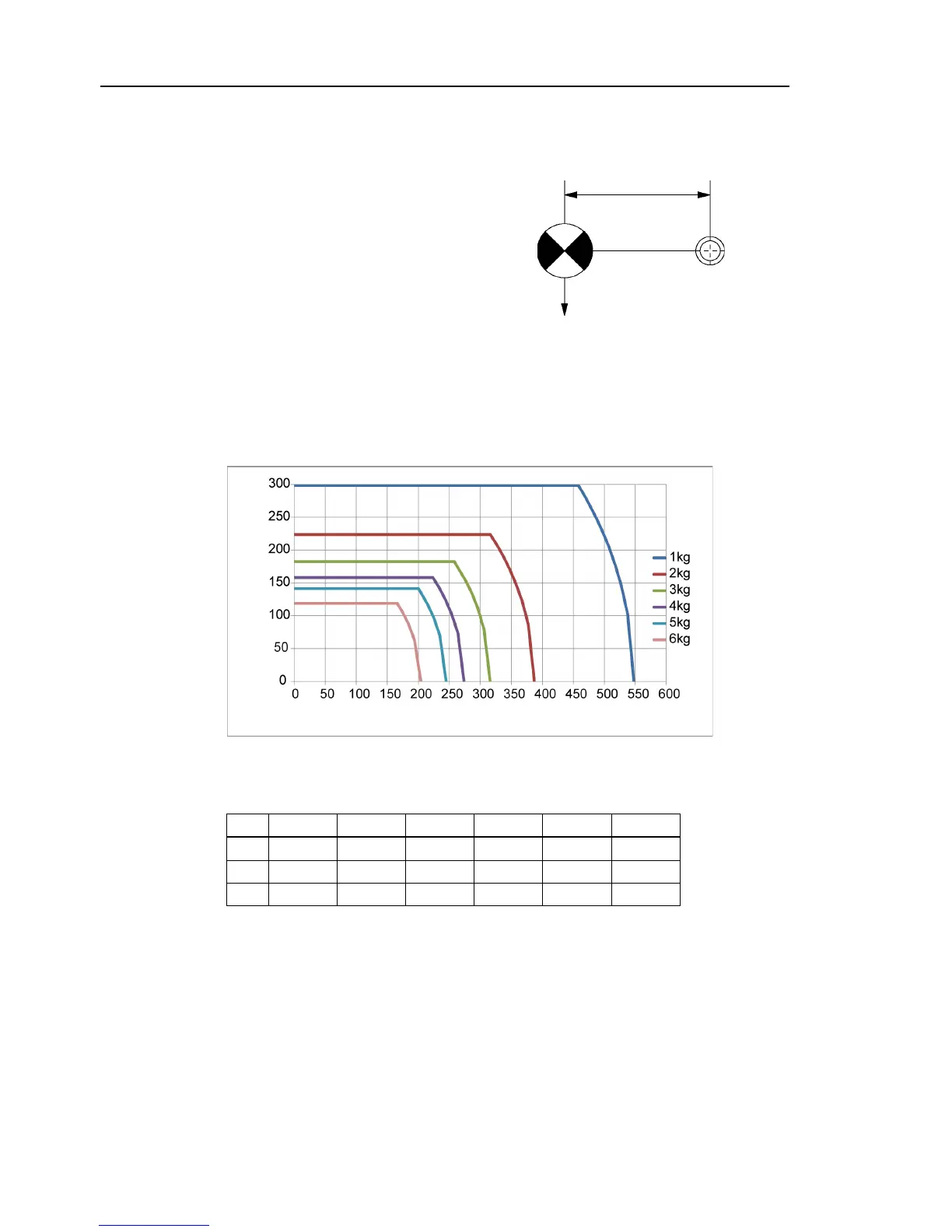
Center of gravity of load from the Arm #5 rotation center [mm]
Center of gravity of load from
the Arm #6 rotation center [mm]
Max. Eccentric Quantity of Load
(Distance between the joint rotation center and the load’s center of gravity)
When calculating the critical dimension of the load using the allowable moment and
inertia moment, the calculated value represents a distance from the Arm #5 rotation center,
not the distance from the flange. To calculate the distance from the flange to the load’s
center of gravity, subtract the distance from the center of the Arm #5 rotation center to the
flange (=80 mm) as shown in the example below.

 Loading...
Loading...