Page 17 of 44
7 Programming
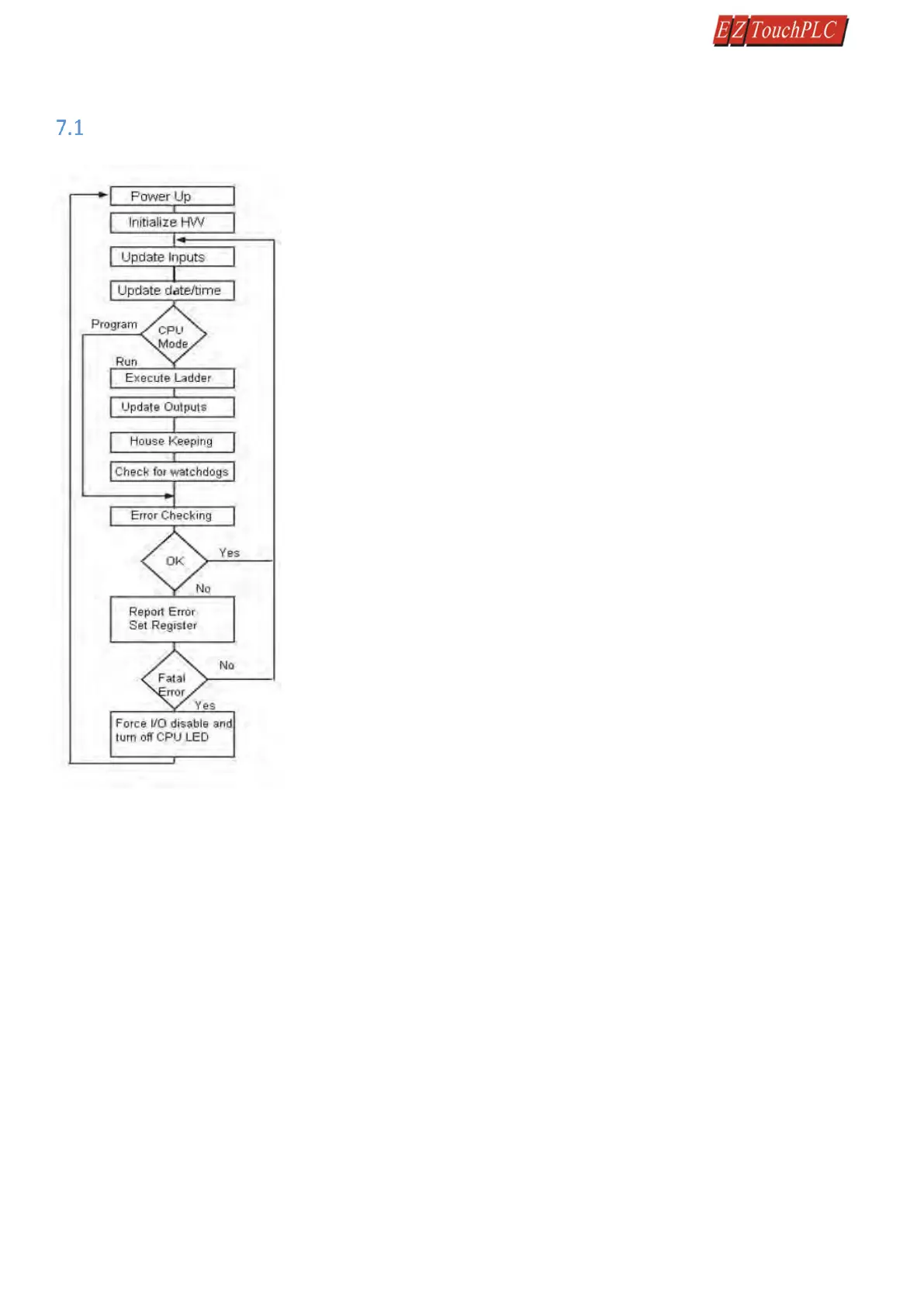
PLC Operation Sequence
A good understanding of the EZ3-TouchPLC Modular CPU operating sequence will
help you achieve the proper control for your equipment or process. The flow chart
on the left shows how the CPU controls all aspects of system operation.
Power-up Initialization
On power-up, the CPU initializes the internal electronic hardware. It also checks
if all the memories are intact and the system bus is operational. It sets up all the
communication registers. If all registers are go, the CPU begins its cyclic scan
activity as described below.
Read Inputs
The CPU reads the status of all inputs, and stores them in an image table. Image
Table is EZ3-TouchPLC Modular internal storage location where it stores all the
values of inputs/outputs for ONE scan while it is executing ladder logic. The CPU
uses this image table data when it solves the application logic program.
Execute Logic Time
This segment is also called Ladder Scan. The CPU evaluates and executes each
instruction in the logic program during the ladder scan cycle. The rungs of a ladder
program are made with instructions that define the relationship between system
inputs and outputs. The CPU starts scanning the first rung of the ladder program,
solving the instructions from left to right. It continues, rung by rung, until it solves
the last rung in the Main logic. At this point, a new image table for the outputs is
updated.
Write Outputs
After the CPU has solved the entire logic program, it updates the output image
table. The contents of this output image table are written to the corresponding
output points.
Immediate Inputs/Outputs
There is a possibility that an input changes after the CPU has read the inputs. If you have an application that cannot
wait until the CPU returns for the next input scan, you can use Immediate Instructions. These instructions do not
use the status of the input from the image table to solve the application program. The Immediate Instructions
immediately read the input status directly from I/O modules and update the image table with appropriate status
of input module read. Similarly, Immediate Output instructions do not wait for the CPU to complete the ladder
scan. Immediate outputs are directly written to the image table and Outputs are updated accordingly.
Subroutines
The CPU executes subroutines when called for in the ladder program. These subroutines are useful in performing
the same logic operation time and time again just upon one call so you do not have to repeat the rung logic over
and over again.
 Loading...
Loading...