Troubleshooting | 73
FRAKO | Operating Manual | Power Quality Controller – PQC
9 Troubleshooting
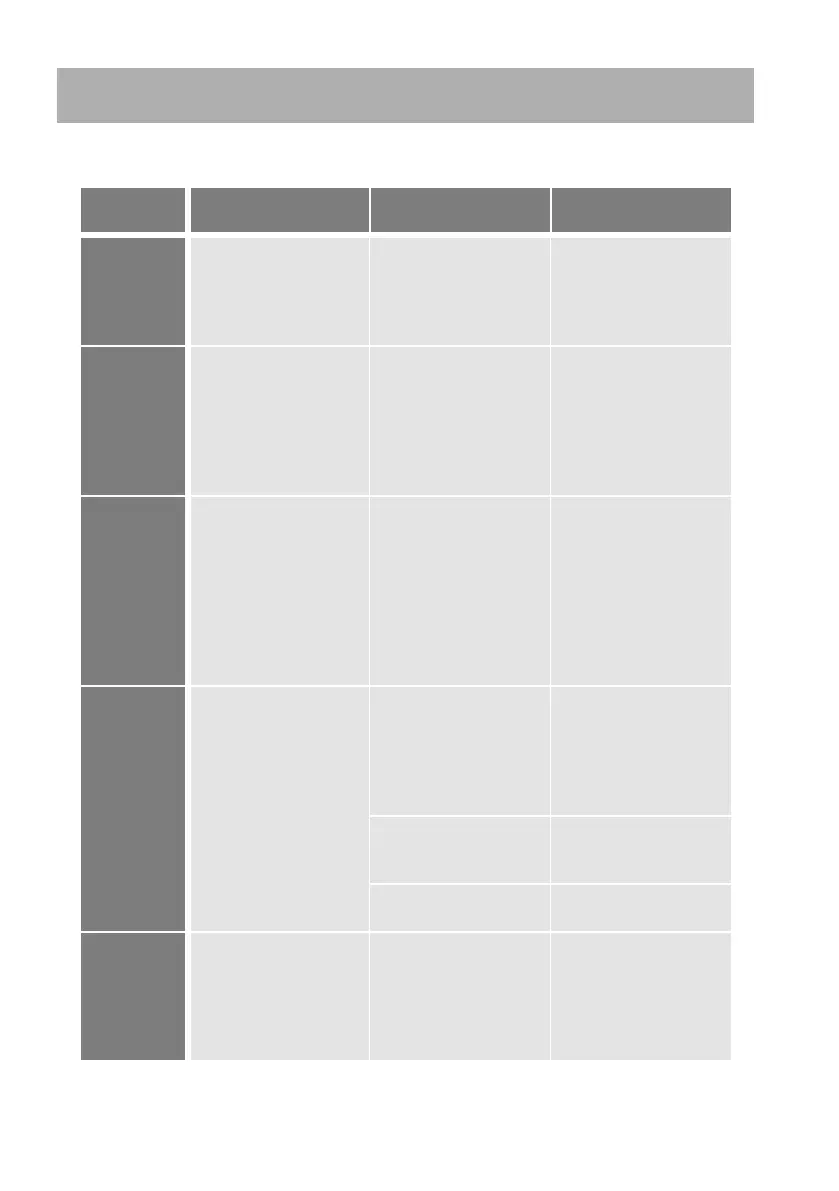
If alarms occur during operation of the PQC, the following table provides assistance
in identifying and remedying the faults.
Alarm
message
Fault Possible cause Remedial action
PQC not working;
no display at front of
instrument
No power – or the wrong
voltage – connected
Check that the correct
instrument power supply
is connected and that
the fuse in the circuit has
not blown.
cosφ cannot
be achieved
PQC gives a cosφ alarm
although the momentary
cosφ is better (nearer to
1) than the target value.
More capacitive than
the control band but still
inductive
See Section 6.3.4.2
“Cosφ Alarm”
for control band alarm
settings.
See Section 6.3.4.2
“Cosφ Alarm”
for control band alarm
settings.
Voltage < set
limit
PQC indicates or states
that voltage is less than
set alarm limit, although
a voltage is shown on
the screen.
The alarm limit has not
been adjusted for the
network nominal voltage.
Default setting is for 400
V networks.
Triggered when the
network voltage is less
than 85 % of the nominal
voltage.
Set the correct alarm
limit for the network
nominal voltage (see
Section 6.3.1 “System
parameters”)
Current < set
limit
No value for current
shown in the display
(0 A)
Break or short-circuit in
the current transformer
cable
Use an ammeter to
check current in current
path (I
min
* 0.015 A).
Danger: see
Section 5.2.7 “Current
measurement”
The current in the current
path is too low.
(I
min
* 0.015 A)
Install a smaller current
transformer.
Defective current
transformer
Check the current
transformer.
Voltage <
set limit +
Current < set
limit
PQC shows no meas-
ured voltage and no
current, although it has
been verified that power
is connected and a
current is flowing.
Multiple zero-voltage
crossings in measured
voltage.
Settings for the Network
nominal parameters
–> Change setting from
Auto to the appropriate
network frequency (50
Hz or 60 Hz).
 Loading...
Loading...