2–12 MULTILINK ML1200 MANAGED FIELD SWITCH – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION CHAPTER 2: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The ML1200 Managed Fiber with the Ring-Only Mode feature easily fulfill the redundant
requirement with a secure and fast reconfiguration time for cable breakup when set up in
a ring topology. The Gigabit port option boosts the bandwidth for high speed to support
the peak traffic and minimize congestion.
Example 3:
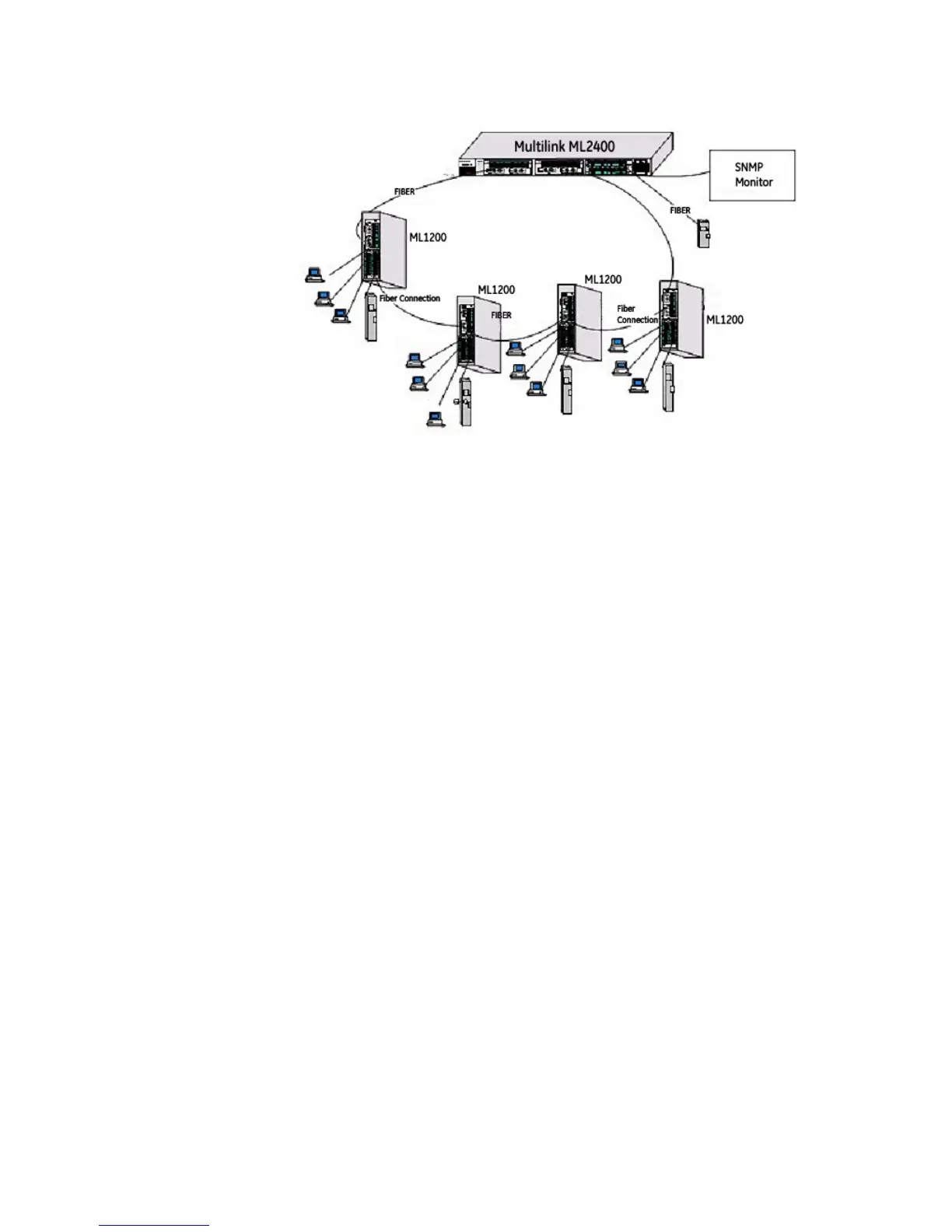
In another application in an industrial environment, a 12 port Nebs compliant, -24VDC
managed switch is required to meet the fiber and copper connections to cover the wider
area of video CCTV. The switch must be SNMP enabled and managed to easily monitor the
whole setup.
The Multilink managed field switch easily qualifies for this requirement with the various
features and modularity it has. Loaded with management software, the field switch
provides a very effective and economical solution for the video -vignette environment.
The security features (e.g. port-security, VLANs, SNMPv3, secure telnet, etc.) also boost the
Multilink managed switches to provide a very effective and reliable solution. The
modularity feature to support both copper and fiber at either 10/100/1000Mb speeds
easily meets the various speeds of legacy and future broadband requirements.
In a fast growing secure video environment, the ML1200 is a reliable and secure solution.
The modular design of the Multilink ML1200s, provide a wide range of copper/fiber options
to meet requirements. The Gigabit uplink for storage or broadband uplink allows the
telecom user a very effective solution to store their sensitive data securely.
 Loading...
Loading...