STP protocol has a limitation regarding the time needed to rebuild a topology when
there is a topology change. As shown in the previous section, the protocol waits for
its timers to expire and then takes action, causing it to take several seconds to
converge to a new topology. A faster protocol was required, leading to the creation
of the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol.
RSTP is not necessary a new protocol, but an evolution from the STP protocol. It uses
the same philosophy, such as the election of root bridge, but it has added some new
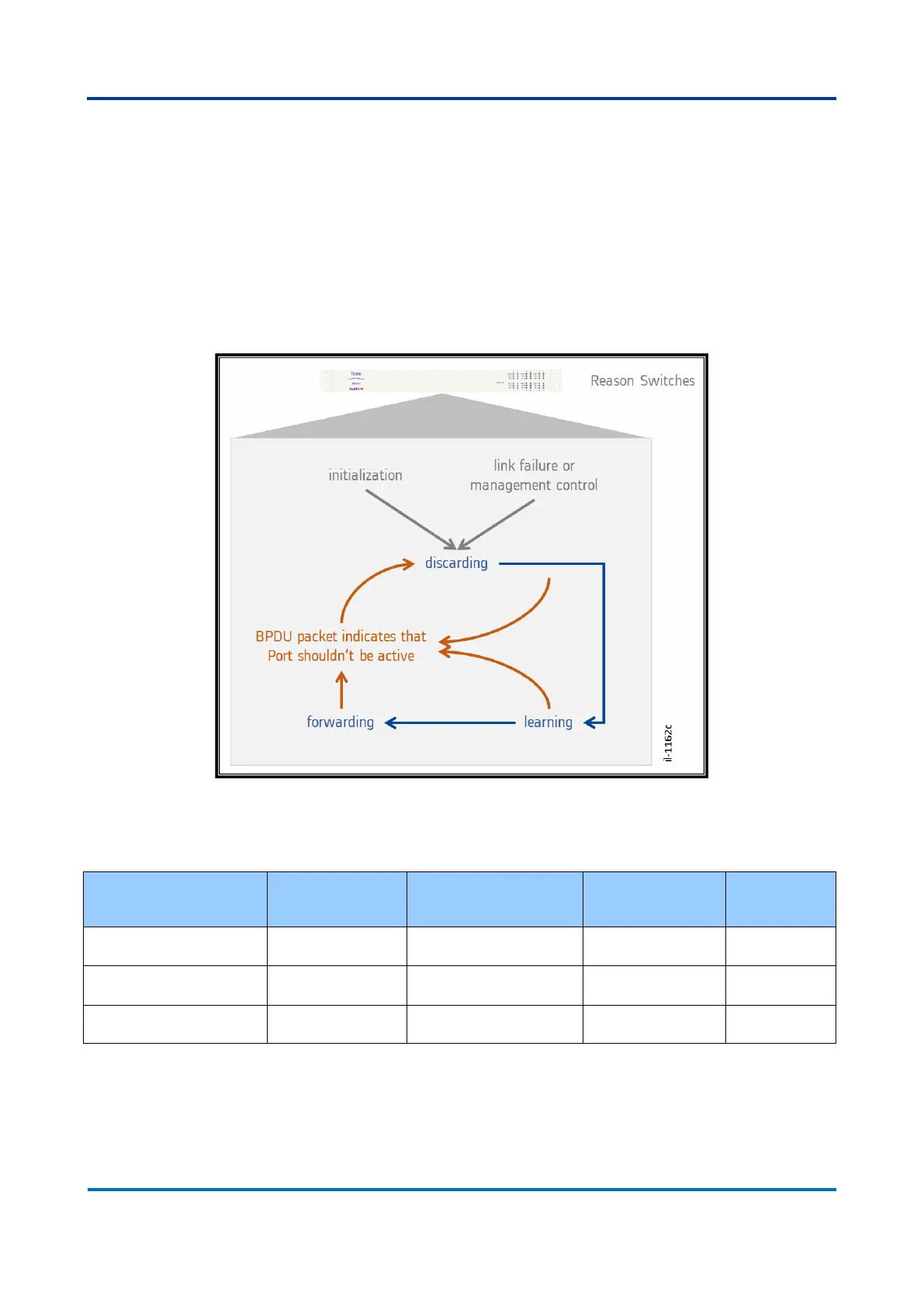
characteristics and concepts to the STP protocol. The figure below shows the
expected port behavior when using RSTP.
Figure 24: RSTP protocol mechanism
The table below illustrates the port state behaviour over the RSTP protocol.
Compared to the STP protocol, the number of port states has decreased. In STP when
a port is disabled, blocking traffic or listening to BPDU packets over the network
equates to discarding state in RSTP. Learning and forwarding states remain as
explained at the Spanning Tree fundamentals section.
 Loading...
Loading...