31
8.2.1 Cavitation Symptoms, Causes, And Remedies
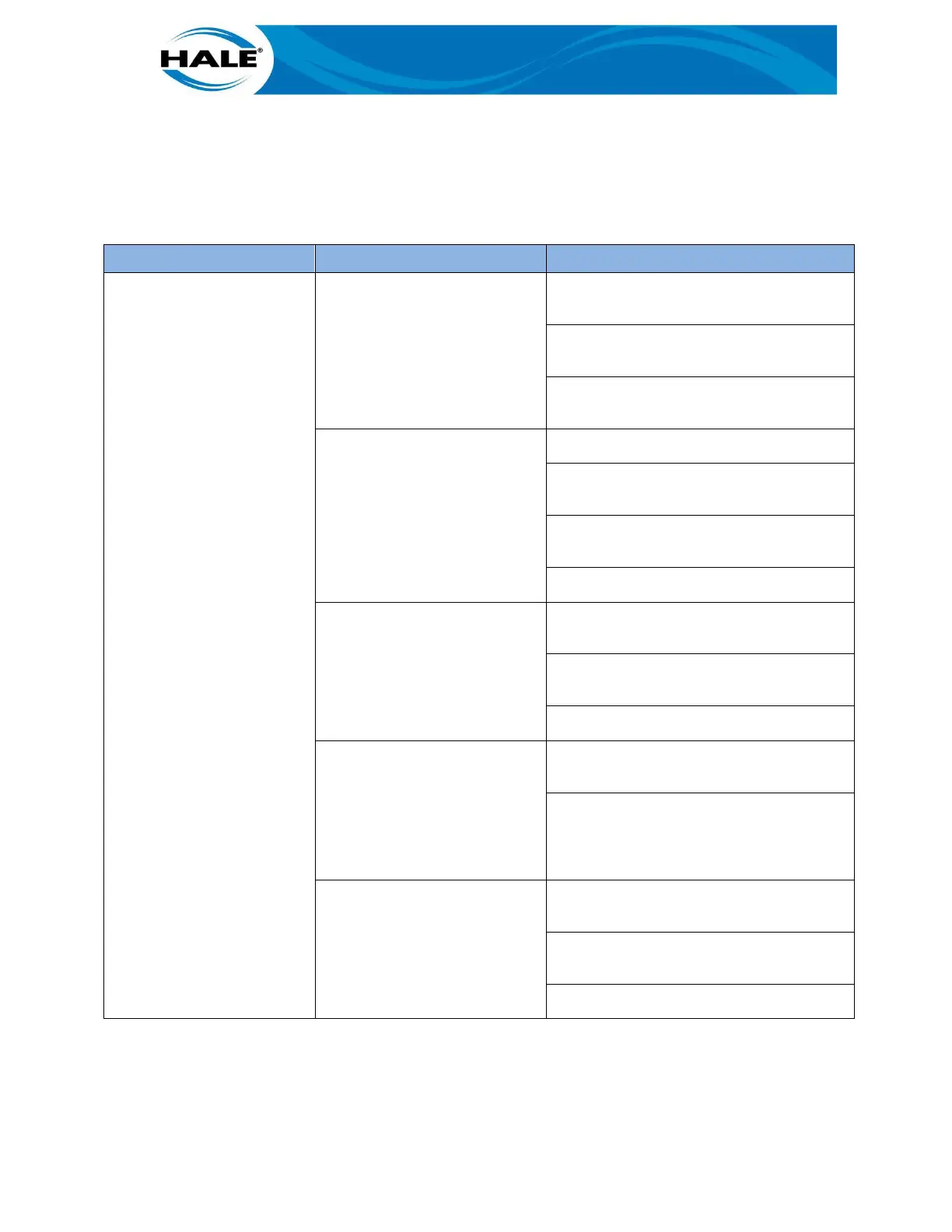
Table 7 provides the primary symptoms, causes, and remedies for troubleshooting cavitation issues.
Cavitation limits pump performance and can damage the pump. Refer to Technical Manual for more
information.
Table 7. Cavitation SCR Table
Pump Is Cavitating
• Pump makes excessive
rattling noise while
pumping and/or un-
steady discharge pres-
sure gauge.
• Note as the throttle is
increased there should
be a corresponding in-
crease in pump dis-
charge pressure. If the
throttle is increased and
the discharge pressure
does not increase or de-
creases, the pump is op-
erating in cavitation.
Operating Beyond Pump Capa-
bility
Reduce pump’s RPM to either reduce flow
rate and/or reduce discharge pressure.
Gate the discharge valve(s) to reduce flow
and maintain pressure.
Add more and/or larger intake lines to in-
crease flow rate to pump.
Intake Restriction
• Collapsed Suction Hose
• If Equipped, Partially Closed
Intake Valve(s)
• Suction Hose Strainer
Clogged
Replace with different hose(s).
If equipped, make sure all intake valves are
fully opened.
Clean strainer and remove debris from wa-
ter around strainer.
Keep strainer off bottom of water source.
Pump Too Far From Water
Source
• Suction Hose Too Long
• Suction Lift Too High
Move pump closer to water source and re-
move a section length of suction hose or.
Use a larger diameter size of suction hose
or.
Operate pump at a reduced flow rate.
Exceeding Capacity Of Supply
Source
• Hydrant Operation
• Relay Operation
Do not reduce the pressure on the intake
gauge below department limits.
If department does not have an intake
gauge pressure limit, do not allow intake
gauge pressure to fall below 15 psig
(105 kPa).
Water Temperature Too High Reduce pump’s RPM to either reduce flow
rate and/or reduce discharge pressure.
Gate the discharge valve(s) to reduce flow
and maintain pressure.
Locate a source of cooler water.

 Loading...
Loading...