IntuVue RDR-4000 Weather Radar Pilot's Guide
Expanded Operating Instructions 060-4492-000
28 Rev 7, February 2015
information along with the strongest cells. This is important since the
presence of turbulence along with high levels of reflectivity often
indicates convective weather. In areas of heavy stratus rain, the display
can show large areas of strong returns, but with little associated
turbulence.
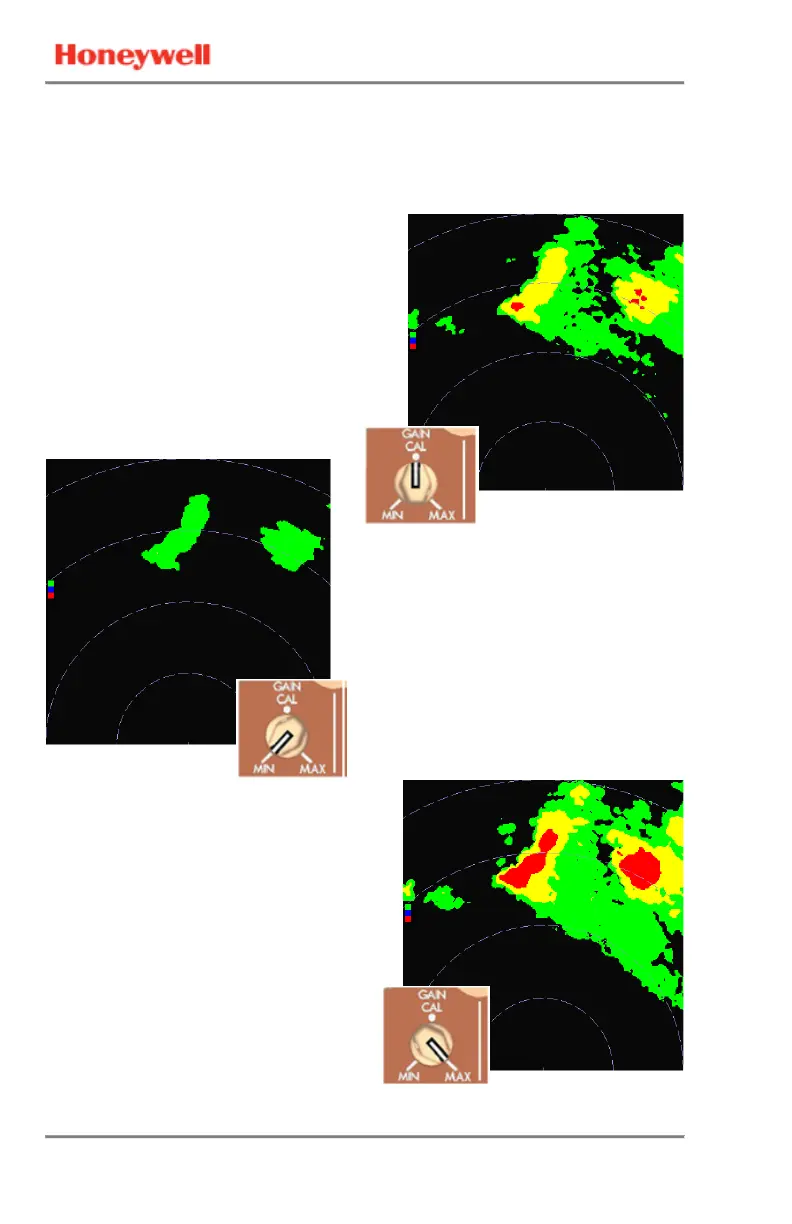
Reducing the gain can also help
identify embedded storm cells
within the stratus rain. It can help
identify areas of significant
attenuation by making radar
shadows more prominent. Areas
of missing terrain returns in MAP
mode that correspond with strong
weather echoes may indicate a
larger area of precipitation than is
apparent on the weather display.
(See SHADOWED AREAS on page
45.)
Use MAX gain only when at cruise
altitudes. In MAN mode, MAX gain
is useful when looking at altitude
slices above the freezing level
where particles are less reflective.
High levels of moisture above the
freezing level are key ingredients in
hail formation.
Increase the gain briefly at any
altitude to discover the relative
reflectivity of a weather formation
that is visible out the window but
does not initially appear on the
display. This occurs when the
reflectivity of the cloud is below the
standard threshold for green
weather.
AUTO POSITION
GAIN CONTROL AT
THE MIN POSITION
MAX POSITION

 Loading...
Loading...