Chapter 4 Splice Programs 27
Arc discharge conditions
General splicing steps
This section explains the steps involved in automatic splicing process and
describes how various program parameters are related to this process. The normal
splicing process can be divided into two sections; pre-fusion and fusion.
Pre-fusion
During pre-fusion, the splicer performs automatic alignment and focusing, where
the bers are subjected to a low pre-fuse current for cleaning purposes; a pre-fuse
image is also taken. At this point, the user is informed of any problems recognized
in the pre-fuse image, such as a poorly prepared ber. The splicer will then issue a
warning before the bers are fused together.
Fusion
During fusion, the bers are joined together and subjected to ve different
currents as illustrated below. An important parameter, which changes during
splicing, is the distance between the bers. During pre-fusion, the bers are apart.
With the current phase changing, bers are spliced gradually.
Splicing process
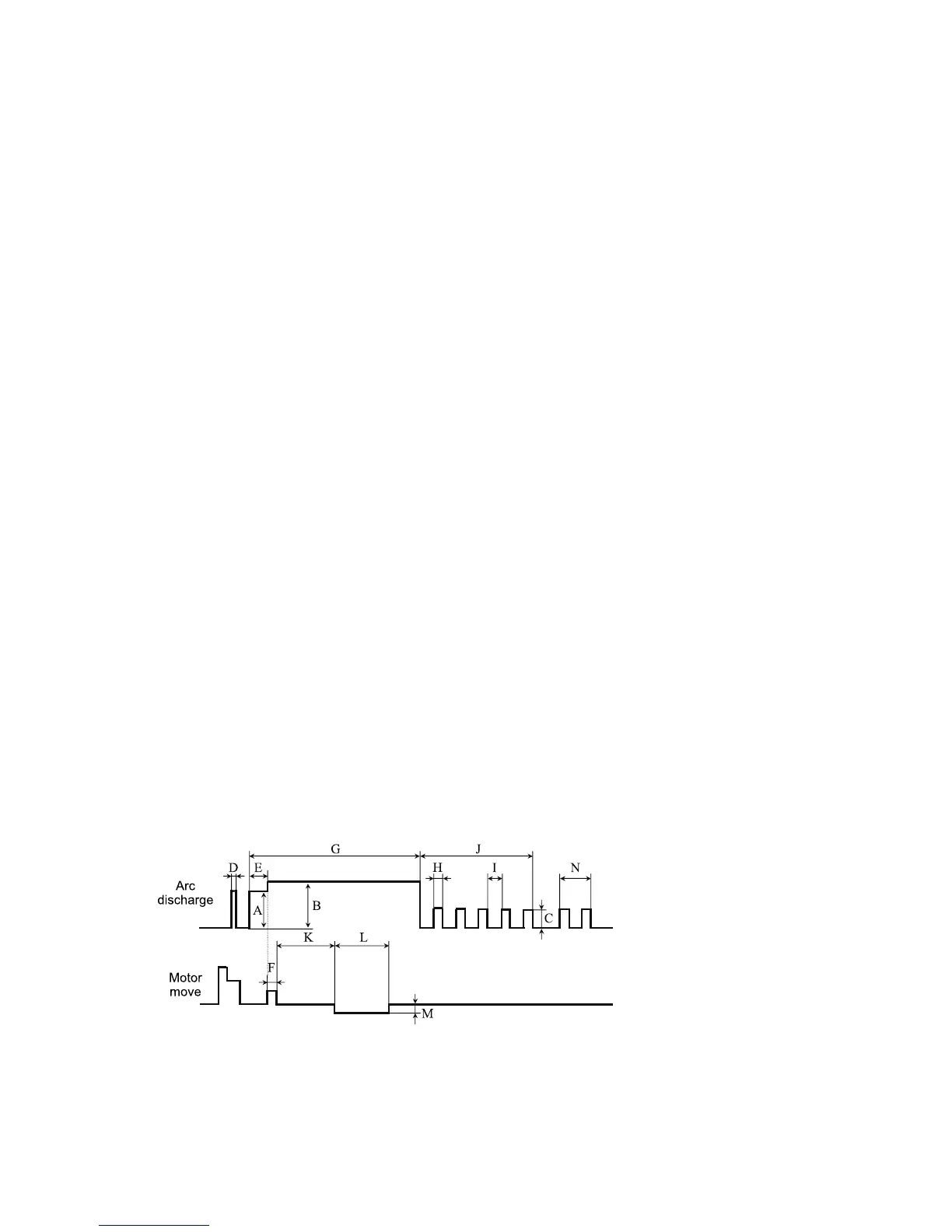
Arc power and arc time are considered as the two most important parameters (as
shown in the gure below). The name and purpose of those parameters as well as
the effect and importance of the parameters will be described in the next section
“Splice program parameters under general splicing process”. The below gure
shows the arc discharge conditions (relationship between “Arc power” and “Motor
motion”). These conditions can be modied by changing the splicing parameters
listed below. However, depending on the splice mode, certain parameters cannot
be changed.
A: Prefuse Power
B: ARC1 Power
C: ARC2 Power
D: Cleaning ARC
E: Prefuse Time
F: Overlapping Time
G: ARC1 Time
H: ARC2 On Time
I: ARC2 Off Time
J: ARC2 Time
K: Taper Splicing Wait Time
L: Taper Splicing Time
M: Taper Splicing Speed
N: Rearc Time
 Loading...
Loading...