Motors
The SCORBOT-ER IX robot arm is driven by DC electric motors. These actuators
converts signals from the controller (electric power) into rotations of the motor
shaft (mechanical power).
A robot arm such as the SCORBOT-ER IX imposes severe requirements on the
actuators, such as the following:
•
The robot motor must rotate at different speeds, and with a high degree of
accuracy. For example, if the robot is to be used for a spray painting
application, it must be able to accurately follow the defined path at the
specified speed.
•
The robot motor must allow fine speed regulation so that the robot will
accelerate and decelerate as required by the application.
•
The robot motor must supply large torques throughout its speed range and
also when the joint is stationary.
•
The robot motor must be able to stop extremely quickly without overshooting
the target position, and perform rapid changes in direction.
•
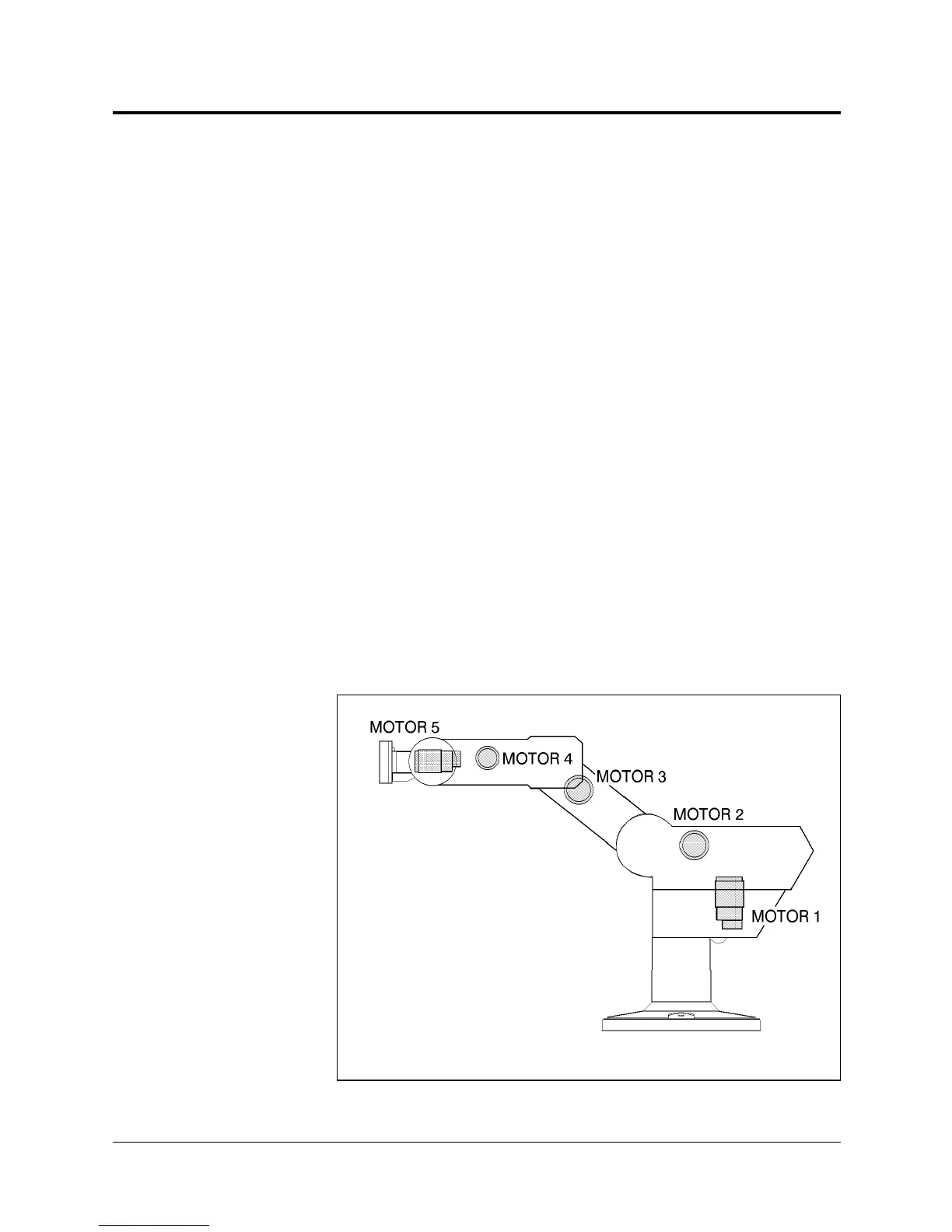
Since mounting motors on the robot arm adds to the robot’s weight and
inertia, the robot motors must be light and compact, yet powerful. As shown
in Figure 6-2, the motors of the
SCORBOT-ER IX
are located on the axes
they drive, with a two-stage (axes 1–4) or one-stage (axis 5) transmission.
Figure 6-2: Motor Locations in SCORBOT-ER IX
SCORBOT-ER IX 6 - 2 User’s Manual
9603
 Loading...
Loading...