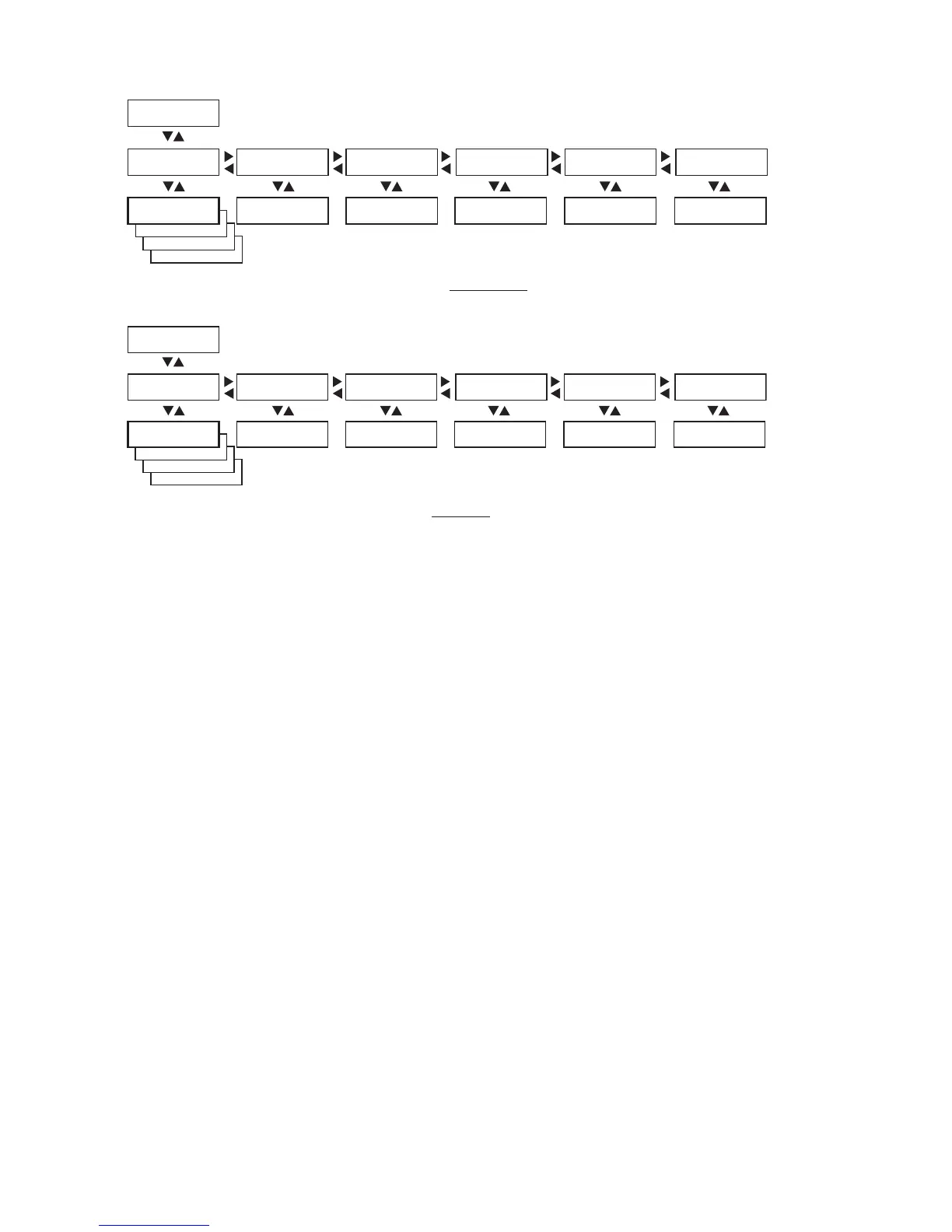
Example of the network setup when an automatic IP selection method is used.
PARITY:
BOOTP
PARITY:
DHCP
PARITY:
MANUAL
SETUP:
NETWORK
NETWORK:
IP SELECTION
NETWORK:
IP ADDRESS
NETWORK:
NETMASK
NETWORK:
DEFAULT ROUTER
NETWORK:
NAMESERVER
IP SELECTION:
DHCP+BOOTP
IP ADDRESS:
192.168.1.79
NETMASK:
255.255.255.0
DEFAULT ROUTER:
192.168.1.1
NAMESERVER:
192.168.1.7
NETWORK:
MAC ADDRESS
MAC ADDRESS:
00104017b80e
Read-only Read-only Read-only Read-only Read-only
These menus will only be displayed when an optional EasyLAN interface board is installed.
PARITY:
DHCP+BOOTP
PARITY:
BOOTP
PARITY:
DHCP
SETUP:
NETWORK
NETWORK:
IP SELECTION
NETWORK:
IP ADDRESS
NETWORK:
NETMASK
NETWORK:
DEFAULT ROUTER
NETWORK:
NAMESERVER
IP SELECTION:
MANUAL
IP ADDRESS:
0.0.0.0
NETMASK:
0.0.0.0
DEFAULT ROUTER:
0.0.0.0
NAMESERVER:
0.0.0.0
NETWORK:
MAC ADDRESS
MAC ADDRESS:
00104017b80e
Read-only Read-only Read-only Read-only Read-only
These menus will only be displayed when an optional EasyLAN interface board is installed.
Example of the network setup when the manual IP selection method is used or when
the network does not have an DHCP or BOOTP server.
16 Intermec EasyLAN Interface Kit Installation Instructions
Chapter 3 —Setup in IPL
Using ARP’n’PING to set an IP Address (Windows)
The ARP’n’PING method is intended for networks that does not have an
DHCP or BOOTP server.
You must have a free IP address, which will be permanently assigned to
the printer. However, it could be changed later from the printer’s home
page once the communication is established.
You must also have the printer’s MAC address. You can get the MAC
address from the Setup Mode as shown above or from the serial number
label for the EasyLAN board attached to the printer’s rear plate.
If the printer is started with DHCP and/or BOOTP, the printer will try
to fi nd and IP address fi ve times before it consider it a failure. This takes
about 2 minutes during which you cannot start using the ARP’n’PING
method.
The following instructions apply to Windows 2000, but similar methods
can be used on other operating systems, both in Windows and in Unix.
In Windows, the groups of digits in the MAC address are separated by
hyphens (-), and in Unix by colons (:).
 Loading...
Loading...





