Programming Examples
Copyright © Itech Electronic Co., Ltd. 114
levels, The rate at which the level changes is determined by the slew rate (see
slew rate descriptions for CV, CR, or CV mode as applicable). In addition, Use
the following commands to program continuous transients:
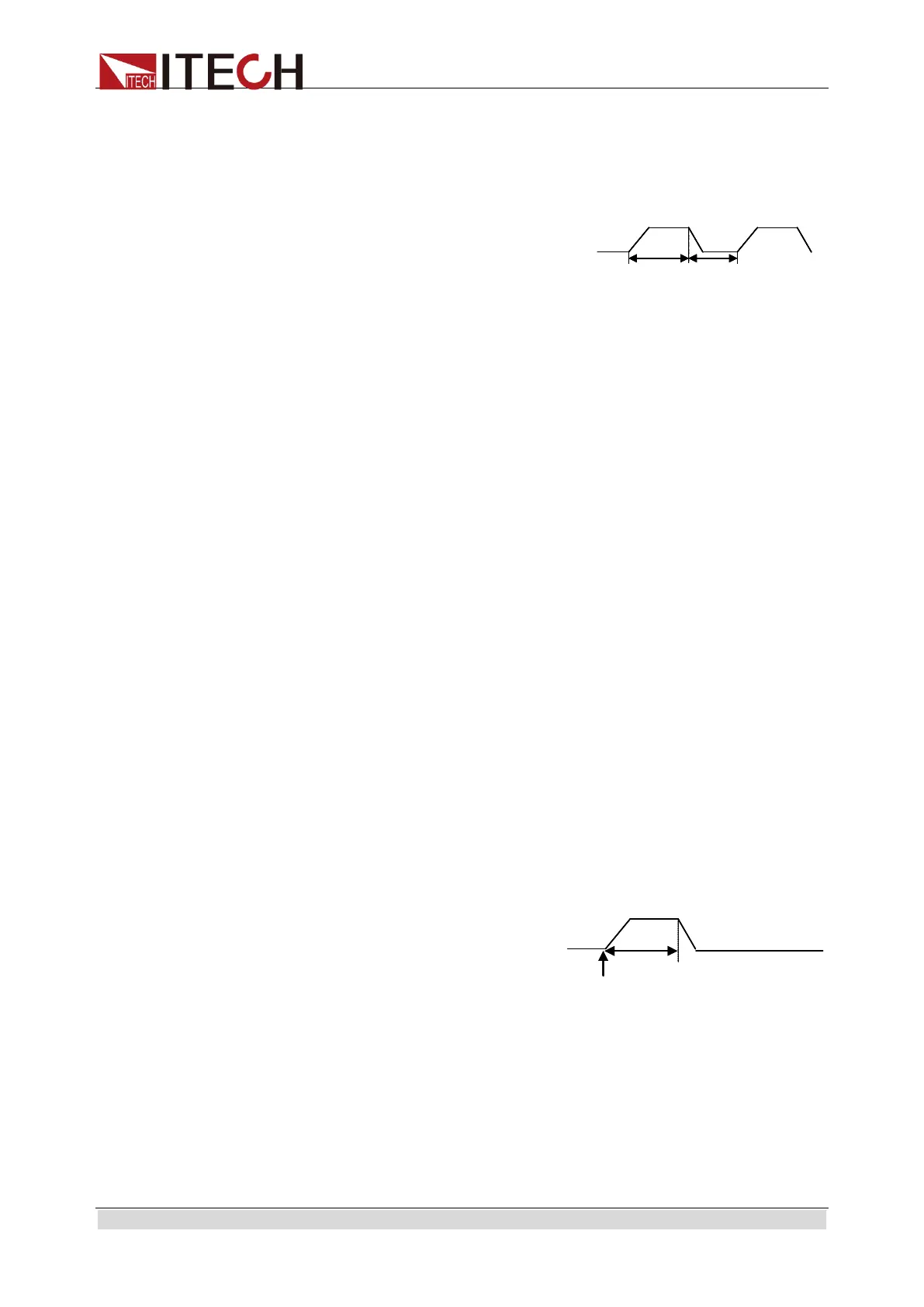
CURRent:TRANsient:MODE CONTinuous
CURRent:TRANsient:ALEVel 5
CURRent:TRANsient:AWIDth 0.6mS
CURRent:TRANsient:BLEVel 10
CURRent:TRANsient:BWIDth 0.7mS
TRANsient ON
TRIGger:IMMediate
This example assumes that the CC mode is active and the slew rate is at the
default setting (maximum rate). The load module starts conduction at the main
level (in this case 5 amps). When transient operation is turned on, the module
input current will slew to and remain at 10 amps for 40% of the period (400s).
The input current will then slew to and remain at 5 amps for the remaining 60%
(600s) of that cycle.
Pulse Transients
Pulsed transient operation generates a load change that returns to level B state
after some time period. It is similar to continuous operation with the following
exceptions:
a) To get a pulse, an explicit trigger is required. To specify the trigger source,
use TRIGger:SOURce. See "Triggering Transients".
b) One pulse results from each trigger. Therefore, frequency cannot be
programmed.
Use the following commands to program pulsed transients:
CURRent:TRANsient:MODE PULSe
CURRent:TRANsient:ALEVel 5
CURRent:TRANsient:AWIDth 10mS
CURRent:TRANsient:BLEVel 10
TRANsient ON
TRIGger:IMMediate
This example assumes that the CC mode is active, the slew rate is at the
factory default setting (maximum rate), and a trigger signal is connected to the
mainframe's external trigger input. The load module starts conduction at the
10A
0.6ms
5A
0.4ms
10A
0.6ms
5A
0.4ms0.6ms
5A
0.4ms
5A
10A
Trg 10ms
5A
10A
Trg 10ms
 Loading...
Loading...