Electrical Installation
Connections
IDX 70 User Manual
4-38 mmag | 2022-04 | rel10520
4.3.5.1 Power Supply Voltage +V
CC
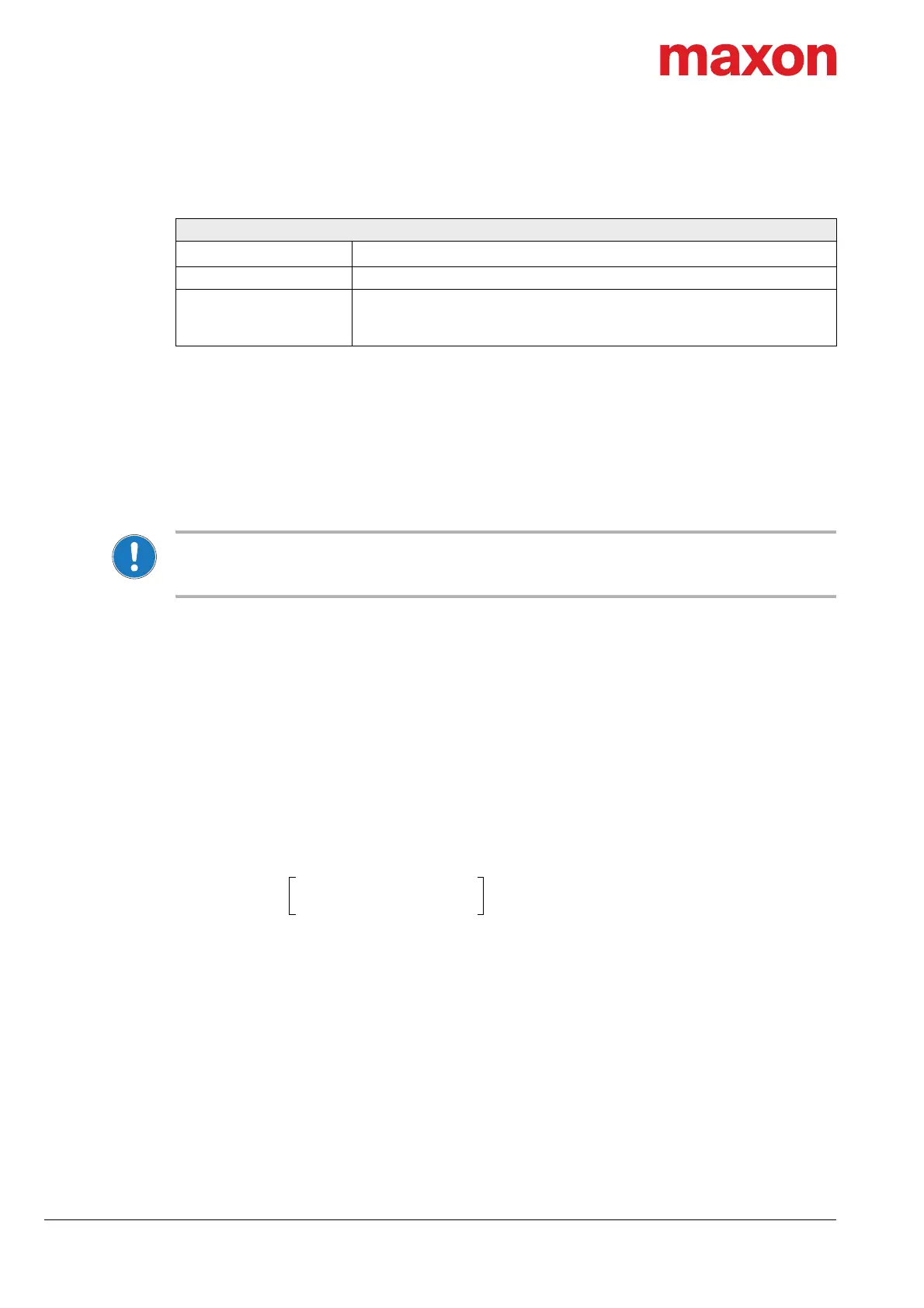
Table 4-27 Power supply requirements
1) Use the formula below to calculate the required voltage under load.
2) Choose a power supply according to the calculated voltage. Thereby consider:
a) During braking of the load, the power supply must be capable of buffering the recovered
kinetic energy (for example, in a capacitor).
b) If you are using an electronically stabilized power supply, make sure that the overcurrent pro-
tection circuit is configured inoperative within the operating range.
The formula already takes the following into account:
• Maximum PWM duty cycle of 90 %
• Controller’s max. voltage drop of 1 V @ 12 A
KNOWN VALUES:
• Operating torque M [mNm]
• Operating speed n [rpm]
• Nominal motor voltage U
N
[Volt]
• Motor no-load speed at U
N
; n
O
[rpm]
• Speed/torque gradient of the motor Δn/ΔM [rpm/mNm]
SOUGHT VALUE:
• Supply voltage +V
CC
[Volt]
SOLUTION:
Continued on next page.
Power supply requirements
Output voltage
+V
CC
12…60 VDC
Absolute output voltage min. 10 VDC; max. 70 VDC
Output current
Depending on load
• continuous max. 30 A
• short-time (acceleration, <10 s) max. 48 A
V
CC
U
N
n
O
-------
n
Δn
ΔM
---------
M⋅+
1
0.9
-------
⋅⋅1 V[]+≥
 Loading...
Loading...