7-276
RADD(P)
7.12.14 Conversion from floating-point angle to radian
(Double precision) (RADD(P))
RADD(P)
Function
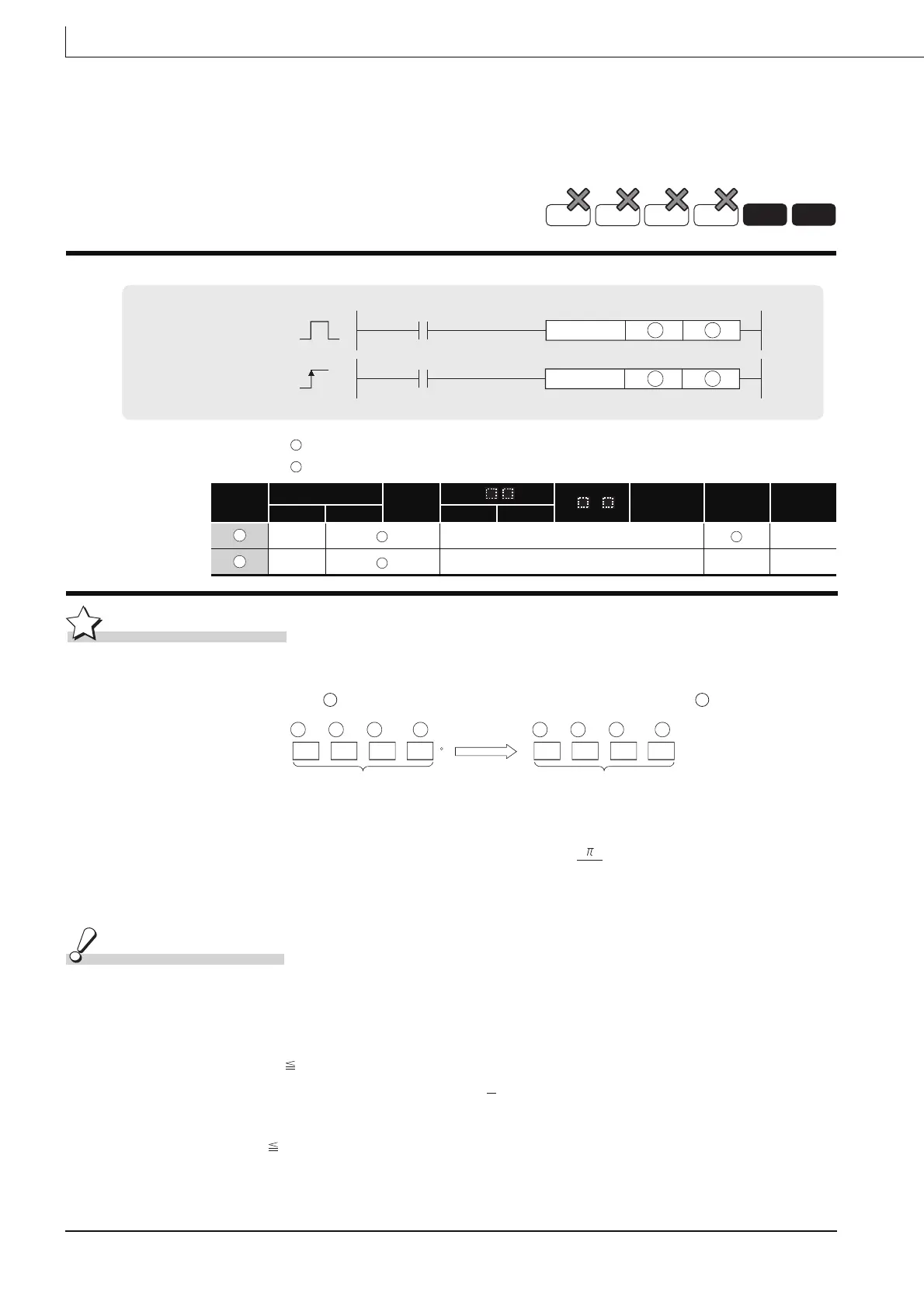
(1) The unit expressing the size of an angle is converted into the radian unit from the degree
unit specified by , and its result is stored into the device specified by .
(2) Conversion from degree to radian units is performed according to the following equation:
(3) When the operation results in -0 or an underflow, the result is processed as 0.
Operation Error
(1) In any of the following cases, an operation error occurs, the error flag (SM0) turns ON, and
an error code is stored into SD0.
• The value of the specified device is not in the following range: (Error code: 4140)
0,2
-1022
| value of specified device | < 2
1024
• The value of the designated device is 0. (Error code: 4140)
• The result exceeds the following range (Operation results in an overflow):
2
1024
| Operation result | (Error code: 4141)
: Angle to be converted to radian units or head number of the devices where the angle is stored (real number)
: Head number of the devices where the value converted in radian units will be stored (real number)
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
E
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– –– ––
–– –– –– ––
Universal
Basic
Process
High
performance
Redundant
LCPU
Command
Command
RADDP
RADD
RADDP
RADD S D
S D
S
D
S
D
S
D
(
)
( )rad
64-bit floating-point
real number
64-bit floating-point
real number
+3
S
+2
S
S
+1
S
+3
D
+2
D
D
+1
D
Radian unit = Degree unit x
180

 Loading...
Loading...











