marking/re-marking), and is then sorted into the appropriate queue. The switch then forwards packets from
each queue.
Moxa switches support two different queuing mechanisms:
• Weight Fair: This method services all the traffic queues, giving priority to the higher priority queues.
Under most circumstances, the Weight Fair method gives high priority precedence over low priority, but in
the event that high priority traffic does not reach the link capacity, lower priority traffic is not blocked.
• Strict: This method services high traffic queues first; low priority queues are delayed until no more high
priority data needs to be sent. The Strict method always gives precedence to high priority over low priority.
Configuring Traffic Prioritization
Quality of Service (QoS) provides a traffic prioritization capability to ensure that important data is delivered
consistently and predictably. The Moxa switch can inspect IEEE 802.1p/1Q layer 2 CoS tags, and even layer 3
TOS information, to provide a consistent classification of the entire network. The Moxa switch’s QoS capability
improves your industrial network’s performance and determinism for mission critical applications.
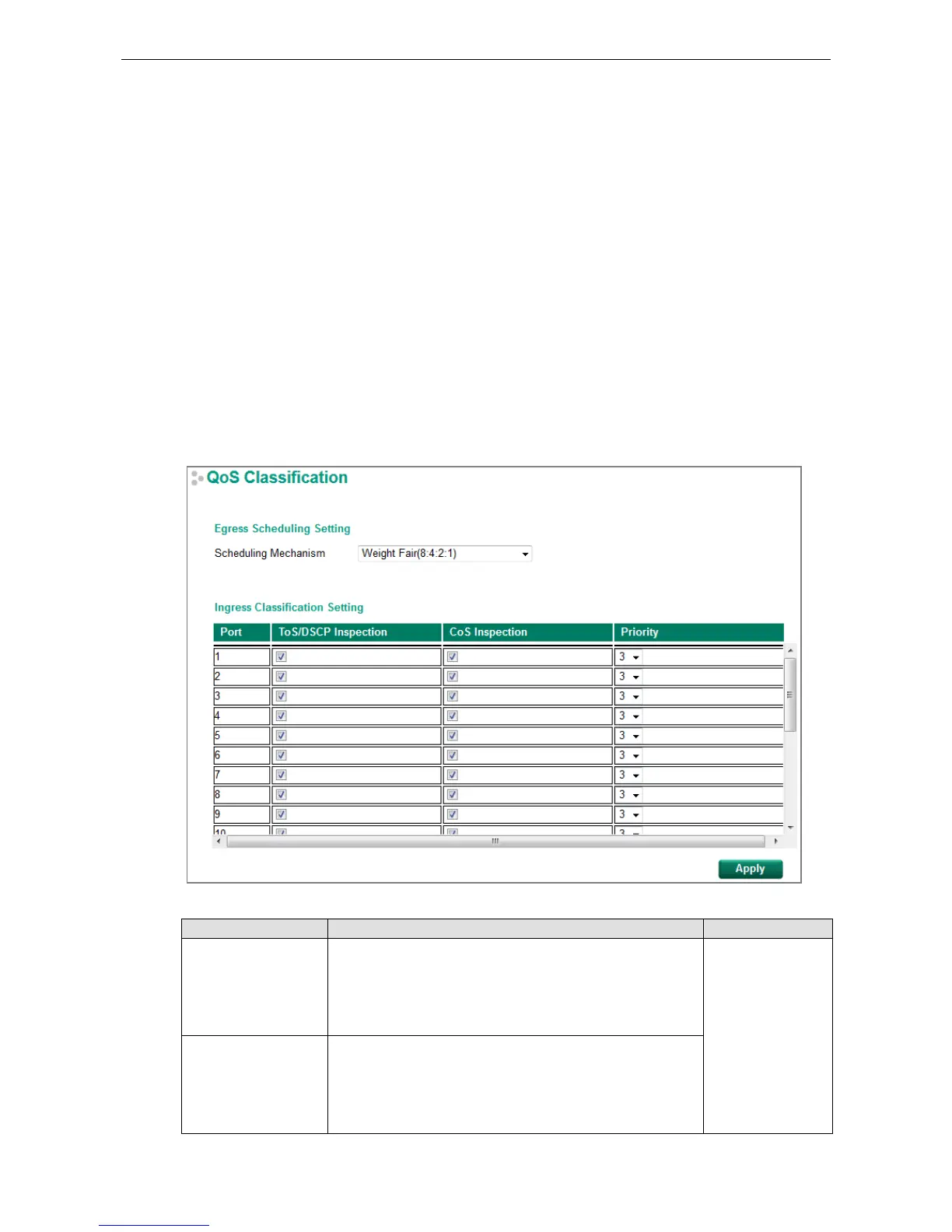
CoS Classification
Scheduling Mechanism
Setting Description Factory Default
Weight Fair The Moxa switch has 4 priority queues. In the weight fair
scheme, an 8, 4, 2, 1 weighting is applied to the four priorities.
to the higher priority frames
Weight Fair
Strict In the Strict-priority scheme, all top-priority frames egress a

 Loading...
Loading...