© National Instruments | 6-1
6
Digital Routing and Clock
Generation
This chapter describes the digital routing and clock routing circuitry on the cDAQ chassis. Refer
to the Digital Routing and Clock Routing sections.
Digital Routing
The digital routing circuitry has the following functions:
• Manages the flow of data between the bus interface and the acquisition/generation
sub-systems (analog input, analog output, digital I/O, and the counters). The digital routing
circuitry uses FIFOs (if present) in each sub-system to ensure efficient data movement.
• Routes timing and control signals. The acquisition/generation sub-systems use these
signals to manage acquisitions and generations. These signals can come from the following
sources:
– Your C Series I/O modules
– User input through the PFI terminals using parallel digital C Series I/O modules or the
NI cDAQ-9178 chassis PFI terminals
• Routes and generates the main clock signals for the cDAQ chassis. To determine the signal
routing options for C Series I/O module(s) installed in the cDAQ chassis, refer to the
Device Routes tab in MAX.
Clock Routing
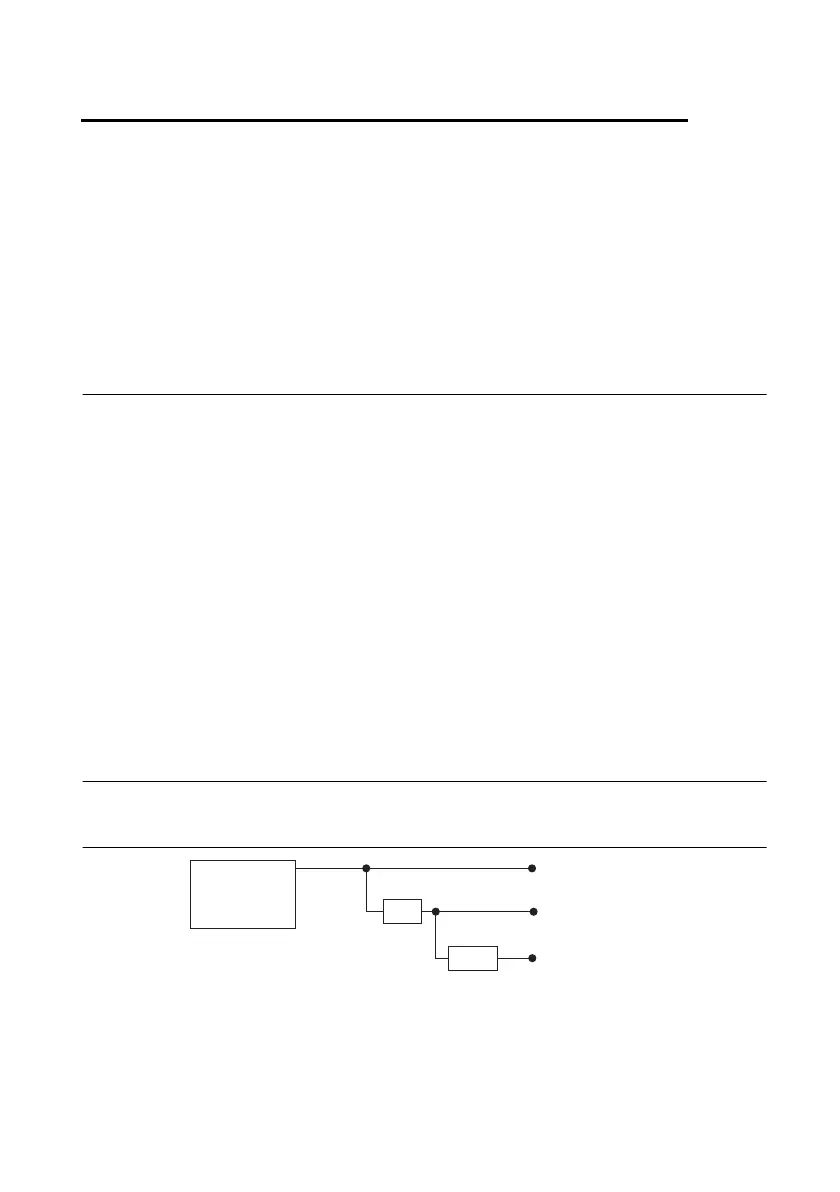
Figure 6-1 shows the clock routing circuitry of the cDAQ chassis.
Figure 6-1. Clock Routing Circuitry
80 MHz Timebase
You can use the 80 MHz Timebase as the Source input to the 32-bit general-purpose
counter/timers.
÷ 4
÷ 200
80 MHz Timebase
100 kHz Timebase
20 MHz Timebase
Onboard
80 MHz
Oscillator
 Loading...
Loading...