6 DriveProgramming Commands
6 - 36
DriveProgramming User’s Manual (I622-E1)
6-6 I/O Control Commands
Use these I/O control commands to control inputs and outputs. Although you can control I/Os with the =
(Assignment) command, the I/O control commands can efficiently use the program capacity because
their arguments require smaller data size.
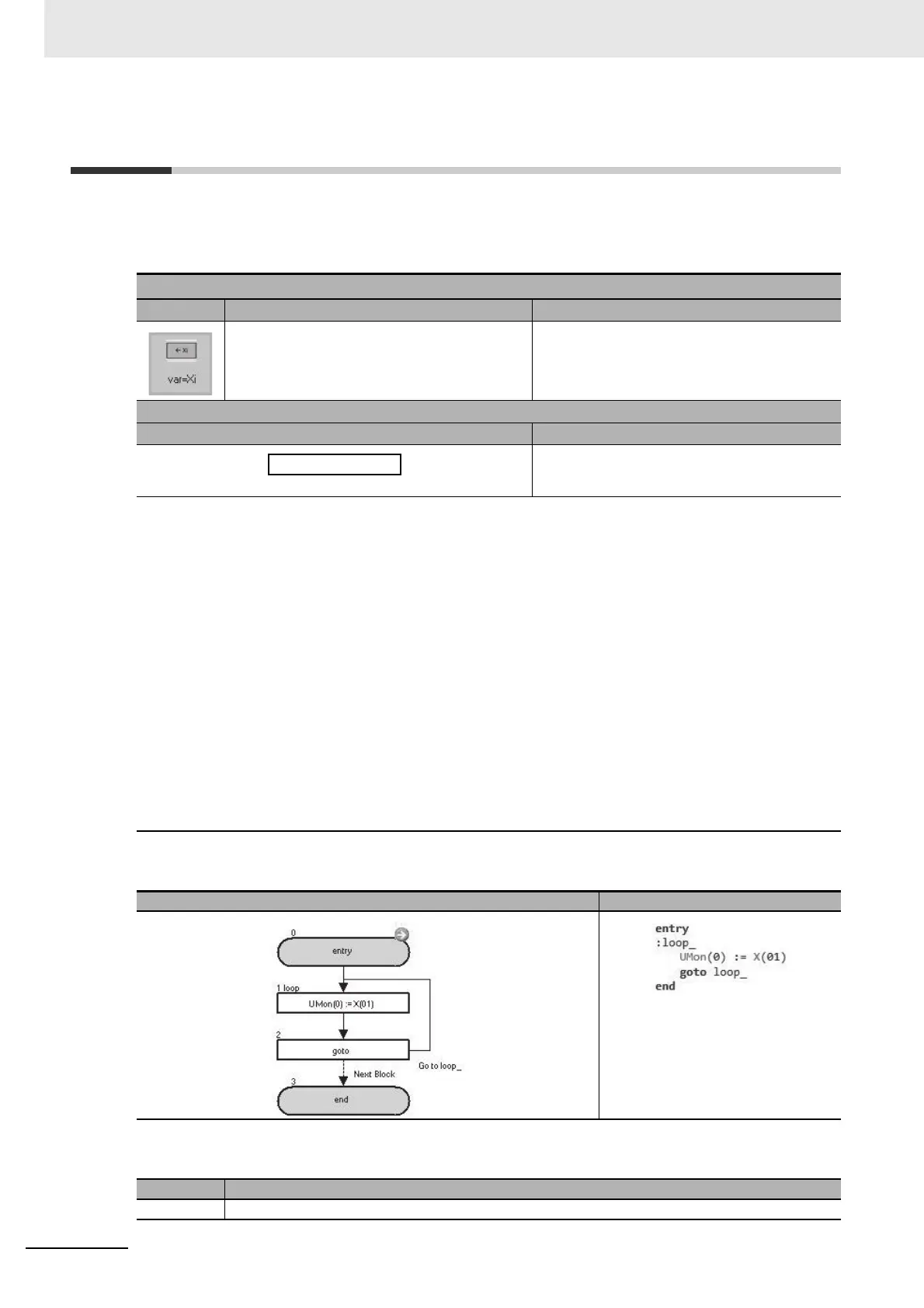
Example
In the above example, the status of the input terminal X(01) is monitored with the parameter UMon(0)
(db-08).
var = X(i)
Command Description Argument
Assigns one bit of the status of the input termi-
nal variable to <variable>.
variable
: any variable (the variable value is 0 or 1)
i: input terminal variable (range 00 to 07)
Format
Flowchart method Text language method
↓
<variable> : = X(i)
Note The input terminal variable is a variable that detects the status of the inverter's input terminal.
The following settings are required. The numerical order of input terminal variables follows the
numerical order of the set general-input numbers.
Set the Input Terminal 1 to 9, A and B Selection (CA-01 to CA-11) to MI1 to MI11 (86 to 96).
<Assignment example>
X(00) = MI1 (function No. 86)
X(01) = MI2 (function No. 87)
X(02) = MI3 (function No. 88)
X(03) = MI4 (function No. 89)
X(04) = MI5 (function No. 90)
X(05) = MI6 (function No. 91)
X(06) = MI7 (function No. 92)
X(07) = MI8 (function No. 93)
X(08) = MI9 (function No. 94)
X(09) = MI10 (function No. 95)
X(10) = MI11 (function No. 96)
Note For details, refer to 5-2 Input/Output Terminal Variables on page 5-5.
Flowchart Text
Block number
Operation
1 Assigns X(01) to UMon(0).

 Loading...
Loading...











