141
ST Language Configuration Section 5-4
5-4 ST Language Configuration
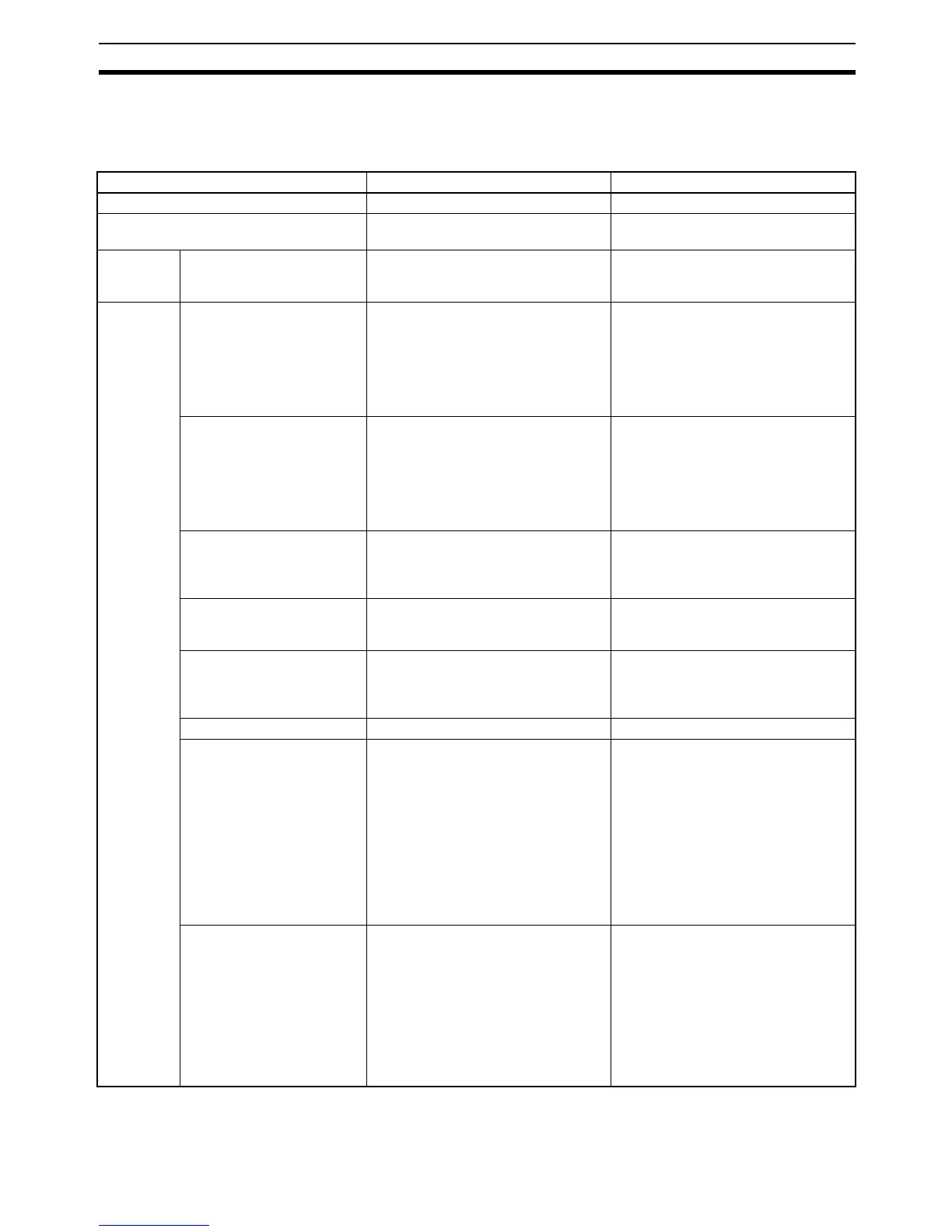
5-4-1 Statements
Statement Function Example
End of statement Ends the statement ;
Comment All text between (* and *) is treated as
a comment.
(*comment*)
Assign-
ment state-
ment
Assignment Substitutes the results of the expres-
sion, variable, or value on the right for
the variable on the left.
A:=B;
Control
statements
IF, THEN, ELSIF, ELSE,
END_IF
Evaluates an expression when the
condition for it is true.
IF (condition_1) THEN
(expression 1);
ELSIF (condition_2) THEN
(expression 2);
ELSE
(expression 3);
END_IF;
CASE, ELSE, END_CASE Evaluates an express based on the
value of a variable.
CASE (variable) OF
1: (expression 1);
2: (expression 2);
3: (expression 3);
ELSE
(expression 4);
END_CASE;
FOR, TO, BY, DO,
END_FOR
Repeatedly evaluates an expression
according to the initial value, final
value, and increment.
FOR (identifier) := (initial_value) TO
(final_value) BY (increment) DO
(expression);
END_FOR;
WHILE, DO, END_WHILE Repeatedly evaluates an expression
as long as a condition is true.
WHILE (condition) DO
(expression);
END_WHILE;
REPEAT, UNTIL,
END_REPEAT
Repeatedly evaluates an expression
until a condition is true.
REPEAT
(expression);
UNTIL (condition)
END_REPEAT;
EXIT Stops repeated processing. EXIT;
RETURN ST program:
Ends the ST task that is being exe-
cuted, and executes the next task.
ST used in SFC:
Ends the SFC action program that is
being executed, and executes the
next action program.
ST used in a function block:
Returns from the called program to
the point in the calling program
where the call occurred.
RETURN;
Function block instance call Calls a function block definition. When used in a function block:
Variable name with FUNCTION
BLOCK data type (called function
block definition’s input variable name
:= calling function block definition’s
variable name or constant, ..., called
function block definition’s output vari-
able name or constant => calling func-
tion block definition’s output variable
name, ...);
 Loading...
Loading...











