142
ST Language Configuration Section 5-4
5-4-2 Variables
For details on variable specifications and setting methods, refer to the CX-
Programmer Operation Manual (W469).
5-4-3 Inputting Constants
Numerical values can be expressed in decimal, hexadecimal, octal, or binary,
as shown in the following examples.
Notation Method Example
(for the decimal value 12)
Decimal: Numerical value only 12
Hexadecimal: 16# followed by numerical value 16#C
Octal: 8# followed by numerical value 8#14
Binary: 2# followed by numerical value 2#1100
Text string: Place in single quotation marks ‘Hello world’
Note Negative hexadecimal, octal, and binary numbers are expressed as 2’s com-
plements.
The valid range of INT data is -32,768 to 32,767 in decimal, but 0000 to FFFF
in hexadecimal, so the 2’s complement is used for negative integers. For
example, when a value of -10 decimal is set in an INT variable, it will be
expressed as 16#FFF6 in hexadecimal.
5-4-4 Operators
Note Operations are performed according to the data type.
Therefore, the addition result for INT data, for example, must be a variable
using the INT data type. Particularly care is required when a carry or borrow
occurs in an operation for integer type variables. For example, using integer
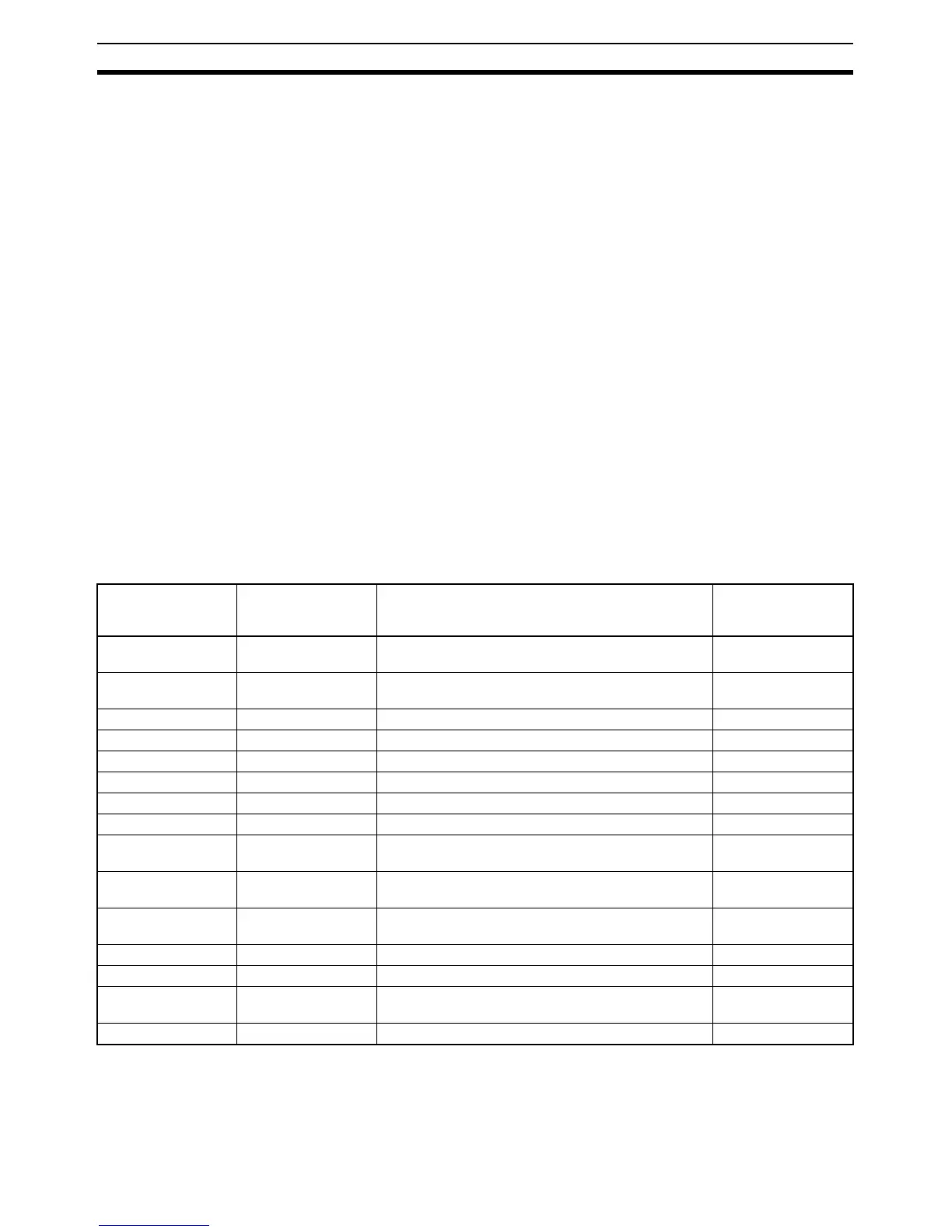
Operation Symbol Data types supported by operator Priority
1: Lowest
11: Highest
Parentheses and
brackets
(expression),
array[index]
1
Function evaluation identifier Depends on the function (refer to Appendix C Func-
tion Descriptions)
2
Exponential ** REAL, LREAL 3
Complement NOT BOOL, WORD, DWORD, LWORD 4
Multiplication * INT, DINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT, REAL, LREAL 5
Division / INT, DINT, LINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT, REAL, LREAL 5
Addition + INT, DINT, LINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT, REAL, LREAL 6
Subtraction − INT, DINT, LINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT, REAL, LREAL 6
Comparisons <, >, <=, >= BOOL, INT, DINT, LINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT,
WORD, DWORD, LWORD, REAL, LREAL
7
Equality = BOOL, INT, DINT, LINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT,
WORD, DWORD, LWORD, REAL, LREAL
8
Non-equality <> BOOL, INT, DINT, LINT, UINT, UDINT, ULINT,
WORD, DWORD, LWORD, REAL, LREAL
8
Boolean AND & BOOL, WORD, DWORD, LWORD 9
Boolean AND AND BOOL, WORD, DWORD, LWORD 9
Boolean exclusive
OR
XOR BOOL, WORD, DWORD, LWORD 10
Boolean OR OR BOOL, WORD, DWORD, LWORD 11
 Loading...
Loading...











