Parker Hannifin
Example 4
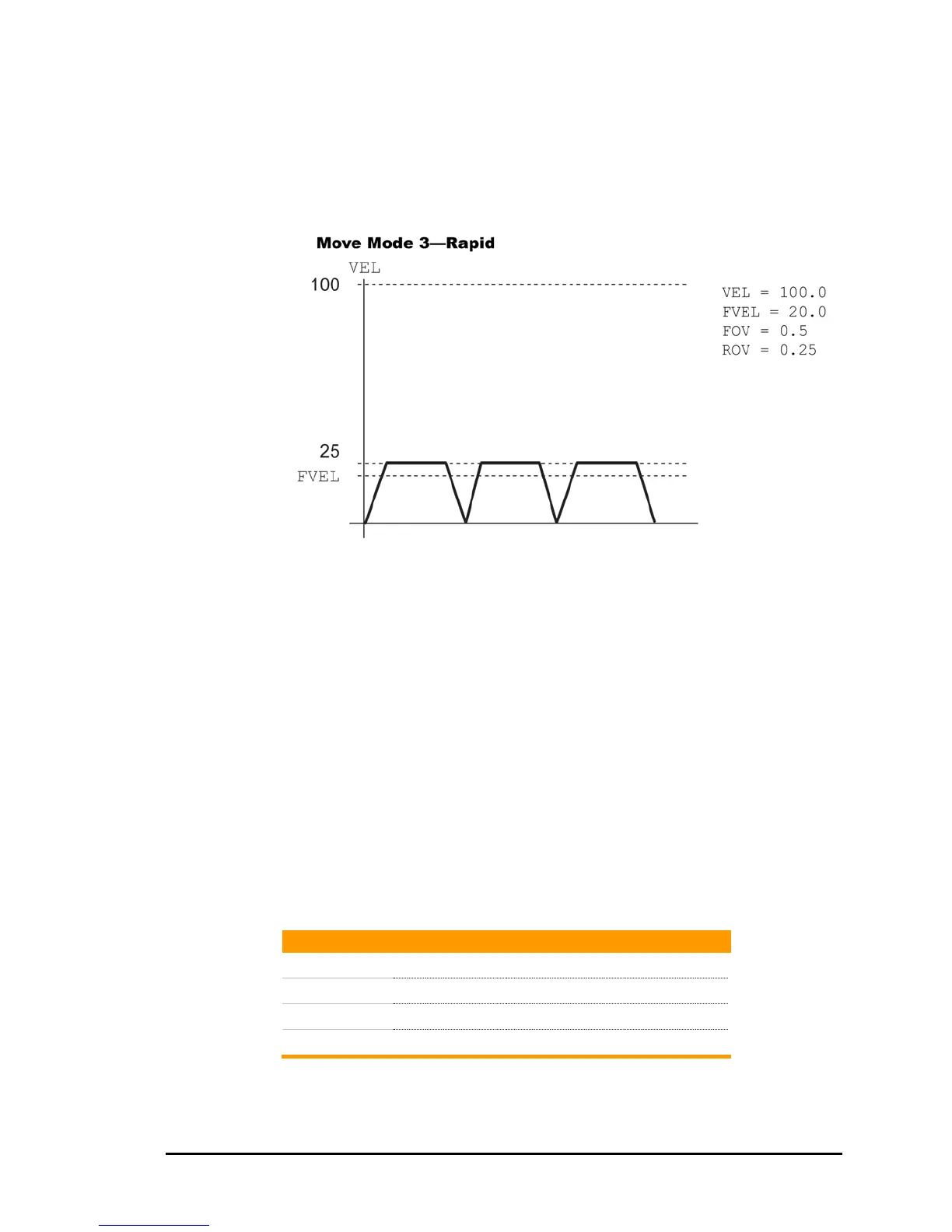
The following illustrates Move Mode 3—Rapid:
Linear Moves
The bits in header code 2 indicate which target positions are
contained in the binary move packet. If the "incremental target" bit
in header code 3 is set, the targets are relative to the current target
positions of the slaves; otherwise, the targets are absolute. The
"floating point data" bit in header code 3 indicates that the target
data is in IEEE floating point format, otherwise they are long integers.
Arc Moves
When the "arc mode" bit in header code 1 is set, a circular arc is
generated using two of the first three slaves attached to a master.
Any slaves that are given a target position, but are not part of the
circular interpolation, are executed as normal linear moves. This
allows for helical interpolation.
The "arc plane" bits in header code 1 are combined to generate a
number from 0 to 3 that defines the primary and secondary axes for
the arc as follows:
Arc Plane Primary Axis Secondary Axis
0 Slave 0 Slave 1
1 Slave 1 Slave 2
2 Slave 2 Slave 0
3 Reserved Reserved
Binary Host Interface 119

 Loading...
Loading...











