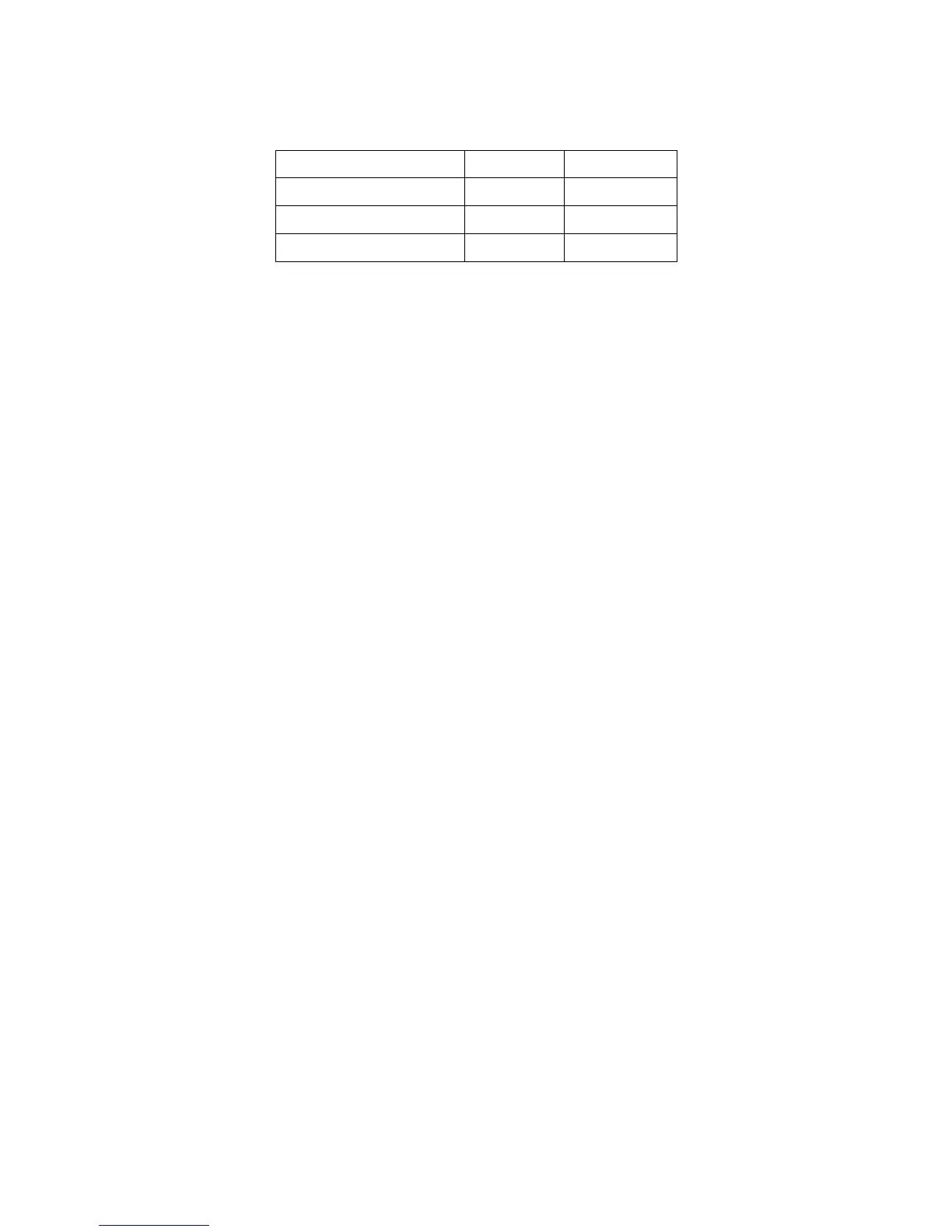
Table 2-3 Extreme Range Error Terms, K
h
and K
l
Accuracy Equations for Specific Measurement Modes
R + Q Accuracy
In the R + Q measurement mode, the basic impedance accuracy A in the equation for
impedance accuracy may be read from Figure 2-1 directly while interpreting the ―imped-
ance‖ as ―resistance.‖ The resistance accuracy is calculated from equation (1) above,
with the additional stipulation that if the measured Q has an absolute value greater than
0.1, then the basic resistance accuracy factor should be multiplied by the factor (1 + |Q|).
Let the basic resistance accuracy factor be denoted A
r
. Then the accuracy of the meas-
urement of Q is given by
Accuracy of Q [(A
r
/100) (1+Q
2
)] (2)
Note that the accuracy of Q is specified as a magnitude, not as a percentage.
L+Q Accuracy
The basic impedance accuracy depicted in Figure 2-1 applies to inductance measure-
ments when the impedance is interpreted to be 2 f L, where f is the test frequency in Hz
and L is the inductance in Henrys. For convenience, Figure 2-1 is redrawn in Figure 2-2
with lines of constant inductance superimposed. Also, Table 2-3 is recreated for inductive
impedances as Table 2-4. Note from Table 2-4 that the range error factor K
l
is negligible
for inductances above 15.9/f H and K
h
is negligible for inductances below 159/f H.
The accuracy of the inductance measurement is calculated from equation (1) above,
with the additional stipulation that if the measured Q has an absolute value less than 10,
then the basic inductance accuracy factor should be multiplied by the factor (1 + |1/Q|).
Let the basic inductance accuracy factor be denoted A
l
. Then the accuracy of the Q cal-
culation is given by equation (2) with A
l
substituted for A
r
.
C+D Accuracy
The basic impedance accuracy depicted in Figure 2-1 applies to capacitance measure-
ments when the impedance is interpreted to be 1/2 f C, where f is the test frequency in
Hz and C is the capacitance in Farads. For convenience, Figure 2-1 is redrawn in Figure
2-3 with lines of constant capacitance superimposed. Also, Table 2-3 is recreated for ca-
pacitive impedances as Table 2-5. Note from Table 2-5 that the range error factor K
l
is
negligible for capacitances below 1590/f F and K
h
is negligible for capacitances above
159/f F.

 Loading...
Loading...