4% 3% 2% 1% 0 1% 2% 3% 4%
Bin 0
Bin 1
Bin 2
Bin 3
Nominal value
Figure 4-1 Example of Nested Bins
Sequential Bins With Different Nominal Values
Suppose that the batch of nominally 100 resistors is to be sorted according to actual
value instead of according to tolerance, as in the previous example. Then the bins can
be set up to have different nominal values, with each bin width expressed as a percent-
age of the nominal value:
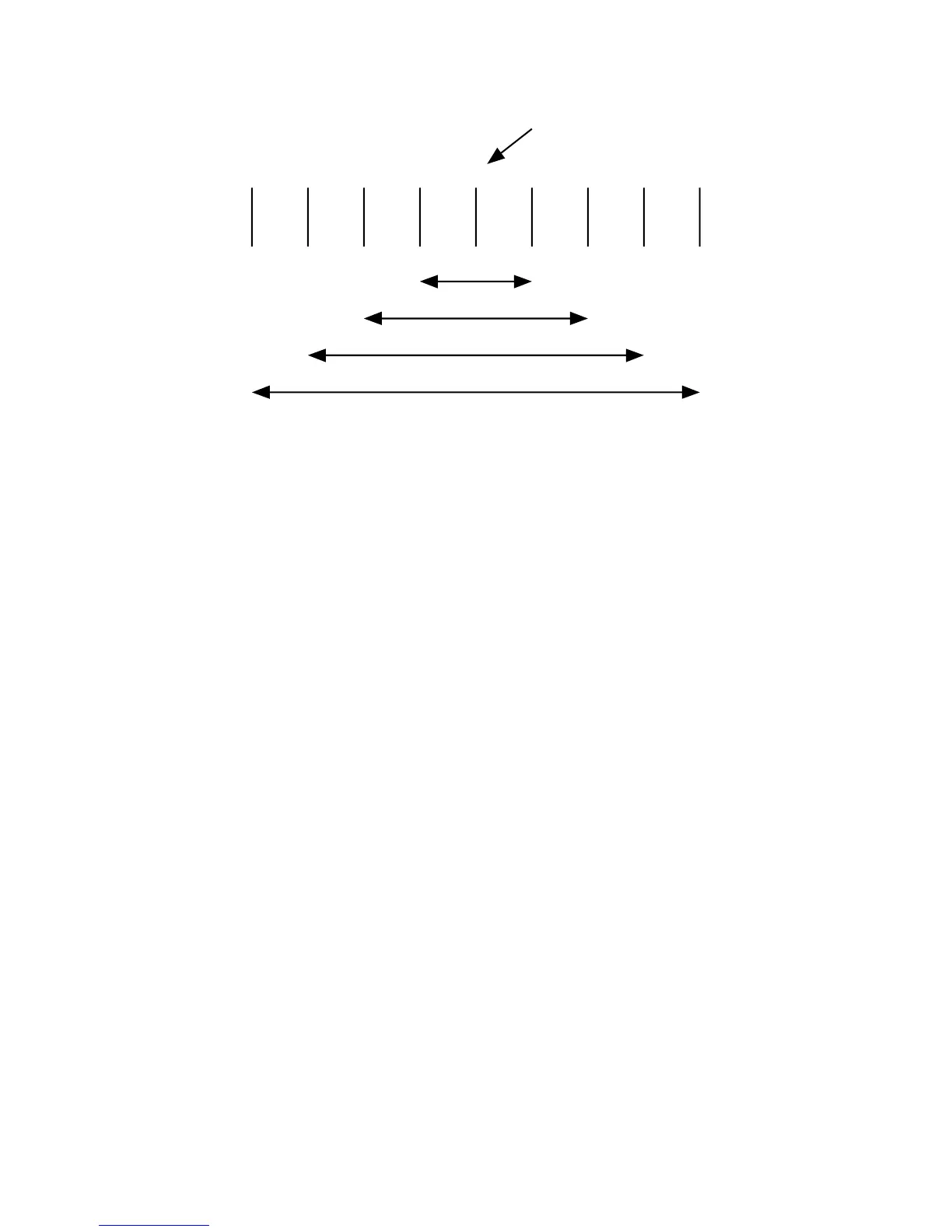
Bin 0: 98 1%
Bin 1: 100 1%
Bin 2: 102 1%
Bin 3: 104 1%
Bin 4: 106 1%
Bin 8: QDR failure (if Q is too high)
Bin 9: General failure bin (parts not falling into any other bin)
Figure 4-2 illustrates this example of sequential bins with different nominal values.
Sequential Bins With a Single Nominal Value
Suppose that the batch of nominally 100 resistors is to be sorted according to tolerance,
as in the first example, but with the ability to distinguish between the low and high values.
Then the bins can be set up to have the same nominal values, with each bin having
asymmetric limits that are expressed as a percentage of the nominal value:
Bin 0: 95 < R < 97 (5%, 3%)
Bin 1: 97 < R < 99 (3%, 1%)
Bin 2: 99 < R < 101 (1%, 1%)
Bin 3: 101 < R < 103 (1%, 3%)
Bin 4: 103 < R < 105 (3%, 5%)
Bin 8: QDR failure (if Q is too high)
Bin 9: General failure bin (parts not falling into any other bin)
Figure 4-3 illustrates this example of sequential bins with different nominal values.

 Loading...
Loading...