Rockwell Automation Publication DRIVES-AT005D-EN-P - May 2022 35
Chapter 3 Shared DC Bus Configuration (Piggyback)
Calculate the AC output power that is required during acceleration time less than 1 minute, taking advantage of the normal duty 110% for 1
minute (OL=1.1) or heavy duty 150% for 1 minute (OL=1.5) overload rating of the AC drive. If acceleration time is greater than 1 minute, use an
overload rating of OL=1.0.
PAccel = (PDrive1 + PDrive2 + …) / OL
4. Determine the total AC output power that is required during steady-state run operation.
• For Motoring Loads: PDrive = PMotor / Motor Efficiency
• For Regenerating Loads: PDrive = PMotor * Motor Efficiency
Calculate the steady-state running AC output power that is required.
PRun = PDrive1 + PDrive2 + …
5. Determine the total AC output power that is required during deceleration.
• For Motoring Loads: PDrive = PMotor / Motor Efficiency
• For Regenerating Loads: PDrive = PMotor * Motor Efficiency
Calculate the AC output power that is required during deceleration time less than 1 minute, taking advantage of the normal duty 110% for 1
minute (OL=1.1) or heavy duty 150% for 1 minute (OL=1.5) overload rating of the AC drive. If deceleration time is greater than 1 minute use an
overload rating of OL=1.0.
PDecel = (PDrive1 + PDrive2 + …) / OL
6. If any of the power levels calculated in Steps 3, 4, and 5 have a negative value, it’s an indication that line regeneration is required. Select a
PowerFlex 755TR regenerative AC drive, otherwise consider a PowerFlex 755TL low harmonic (non-regenerative) AC drive.
7. Compare the absolute values of the normal duty (ND) or heavy duty (HD) AC output power that is required during acceleration, deceleration,
and steady state (steps 3, 4, and 5). The highest numerical output power value is used in step 8 to select the PowerFlex 755TL/TR drive.
8. Select a PowerFlex 755TL/TR AC drive for the system AC voltage based on the normal duty (ND) or heavy duty (HD) AC output power rating
that meets or exceeds the highest calculated AC output power from step 7. See the PowerFlex 755TL/TR AC drive tables in Appendix C
for AC
output power ratings.
9. If the AC drive is rated more than two times the connected motor, consider changing the system design to a separate bus supply solution as
described in Chapters 2, 4, and 5. Otherwise proceed to step 10. It’s recommended that PowerFlex AC drives are rated no more than 2 times
the connected motor power rating.
10. The bus supply selected in step 8 must be able to precharge the total system DC bus capacitance. Sum the internal DC bus capacitance
values for all external connected PowerFlex 750-Series AC drives. Do not include the internal capacitance of the PowerFlex 755TL/TR AC
drive in this calculation. See Appendix A
for PowerFlex 750-Series internal DC bus capacitance and Appendix C for PowerFlex 755TL/TR
maximum external DC bus capacitance values. If the total external capacitance is less than the PowerFlex 755TL/TR maximum external
capacitance rating, then the PowerFlex 755TL/TR AC drive is capable of precharging the external AC drives; otherwise, select a higher rated
PowerFlex 755TL/TR AC drive and repeat steps 8, 9, and 10. In some cases, choosing a separate bus supply converter, as described in
chapters 2, 4, 5, and 6, may be a better solution.
11. Verify that the interconnecting DC bus cables or bus bars are adequate for the expected DC bus current to each externally connected
inverter/drive. Use the tables in Appendix A
to determine the inverter/drive rated DC input currents.
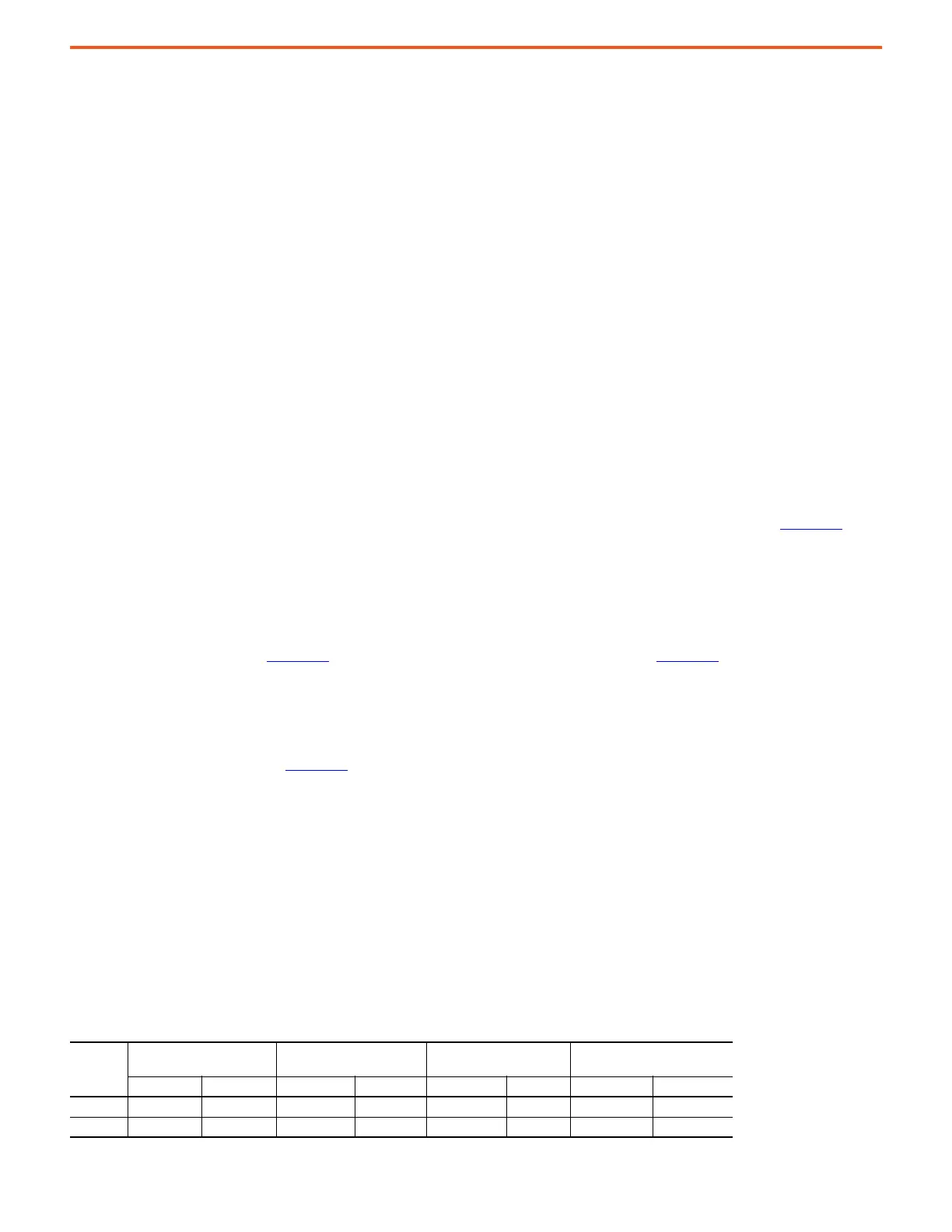
Example PowerFlex 755TL/TR Shared DC Bus Advanced Calculation
This example represents a 480V AC input system with three motors and drives. Bold text in the table represents calculated values based on the
method described earlier.
Drive 2, the 45 kW AC motor, is the highest power and should be connected to the PowerFlex 755TL/TR AC drive.
Steps 1…5 are summarized in this table.
• PMaccel, PMrun, and PMdecel are the motor shaft power requirements of the application.
• PAccel, PRun, and PDecel are the calculated AC output power requirements of the drives.
Section
Name
Motor Nameplate
Accel Drive Output Power
(kW)
Run Drive Output Power
(kW) Decel Drive Output Power (kW)
Power (kW) Efficiency PMaccel PAccel PMrun PRun PMdecel PDecel
Motor 1 11 0.9 14.00 15.56 9.00 10.00 -15.00 -13.50
Motor 2 45 0.85 50.00 58.82 35.00 41.18 -20.00 -17.00

 Loading...
Loading...











