50
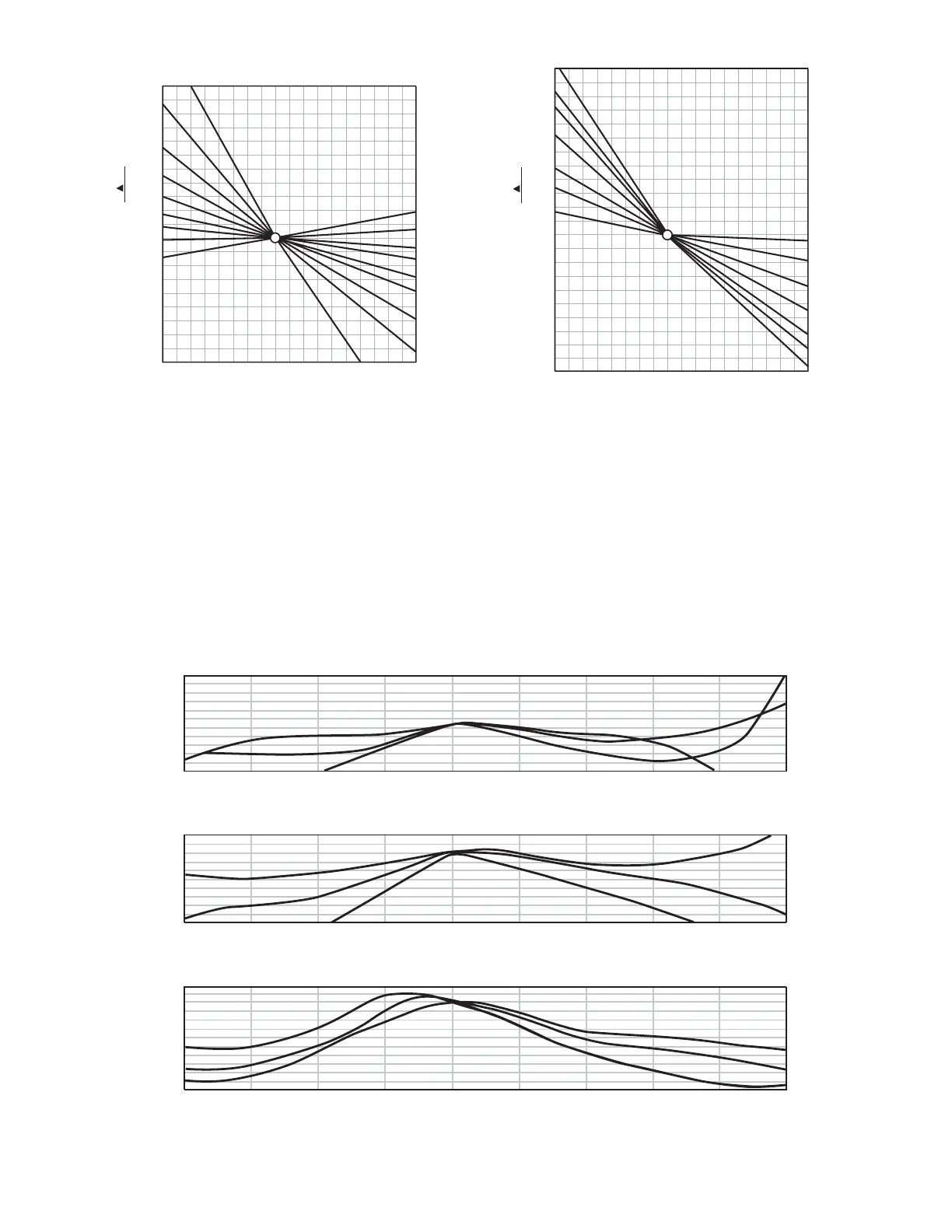
Fig. 39: Temperature change versus capacity change
of P100 to N750 temperature compensated ceramic
disc capacitors.
negative with temperature changes. The Z5U probably
has the greatest change and will only be found in non-
critical applications such as B+ power supply
decoupling. These types of capacitors should not be used
in critical applications such as oscillator and timing
circuits.
A ceramic capacitor marked GMV means that the value
marked on the capacitor is the Guaranteed Minimum
Value of capacity at room temperature. The actual value
Fig. 40: Temperature change versus capacity change
of N750 to N5600 temperature compensated ceramic
disc capacitors.
of the capacitor can be much higher. This type of
capacitor is used in bypass applications where the actual
value of capacity is not critical.
Ceramic capacitors have been the most popular
capacitors in electronics because of the versatility of the
different temperature coefficients and the cost. When
replacing a ceramic disc capacitor, be sure to replace the
defective capacitor with one having the same
characteristics and voltage rating.
Fig. 41: Temperature change versus capacity change of non-temperature compensated ceramic disc capacitors.
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0
-1.0
-2.0
-3.0
-4.0
-55 -45 -35 -25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Temperature CoefficientTemperature Coefficient
Capacitance Change
vs. Temperature
Capacitance Change
vs. Temperature
P100
P100
P
O
3
0
P
O
3
0
N
O
3
0
N
P
O
N
O
3
0
N
P
O
NO80
NO80
N
15
0
N
1
5
0
N
2
2
0
N
2
2
0
N330
N330
N470
N
4
7
0
N750
N
7
5
0
Temperature C
Percent Capacitance Change x 100
C
C@25 C
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-55 -45 -35 -25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Temperature CoefficientTemperature Coefficient
N
1
5
0
0
N
7
5
0
N
3
3
0
0
N
2
200
N
5
6
0
0
N
7
5
0
N1500
N2200
N3300
N4200
N4700
N
5600
N
4
7
0
0
N
4
2
0
0
Temperature C
Percent Capacitance Change x 100
C
C@25 C
% Capacitance Change
+10
+8
+6
+4
+2
0
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
-55 -35 -15 +5 +25 +45 +65 +85 +105 +125
Temperature C
STABLE TYPES
% Capacitance Change
+10
+5
0
-5
-10
-15
-20
-25
-30
-35
-40
-55 -35 -15 +5 +25 +45 +65 +85 +105 +125
Temperature C
SEMI-STABLE TYPES
% Capacitance Change
+20
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
0
+10
-55 -25 -15 +5 +25 +45 +65 +85 +105 +125
Temperature C
GENERAL PURPOSE TYPES
Y5D WSF
X5F, Z5F
X5P, Z5P
Z5D
Z5D
Z5F, X5F
X5P, Z5P
Y5D
W5F
X5R, Y5R, Z5R
X5S, Y5S, Z5S
X5T, Y5T, W5U
X5R, Y5R, Z5R
X5S, Y5S, Z5S
X5T, Y5T, W5U
Z5P, Z5F
Z5T
Z5F, Z5P
Z5T
X5U, Y5U
X
5
U
, Y
5
U
X5V, Y5V, Z5V
Z5U
Z
5
U
X5V,
Y5V,
Z5V
 Loading...
Loading...