49
CAPACITOR TYPES
There are many different types of capacitors, using
different types of dielectrics, each with its own best
capability. When replacing capacitors, it is best to
replace with a capacitor having not only the same
capacity and tolerance, but the same type of dielectric
and temperature characteristics as well. This will insure
continued performance equal to the original.
The capacitor is often named according to the type of
dielectric which is used, such as paper, mylar, ceramic,
mica or aluminum electrolytic.
Paper and mica were the standard dielectric materials
used in capacitors for years. Ceramic became popular
due to its stability and controlled characteristics and
lower cost over mica. Today, there are many dielectrics
with different ratings and uses in capacitors. Plastic
films of polyester, polycarbonate, polystyrene,
polypropylene, and polysulfone are used in many of the
newer large value, small size capacitors. Each film has
its own special characteristics and is chosen to be used in
the circuit for this special feature. Some of the plastic
films are also metalized by vacuum plating the film with
a metal. These are generally called self-healing type
capacitors and should not be replaced with any other
type.
Aluminum Electrolytics
The aluminum electrolytic capacitor or “Lytic” is a very
popular component. Large value capacity in a relatively
small case with a fairly high voltage rating can be
obtained quite easily. The aluminum lytic is used in
power supply filtering, audio and video coupling and in
bypass applications.
The aluminum lytic is made by using a pure aluminum
foil wound with a paper soaked in a liquid electrolyte.
When a voltage is applied to the combination, a thin
layer of oxide film forms on the pure aluminum forming
the dielectric. As long as the electrolyte remains liquid,
the capacitor is good or can be reformed after sitting for
a while. When the electrolyte dries out, the leakage goes
up and the capacitor loses capacity. This can happen to
aluminum lytics just sitting on the shelf. When an
aluminum lytic starts drying out, the capacitor begins to
show dielectric absorption. Excessive ESR is also a
common failure condition for aluminum lytic capacitors.
Tantalum Electrolytics
The tantalum electrolytic capacitor is also quite popular.
While the leakage in the aluminum lytic is very high due
to the nature of its construction, leakage in tantalum
capacitors is very low. In addition, tantalum capacitors
can be constructed with much tighter tolerances than the
aluminum lytic. The tantalum is much smaller in size for
the same capacity and working voltage than an
aluminum lytic. Tantalum lytics are popular in circuits
where high capacity and low leakage is required. The
capacity and voltage rating of the tantalum lytic is
limited, and for extremely large values of capacity and
higher voltages in power supply filtering, the aluminum
lytic is still the first choice.
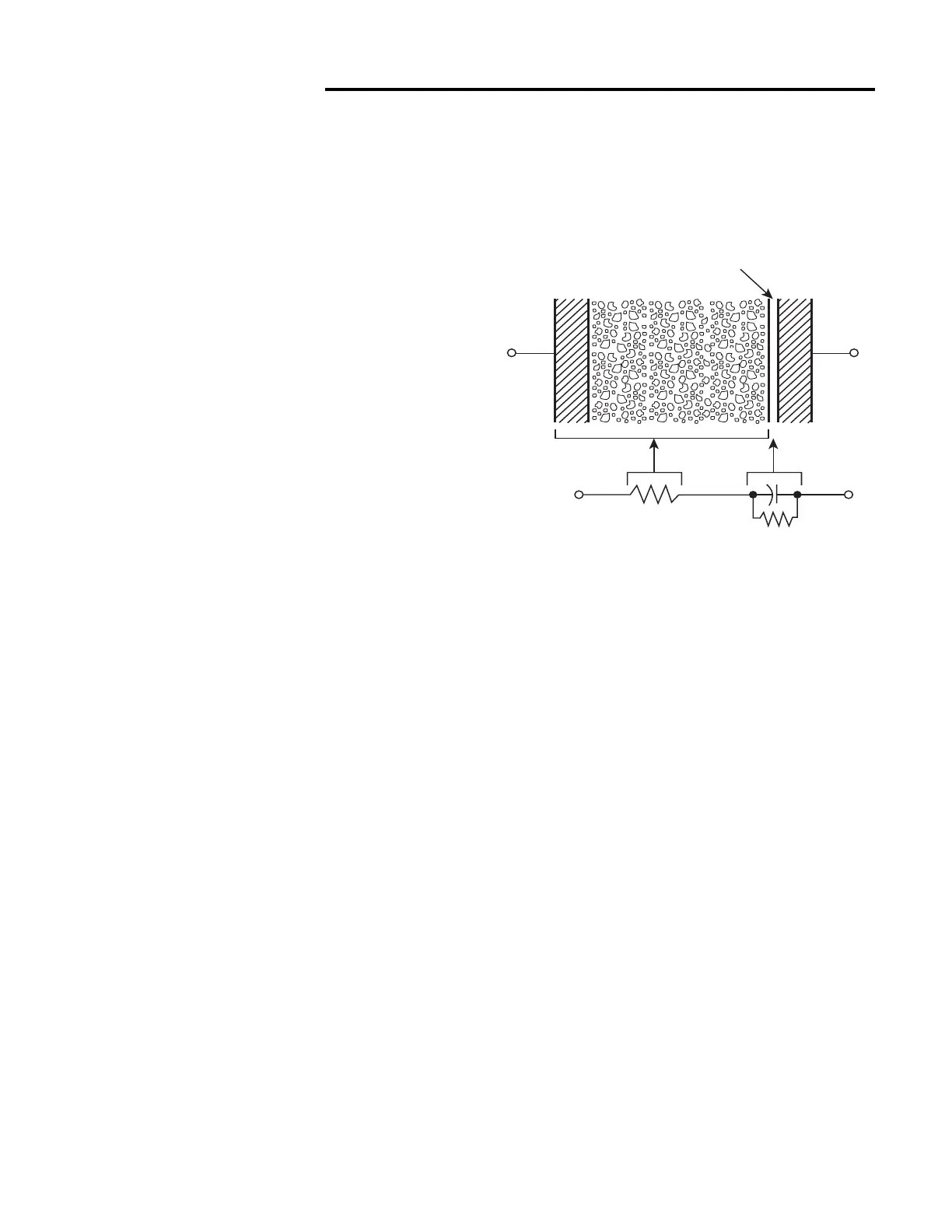
Fig. 38: Construction of an electrolytic capacitor and
its equivalent circuit.
Ceramics
Ceramic dielectric is the most versatile of all. Many
variations of capacity can be created by altering the
ceramic material. Capacitors that increase, stay the same
value, or decrease value with temperature changes can
be made. If a ceramic disc is marked with a letter P such
as P100, then the value of the capacitor will increase 100
parts per million per degree Celsius increase in
temperature. If the capacitor is marked NPO or COG,
then the value of capacity will remain constant with an
increase in the temperature.
Ceramic disc capacitors marked with an N such as
N1500 will decrease in capacity as the temperature
increases. The negative temperature coefficient is
important in many circuits such as the tuned circuits of
the radio and television IF. The temperature coefficient
of an inductor is positive and the inductance will
increase as the temperature rises. If the tuning capacitor
across the coil is a negative coefficient, then the net
result will be a zero or very little change.
General type ceramic discs are often marked with such
letters as Z5U, Z5F, Y5V, X5V, and so forth. This
indicates the type of temperature curve for the particular
capacitor. Ceramic capacitors that are not NPO or rated
with N or P type characteristics will have wider
temperature variations and can vary both positive and
Dielectric
Oxide Layer
Anode
Electrode
Cathode
Electrode
+
–
C
R
s
R
p
= Series Resistance
(Leads, Electrodes,
And Electrolyte)
= Leakage Resistance
Of Dielectric Film
Conducting
Electrolyte
Conducting
Electrolyte

 Loading...
Loading...