Sin-Cos Commutation Sensor
Analogue sin-cos encoders generate a number of sin and cosine waves per mechanical rotation of the
motor.
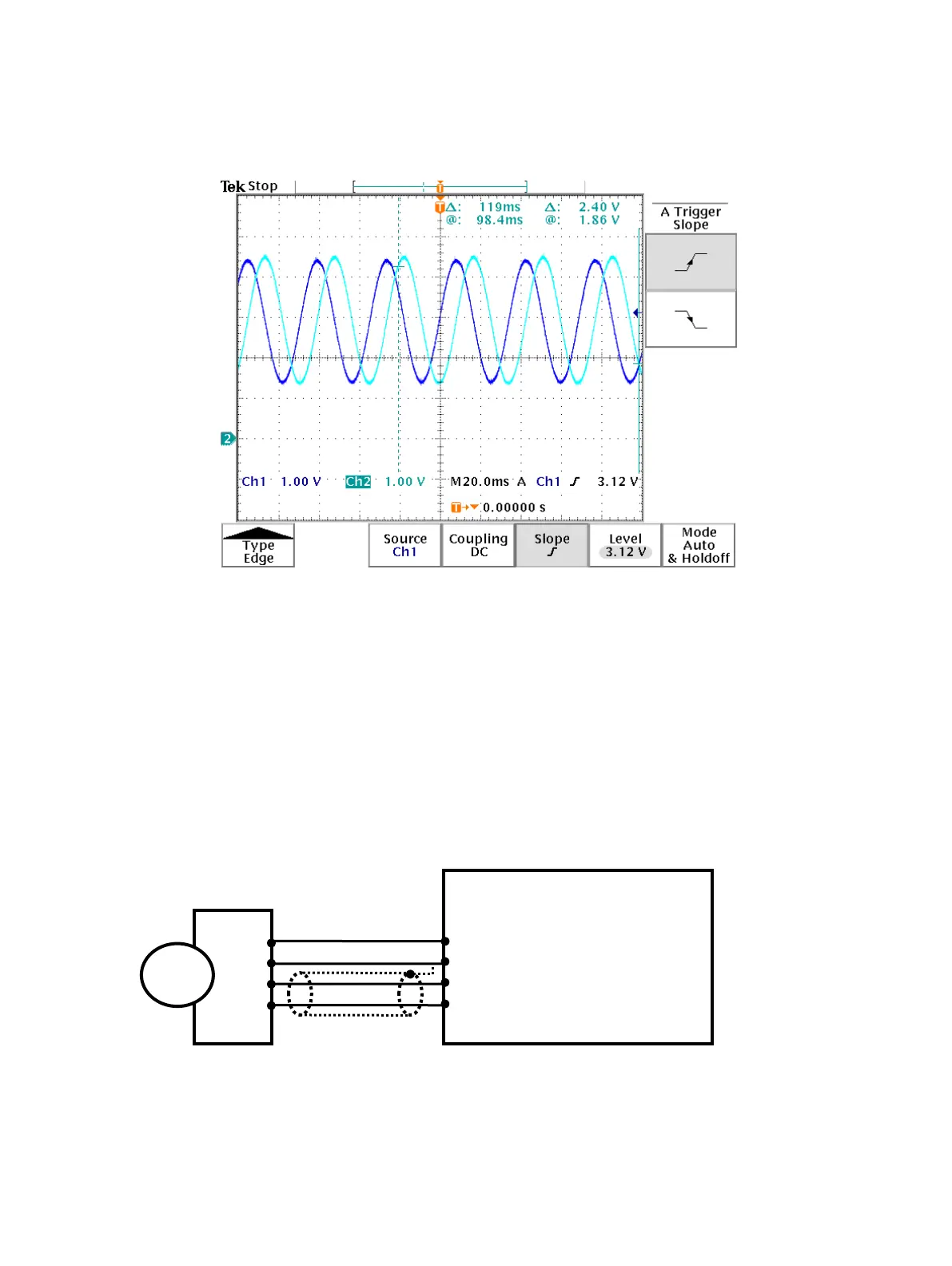
Figure 17 - Example of signals from a sin-cos position sensor
The controller is able to control motors with sin-cos sensors that produce multiple sin and cosine waves
per mechanical rotation. However, it is required that the number of pole pairs in the motor is an integer
multiple of the number of sin-cos waves per rotation (itself an integer only).
For examples:
• An encoder that produces 1 wave per rotation can be used with motors with 1 pole pair, 2 pole pairs,
3 pole pairs, etc…
• An encoder that produces 3 waves per rotation can be used with motors with 3 pole pairs, 6 pole
pairs, 9 pole pairs, etc…
• An encoder that produces 5 waves per rotation can be used with motors with 5 pole pairs, 10 pole
pairs, 15 pole pairs, etc...
Figure 18 - Sample wiring for a sin-cos commutation sensor
 Loading...
Loading...