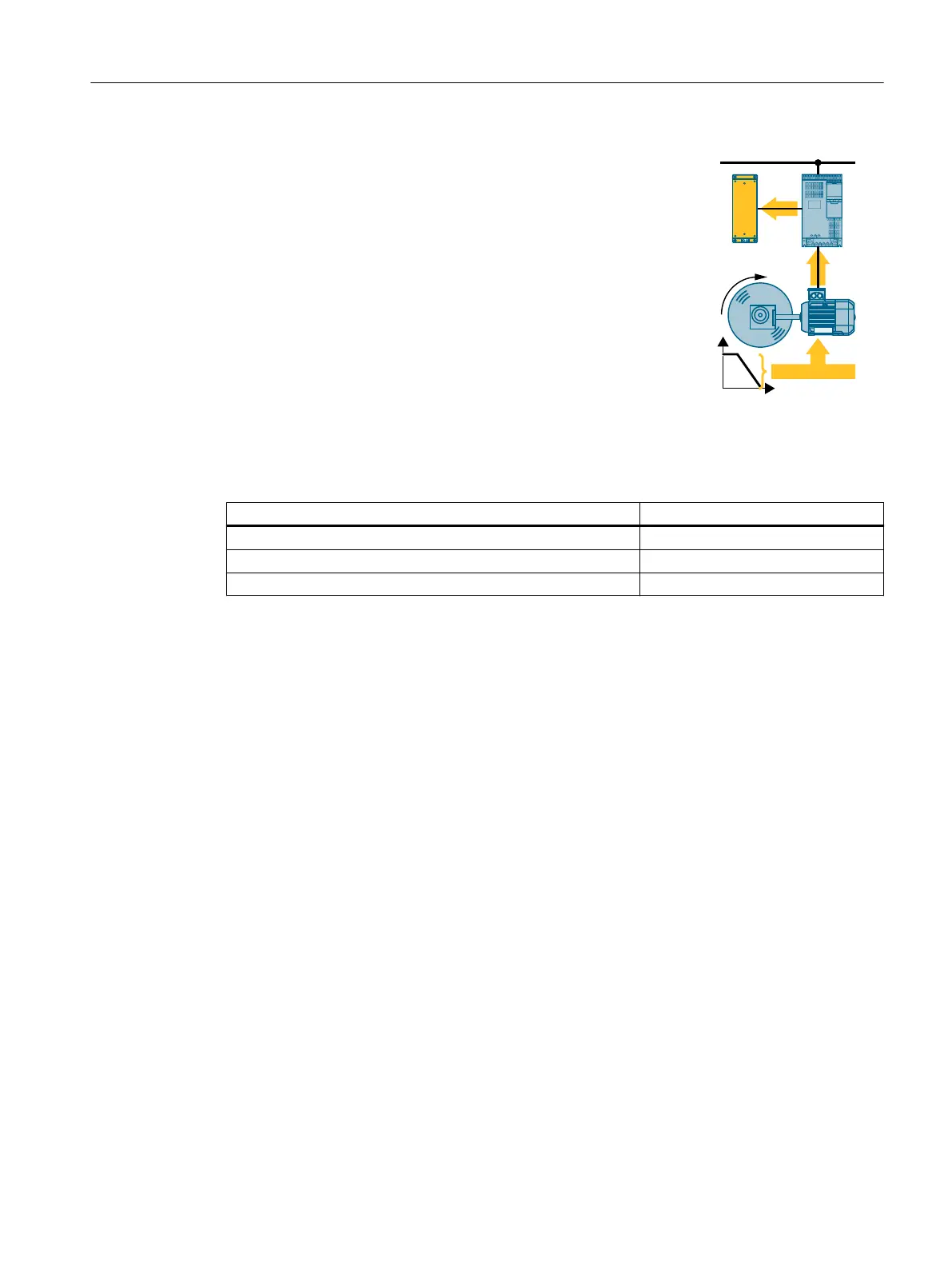
Dynamic braking
Using a braking resistor, the converter converts the electrical en‐
ergy into heat.
• AdvantagesDened braking response; motor temperature
does not increase any further; constant braking torque
• Disadvantages:Braking resistor required; braking energyE is
lost in the form of heat
Braking method depending on the application
Table 8-65 What braking method is suitable for what application?
Application examples Electrical braking method
Pumps, fans, mixers, compressors, extruders Not required
Grinding machines, conveyor belts DC braking, compound braking
Centrifuges, vertical conveyors, hoisting gear, cranes, winders Dynamic braking
Advanced commissioning
8.21Electrically braking the motor
SINAMICS G120C Converters
Operating Instructions, 02/2023, FW V4.7 SP14, A5E34263257B AK 325

 Loading...
Loading...















