Configuration
5.3 Dimensioning
Synchronous Motors 1FK7
66 Configuration Manual, (PFK7S), Edition 12.2006, 6SN1197-0AD16-0BP1
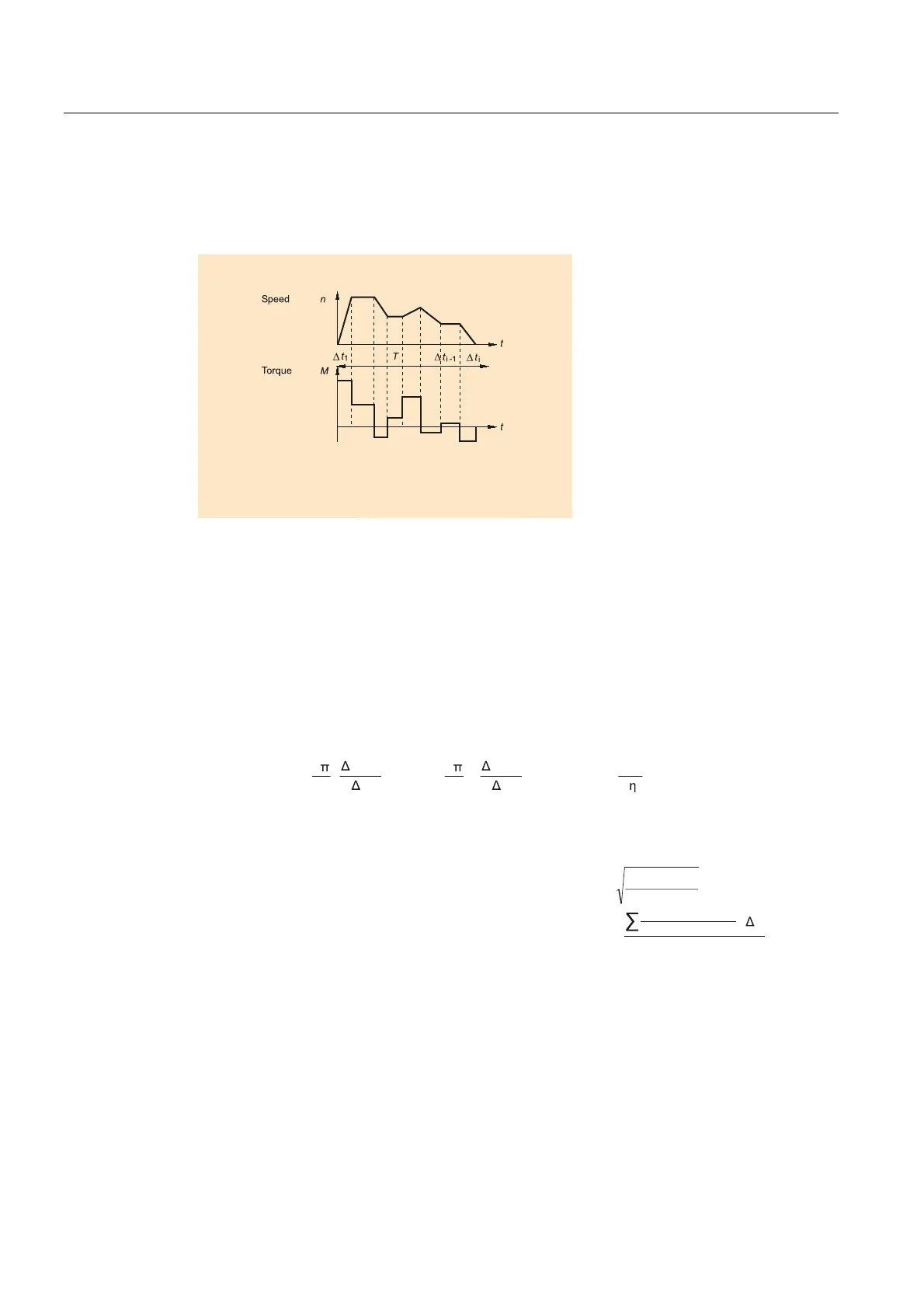
Load cycle
A load duty cycle defines the characteristics of the motor speed and the torque with respect
to time.
Figure 5-8 Example of a load duty cycle
A load torque is specified for each time period. In addition to the load torque, the average
load moment of inertia and motor moment of inertia must be taken into account for
acceleration. It may be necessary to take into account a frictional torque that opposes
the direction of motion.
The gear ratio and gear efficiency must be taken into account when calculating the load
and/or accelerating torque to be provided by the motor. A higher gear ratio increases
positioning accuracy in terms of encoder resolution. For any given motor encoder resolution,
as the gear ratio increases, so does the resolution of the machine position to be detected.
For the motor torque in a time slice Δ
t
i
the following applies:
()
•
1
•
)
++•
60
2
•
(
+••
60
2
•+=
i
MM
t
n
Ji
t
n
JJM
*
5
L/DV t
L
L/Ds W
/DV W
L
L/DV W
*
0
L0RW
The motor speed is:
L/DV WL0RW
nn •=
The RMS torque is obtained as follows:
t
M
M
∑
Δ•
=
2
0RWHII
L
0 RWL
T
The average motor speed is calculated as follows:
H
t
L
0RWN(0RWN$
0RWPLWWHO
t
nn
n
•
2
+
=

 Loading...
Loading...























