Path traversing behavior
9.3 Curve tables (CTAB)
Job planning
Programming Manual, 03/2006 Edition, 6FC5398-2BP10-1BA0
9-15
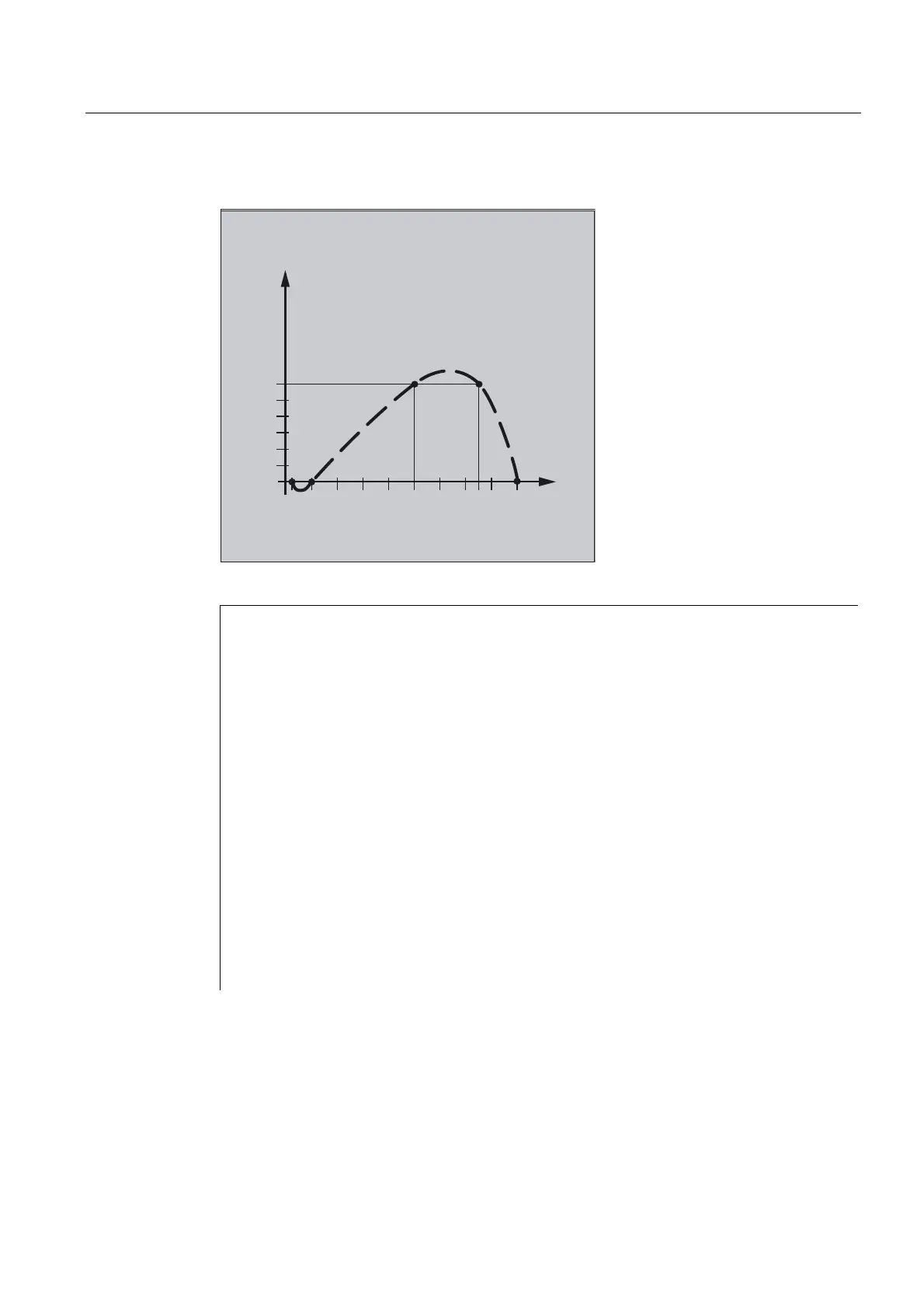
Example of the definition of a curve table
;
<
N100 CTABDEF(Y,X,3,0) ;Begin of the definition of a non-periodic
;curve table with the number 3 definition
;of the curve table
N110 X0 Y0 ;1. traverse statement defines starting
;values and 1st intermediate point:
;Master value: 0; Following value: 0
N120 X20 Y0 ;2. Intermediate point: Master value: 0…20
;Following value: starting value…0
N130 X100 Y6 ;3. Intermediate point:
;Master value: 20…100; Following value: 0…6
N140 X150 Y6 ;4. Intermediate point:
;Master value: 100…150
;Following value: 6…6
N150 X180 Y0 ;5. Intermediate point:
;Master value: 150…180
;Following value: 6…0
N200 CTABEND ;End of the definition; The curve table is
;generated in its internal representation
;as a polynomial up to the 3rd order;
;The calculation of the curve definition
;depends on the modally selected
;interpolation type
;(circular, linear, spline interpolation);
;The parts program state before the
;beginning of the definition is restored.

 Loading...
Loading...























