© Siemens AG All rights reserved. SINUMERIK, Manual, 5-axis machining
Reference section
7.1
101
Jerk
Feedforward control
Programming of velocity/feedrate profiles
To permit flexible definition of the feedrate characteristic, feedrate pro-
gramming according to DIN 66025 has been extended by means of linear
and cubic characteristics. The cubic characteristics can be programmed
either directly or as interpolating splines. These additional characteristics
make it possible to program continuously smooth velocity characteristics
depending on the curvature of the workpiece to be machined.
As a result, limiting acceleration changes can be programmed, enabling
uniform workpiece surfaces to be produced.
FNORM
FLIN
FCUB
F=FPO(..)
Basic setting. The feedrate value is defined via the block's path and sub-
sequently applies as a modal value.
Linear path velocity profile:
The feedrate value is approached linearly using the path, from the current
value at the start of the block right through to the end of the block; it then
applies as a modal value.
Cubic path velocity profile:
The F values that have been programmed block by block are combined
(in relation to the end of the block) by means of a spline. The spline starts
and ends at a tangent to the previous or subsequent feedrate function. If
the F address is missing from a block, the most recently programmed F
value will be used for this purpose.
Path velocity profile via polynomial:
The F address describes the feedrate characteristic on the basis of a
polynomial, from the current value right through to the end of the block.
The end value subsequently applies as a modal value.
endfeed
quadf
ubf
Feedrate at end of block
Quadratic polynomial coefficient
Cubic polynomial coefficient
FGROUP(X, Y,
Z,...)
Path reference
Defines the path axes in relation to the feedrate, i.e. the overall feedrate
relates to the axes defined here.
Example: FGROUP(X, Y), so the following then applies:
SOFT
BRISK
Jerk limitation
Acceleration limitation
FFWON
FWOF
Feedforward control on
Feedforward control off

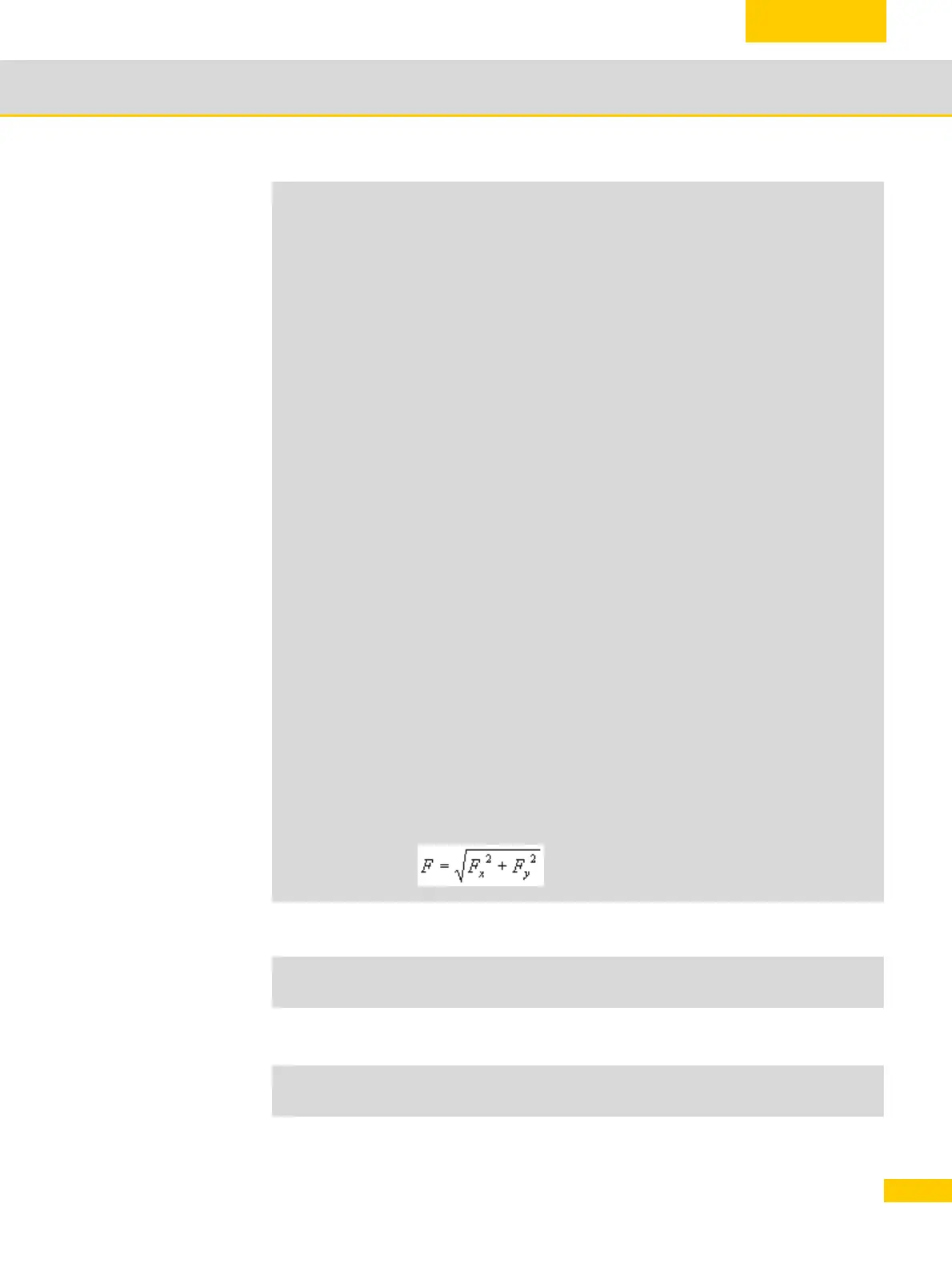 Loading...
Loading...























