89
7
Elastography Imaging
As an adjunct technique for clinical practice, the elastography determines if an area of tissue is hard or soft when
compared with its surroundings. Furthermore, it provides an elastography image to discover tumors (stiffer than
the surrounding tissue). The elastography image displays a range of map shades from the softest tissue in the
image to the stiffest in a given field of view.
Elastography is used in ultrasound diagnosis for small parts applications, such as breast and thyroid examinations.
NOTE:
The following description uses small parts examination performed with the L741 probe as an example.
7.1 Acquiring Elastography Images
Perform the following steps to acquire the elastography image.
1. Select L741 and Small Parts as the desired probe and exam type, the system automatically enters the real-time
B mode.
2. Acquire a high quality B-mode image.
3. Tap
Elasto
on the touch screen to enter the elastography imaging.
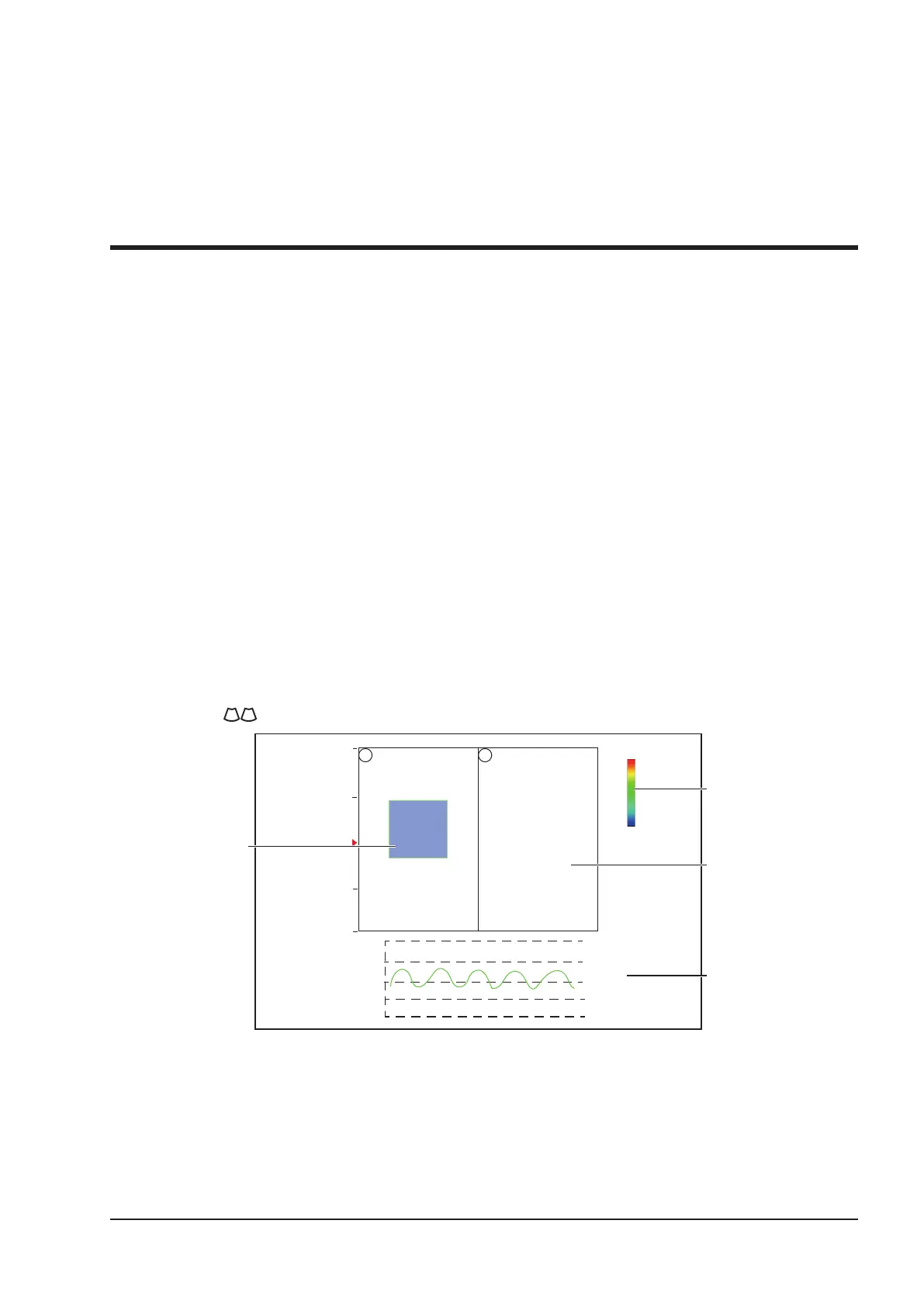
As Figure 7-1 shows, the elastography image is displayed on the left and a real-time B-mode image is displayed
on the right.
Tap on the touch screen to enter the single or dual split screen display.
0
1
2
3
4
soft
hard
+1.0
-1.0
+0.5
-0.5
0.0
Strain Curve
FPS 47
D/G 3/1
GN 255
I/P 3/30
PWR 70
FRQ 3-4.8
D 16.5cm
Elastography
image in ROI
Strain Map
B-Mode Image
S
S
Figure 7-1 Elastography Imaging Screen
−
Elastography map provides color information for tissue stiffness.
−
B-mode image is compared with the elastography image for a real-time assessment.
−
Strain curve displays the compressing frequency and its corresponding displacement. X axis is the frame
number, Y axis is the displacement of the corresponding frame.
−
The Elastography image in the ROI is translucent and overlapped on the B-mode image.
 Loading...
Loading...