SatLink VSAT User Guide
Publication no. 101557
Copyright © 2009 – STM Group, Inc.
Page 78 (160)
17. STM SatLink and DVB-S2
The DVB-S2 standard has become the most widely used standard for forward link transmission in VSAT
satellite communication systems. Advances in the field of digital coding and modulation techniques have
made possible a technology upgrade of the legacy DVB-S standard. In the DVB-S2 standard, there are
primarily four features that directly translate to improved performance:
• Higher order modulation
• Reduced carrier roll-off filtering
• Coding – LDPC-BCH with performance close to the Shannon limit
• Adaptive Coding and Modulation (ACM)
The next paragraphs provide further information on the features of the DVB-S2 standard supported by the
STM SatLink VSATs.
17.1 DVB-S2 Modulation
The STM SatLink IDUs support the following modulation schemes:
• QPSK
• 8PSK
• 16APSK
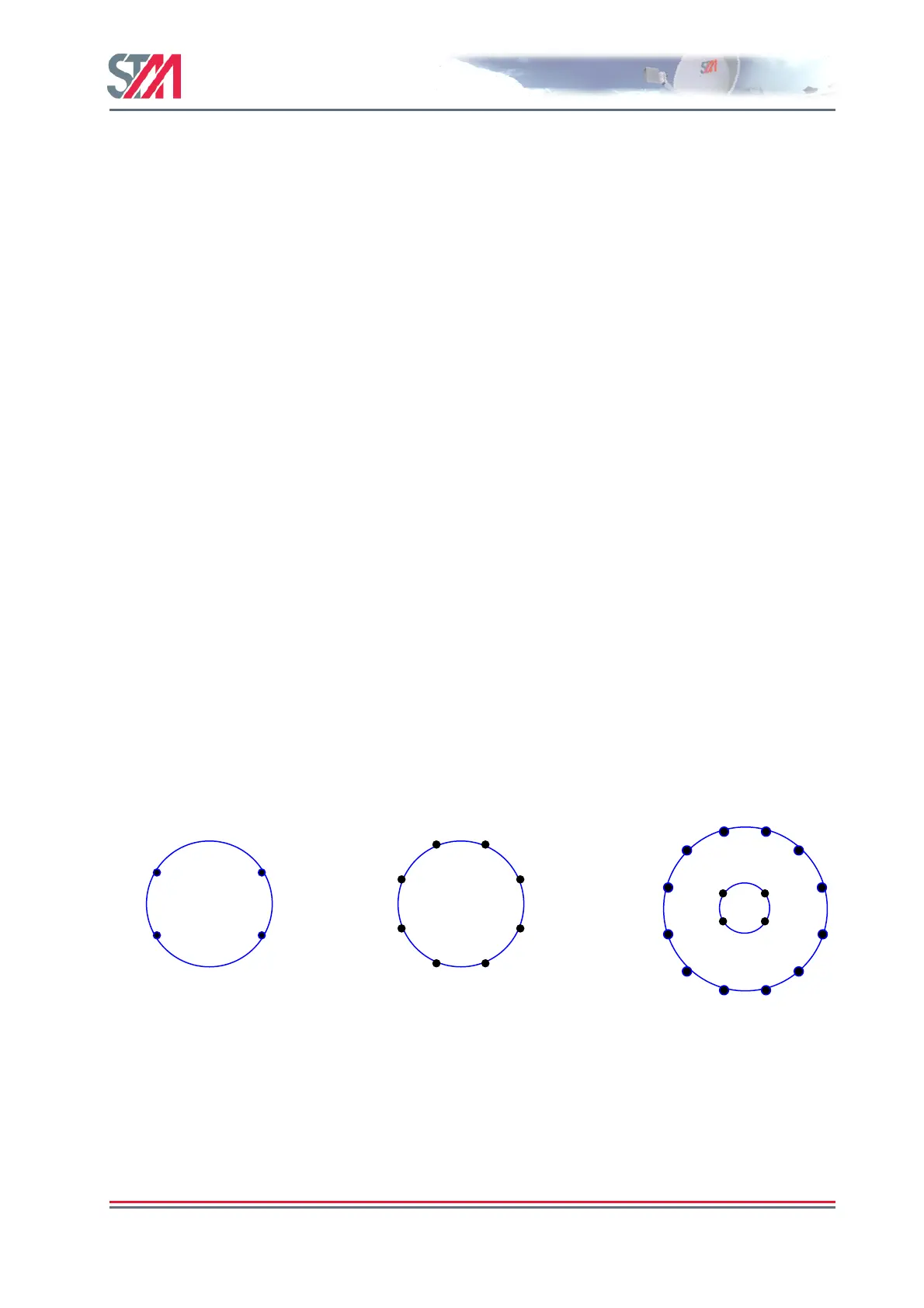
Figure 32 shows the modulation constellations for QPSK, 8PSK and 16APSK. With QPSK,
two FEC-coded bits are transmitted per modulation symbol, while with 8PSK and 16APSK
three and four FEC-coded bits respectively are transmitted per modulation symbol
DVB-S2 may be operated with three different roll-off factors for the pulse shaping filter:
0.35, 0.25 and 0.2.
Figure 32. QPSK and 8PSK and 16APSK constellations
17.2 DVB-S2 Coding
DVB-S2 uses advanced LDPC code concatenated with outer BCH codes. This coding scheme results in a
performance that is only 0.7-1.0 dB short of the theoretical Shannon bound indicated by the dotted red
line in Figure 33 below. This translates to an improvement in coding gain of close to 2 dB compared to
DVB-S systems using concatenated Reed Solomon and Convolutional FEC.
QPSK 8PSK 16APSK
 Loading...
Loading...