SYNRAD® 32-1 Operator’s Manual Version 2.2
34
Technical Reference
Delivery optics
Divergence, or expansion, of the laser beam is important for materials processing since a larg-
er beam entering the focusing optic produces a smaller focused spot. Because the laser beam
diverges slowly, increasing 8 mm in diameter over every meter, 32-1 lasers should be mount-
ed a distance of 1.0–1.5 m (40–60 in) away from the work area. Right angle turning mirrors
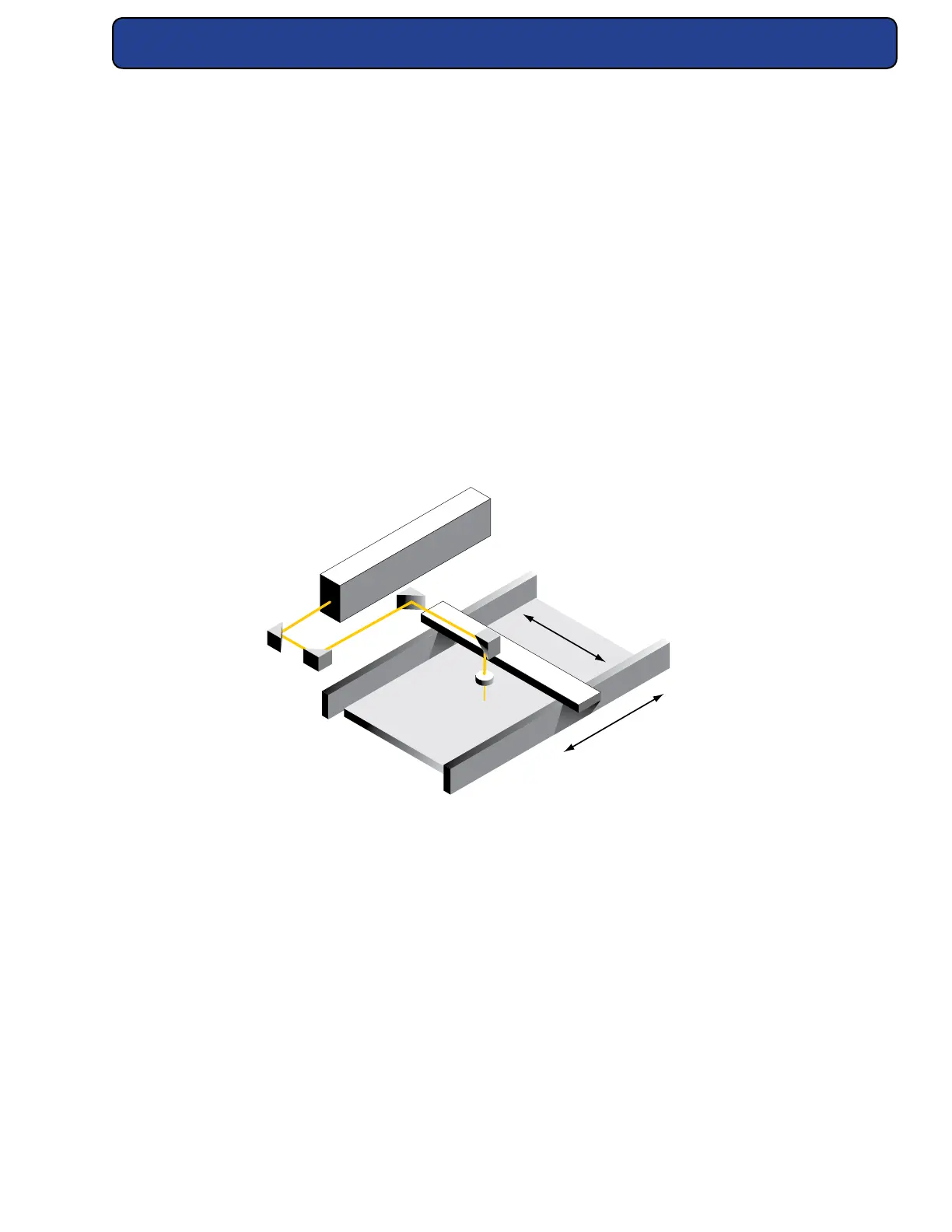
are often used in conjunction with the laser mounting position to obtain this distance. Figure
below shows how right angle turning mirrors in a “ying optics” setup create this longer beam
path.
Expander/collimators are optical devices that reduce beam divergence while at the same time
increasing beam diameter by a selectable magnication factor. Adding an expander/collima-
tor to the “ying optics” setup shown below would substantially reduce beam divergence and
any variance in beam diameter caused by the changing optical path length. In xed-length
delivery systems where the laser is positioned only one meter away from the focusing optic
and a small spot size is required, an expander/collimator is again the best solution to provide
the required beam expansion before reaching the focusing optic.
Figure 4-2 “Flying optics” beam path.
Focusing optics
When selecting a focusing optic, the primary consideration should be material thickness and
any vertical tolerances that occur during nal part positioning rather than making a selection
based only on minimum spot size. The chosen focal length should create the smallest possible
focused spot while providing the depth of eld required for the material to be processed. Op-
tics are fragile and must be handled carefully, preferably by the mounting ring only. Be careful
to select optics that are thick enough to withstand the maximum assist gas pressure available
for the process. This is especially important in metal cutting applications using high-pressure
assist gases.
 Loading...
Loading...