Manual code 75803707A.0708
Page 38 of 64
7.1.7 COOLING CAPACITY CONTROL WITH HOT GAS INJECTION VALVE
Control of cooling capacity is achieved through an electronic hot gas injection system. Injection of hot gas
downstream of the thermostatic valve reduces cooling capacity in proportion to the request from the control system.
With this system it is possible to modulate the cooling capacity between 50% and 100% of the rated capacity,
and obtain a corresponding reduction in power consumption. The opening of the injection valve is controlled by a 0 to
10V signal directly proportional to the percentage difference of the temperature from the set-point in relation to the
proportional band.
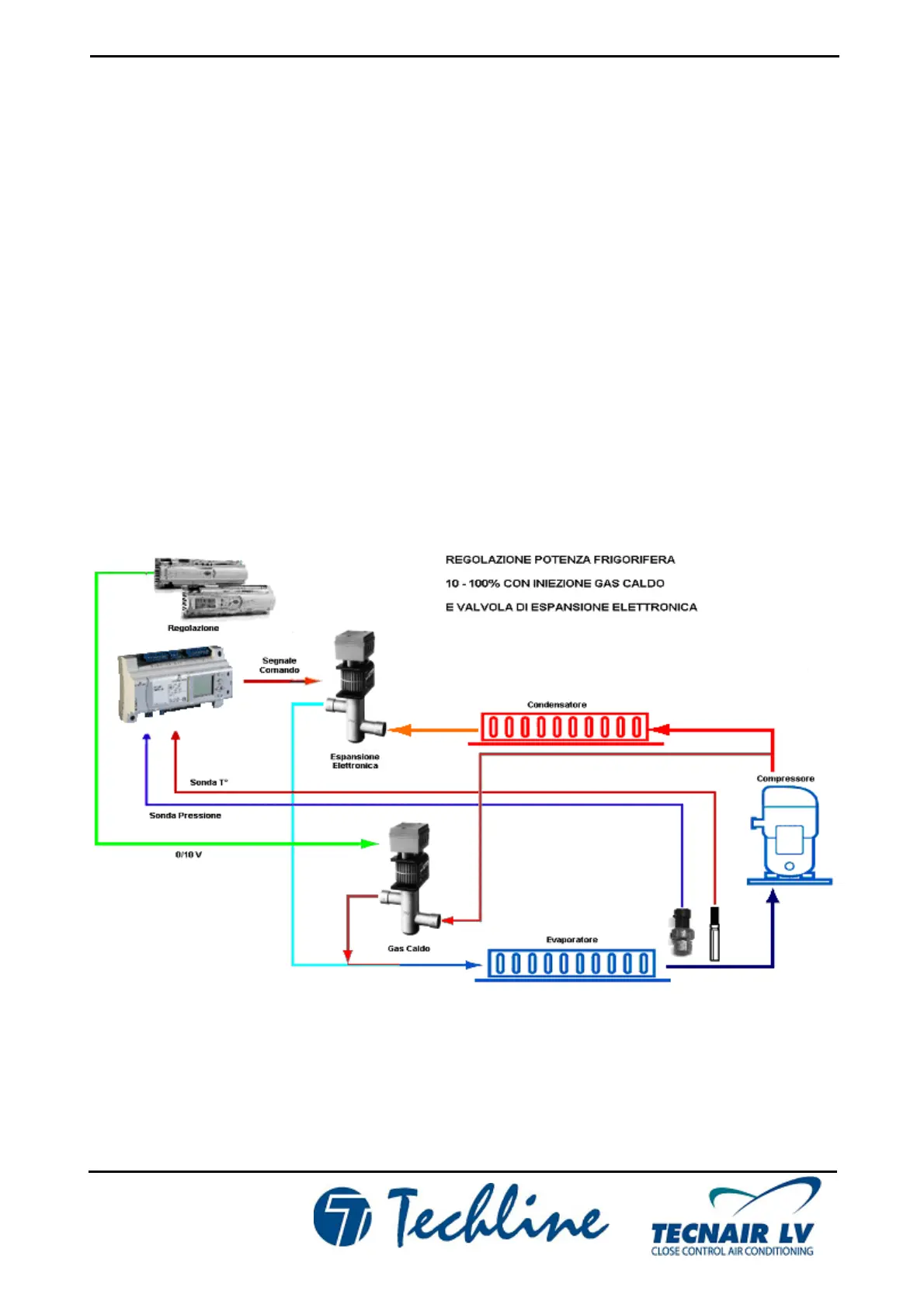
7.1.8 COOLING CAPACITY CONTROL WITH HOT GAS INJECTION VALVE AND ELECTRONIC EXPANSION
VALVE
In cases where a 50% reduction in cooling capacity is not compatible with the requirement for perfect system
control, installation of an electronic expansion valve in place of the standard thermostatic expansion valve allows
electronic control of the hot gas to reduce cooling capacity down to just 10% of the system’s rated capacity.
The electronic expansion valve (EEV) allows control of superheating on the suction line for more efficient and
versatile operation of the refrigeration system.
It is efficient, because the optimisation and stabilization of the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator increases the
overall output of the system while at the same time guaranteeing safety (less frequent tripping of the low pressure control
switch, less liquid refrigerant returning to the compressor, ...).
The following diagram shows a typical system layout. The priorities to be considered for optimal control of the
refrigeration system are a high and constant cooling capacity as well as stable superheating.

 Loading...
Loading...