© Technosoft 2011 31 IDMx40 Technical Reference
E
M
= the overall energy flowing back to the supply in Joules. In case of a rotary motor
and load, E
M
can be computed with the formula:
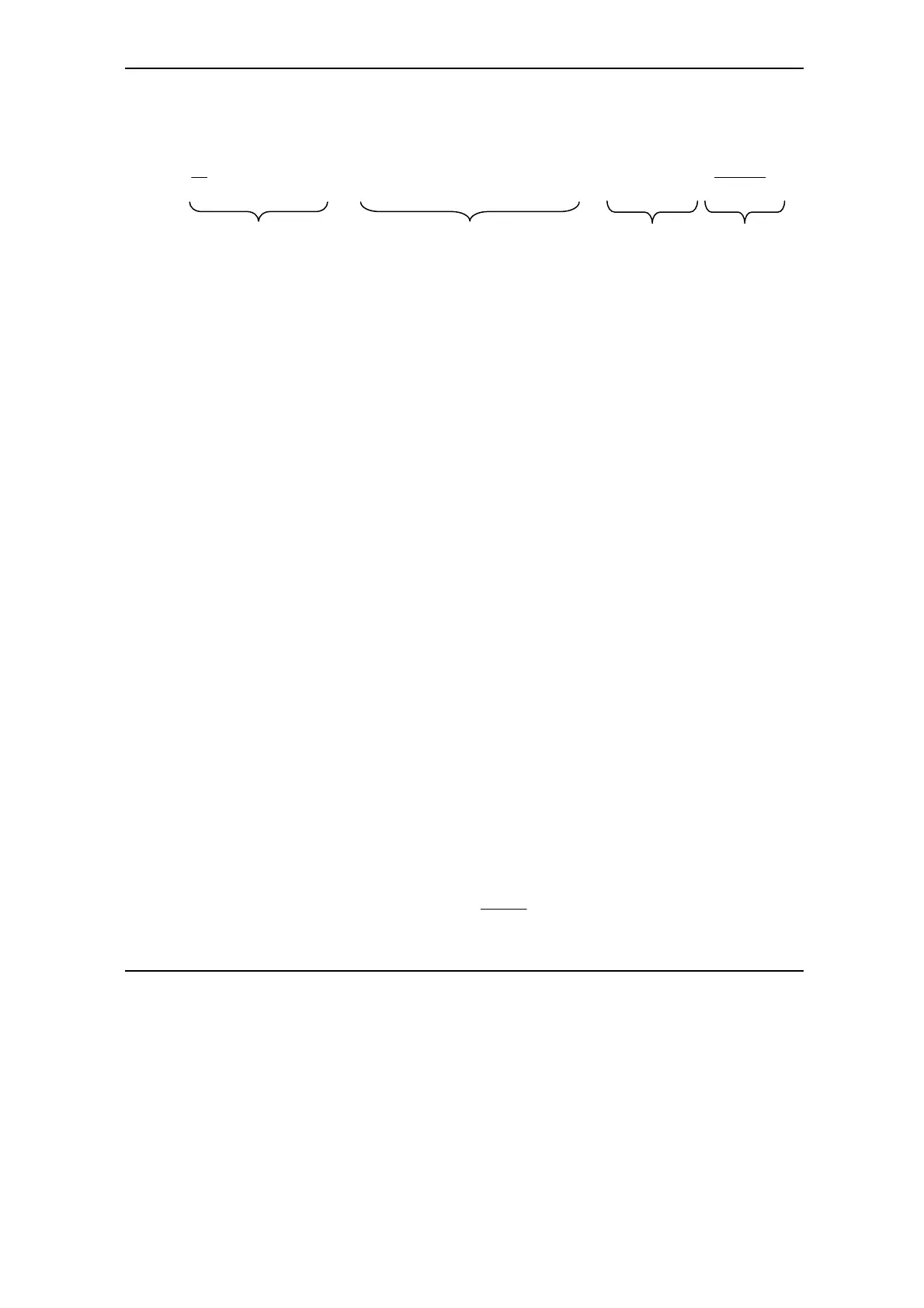
F
Md
dPh
2
MfinalinitialLM
2
MLMM
T
2
t
tR3I)h-)g(hm(m)J(J
2
1
E
ϖ
−−+++=
where:
J
M
– total rotor inertia [kgm
2
]
J
L
– total load inertia as seen at motor shaft after transmission [kgm
2
]
ϖ
M
– motor angular speed before deceleration [rad/s]
m
M
– motor mass [kg] – when motor is moving in a non-horizontal plane
m
L
– load mass [kg] – when load is moving in a non-horizontal plane
g
– gravitational acceleration i.e. 9.8 [m/s
2
]
h
initial
– initial system altitude [m]
h
final
– final system altitude [m]
I
M
– motor current during deceleration [A
RMS
/phase]
R
Ph
– motor phase resistance [Ω]
t
d
– time to decelerate [s]
T
F
– total friction torque as seen at motor shaft [Nm] – includes load and transmission
In case of a linear motor and load, the motor inertia J
M
and the load inertia J
L
will be replaced by
the motor mass and the load mass measured in [kg], the angular speed
ϖ
M
will become linear
speed measured in [m/s] and the friction torque T
F
will become friction force measured in [N].
Remark: If the above computation of E
M
can’t be done due to missing data, a good starting value
for the capacitor can be 10,000 μF / 100V.
Option 2. Connect a brake resistor R
BR
between pin 4 and pin 8 of the Motor & Supply
connector J2 and activate the drive braking circuit from EasySetUp when motor supply voltage
exceeds: U
BRAKE
= 55V (IDM240) / 87V (IDM640). This option is not available when the drive is
used with a step motor.
Remark: This option can be combined with an external capacitor whose value is not enough to
absorb the entire regenerative energy E
M
but can help reducing the brake resistor size.
Brake resistor selection
The brake resistor value must be chosen to respect the following conditions:
1. to limit the maximum current below the drive peak current I
PEAK
= 16.5A
PEAK
MAX
BR
I
U
R >
2. to sustain the required braking power:
Kinetic ener
Co
er losse
Friction losse
Potential ener
 Loading...
Loading...