ME910G1 HW Design Guide
1VV0301593 Rev.7 Page 72 of 98 2021-02-02
In order to easily rework the ME910G1 it is recommended to consider on the application
a 1.5 mm placement inhibit area around the module.
It is also suggested, as common rule for an SMT component, to avoid having a mechanical
part of the application in direct contact with the module.
In the customer application, the region under WIRING INHIBIT
(see figure above) must be clear from signal or ground paths.
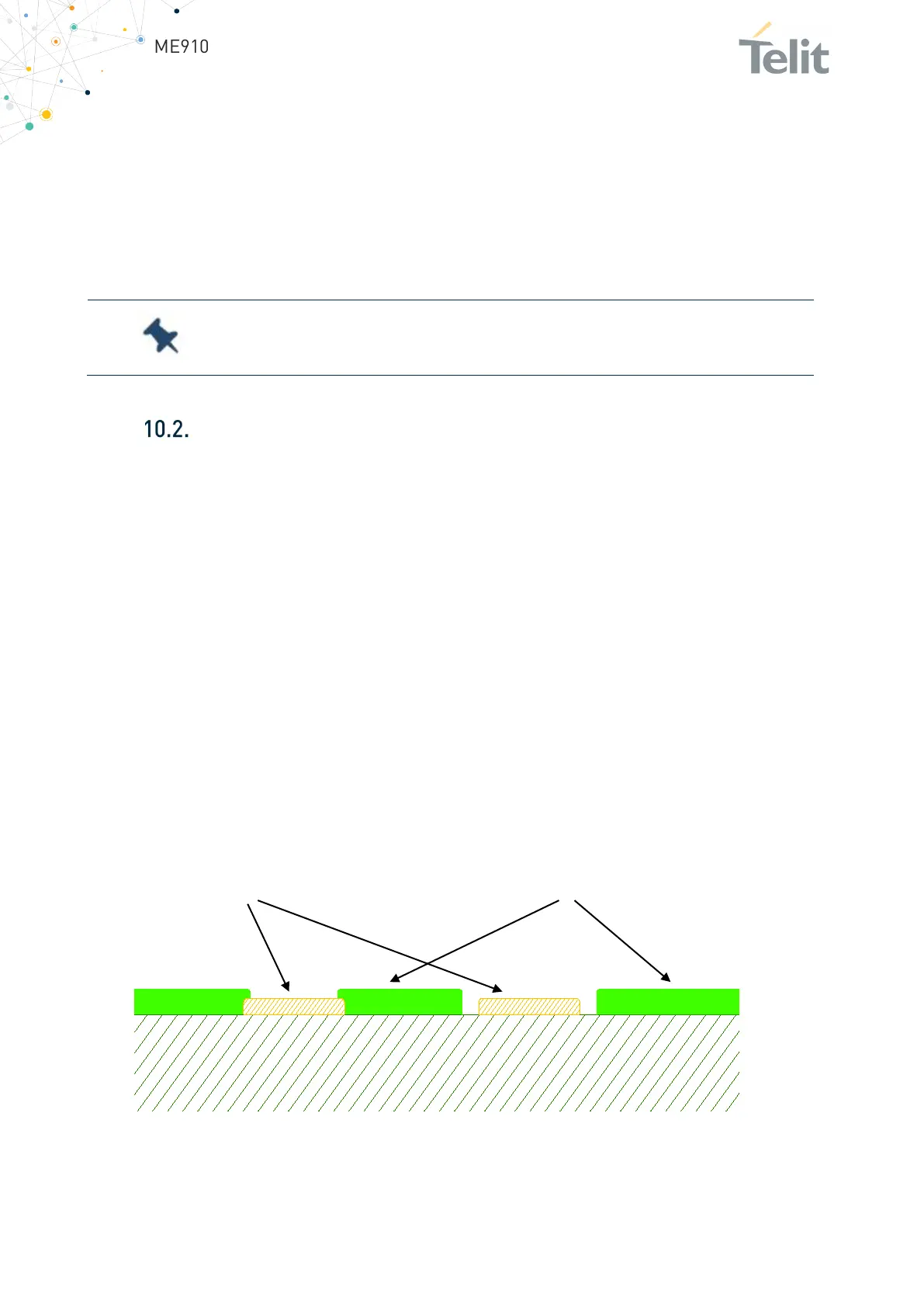
PCB pad design
In PCB design, the solder pads can be defined as either Solder Mask Defined (SMD) or
Non-Solder Mask Defined (NSMD). The difference between these two solder mask pad
definitions, is in the closeness of the solder mask to the metal pad. In SMD pads, the
solder mask opening is smaller than the metal pad and overlaps the metal on all sides.
The solder mask opening defines the solderable area of the pad. In NSMD pads, the
solder mask opening is larger than the metal pad and does not overlap the metal. The
metal edge defines the solderable area of the pad (see Figure below).
Since the metal etching process in PCB manufacture, has significantly tighter alignment
and etching tolerances than the alignment registration of the solder masking process,
which, a more accurate solder pad land pattern can be obtained with NSMD pads. In
addition, with SMD pads, the solder mask that overlaps the metal pad introduces
additional height above the metal surface that may affect solder joint adhesion and
reliability. Non solder mask defined (NSMD) type is recommended for the solder pads on
the PCB.
Figure 28: PCB solder pad recommendations
PCB
Copper Pad Solder Mask
SMD
(Solder Mask Defined)
NSMD
(Non Solder Mask Defined)

 Loading...
Loading...