Static Navigation
Static Navigation is an operating mode in which the receiver will freeze the position fix
when the speed falls below a set threshold (indicating that the receiver is stationary).
The course and altitude are also frozen, and the speed is reported as “0”.
The navigation solution is unfrozen when the speed increases above a threshold or when
the computed position exceeds a set distance (10 m) from the frozen position (indicating
that the receiver is again in motion). The speed threshold can be set via the PMTK386
command.
Set this threshold to zero to disable static navigation.
This feature is useful for applications in which very low dynamics are not expected, the
classic example being an automotive application.
Static Navigation is disabled by default but can be enabled by command $PMTK386.
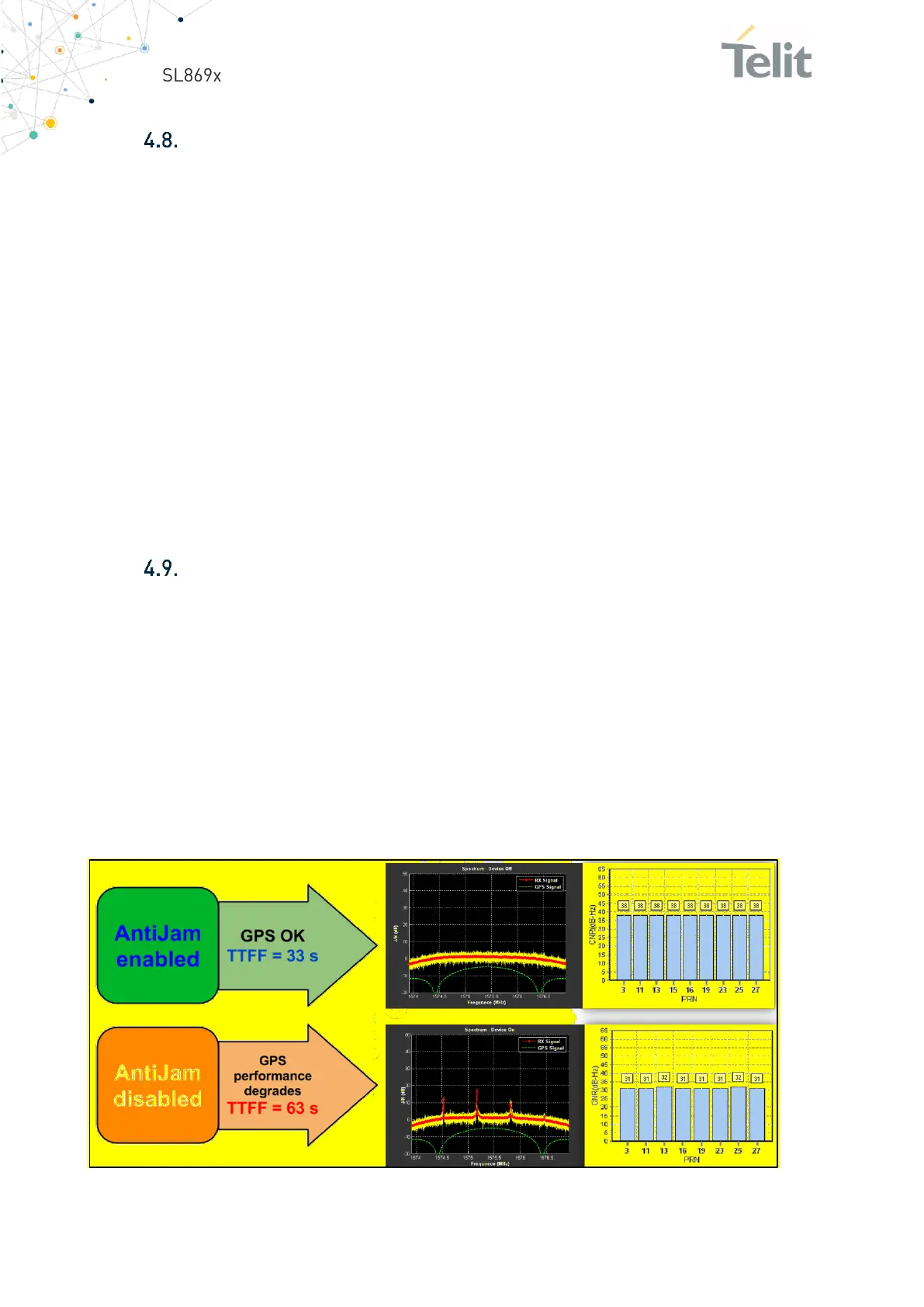
Jamming Rejection – Active Interference Cancellation (AIC)
The receiver module detects and removes narrow-band interfering signals (jamming
signals) without the need for external components or tuning. It rejects up to 12 CW
(Continuous Wave) type signals of up to –80 dBm (total power signal levels). This feature
is useful both in the design stage and during the production stage for uncovering issues
related to unexpected jamming. When enabled, Jamming Rejection will increase current
drain by about 1 mA, and impact on GNSS performance is low at modest jamming levels.
However, at high jamming levels (for example, –90 to –80 dBm), the RF signal sampling
ADC starts to become saturated after which the GNSS signal levels start to diminish.
Jamming rejection is enabled by default but can be disabled with the PMTK286 command.
Figure 12: Jamming Rejection

 Loading...
Loading...