Chapter 6 Deployment CPU 31x with TCP/IP Manual VIPA System 300V
6-38 HB130E - CPU - Rev. 11/50
ORG-identifier 05h-0Ah
CPU-area PB ZB TB DI
ORG-identifier 05h 06h 07h 0Ah
Description source/destination data
from/into peripheral
modules. Input module
for source data, output
module for destination
data.
source/destination
data from/into counter
cells.
Source/destination
data from/into timer
cells.
Source/destination
data from/into
extended data block
DBNO
valid range:
irrelevant irrelevant irrelevant DI, from where the data
can be retrieved or
where it is saved
1...255
Start address
Significance
valid range:
PB-No., from where the
data can be retrieved or
where it is saved.
0...127 digital Periph.
128...255 anal. Periph.
ZB-No., from where the
data can be retrieved or
where it is saved.
0...255
TB-No., from where the
data can be retrieved or
where it is saved.
0...255
DW-No. from where the
data can be retrieved or
where it is saved.
0...2047
Quantity
Significance
valid range:
Length of the
source/destination data
block in bytes.
1...256
Length of the
source/destination
data block in words
(counter cell = 1 word).
1...256
Length of the
source/destination
data block in words
(counter cell = 1 word).
1...256
Length of the
source/destination
data block in words
1...2048
ORG-identifier 81h-FFh
To transfer data blocks of the number range 256 ... 32768 you may use the
ORG identifier 81h-FFh.
For the setting of a DB No. >255 needs a length of one word, the DBNO
new
is assembled from the content of the ORG identifier and the DBNO.
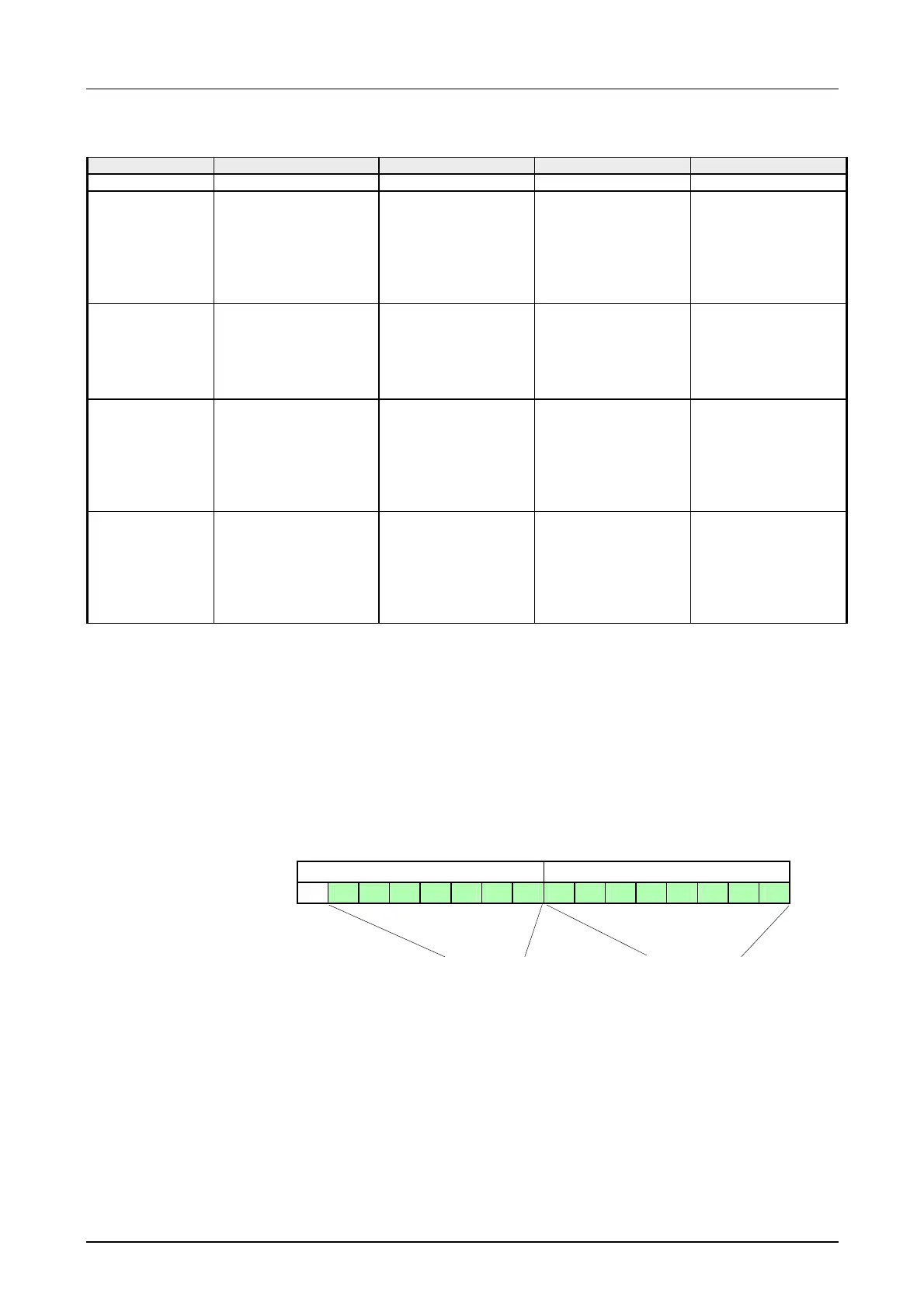
DBNO
new
is created as word as follows:
DBNO
new
High-Byte Low-Byte
0 X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
ORG-identifier (0XXXXXXX)
DBNO (XXXXXXXX)
If the highest Bit of the ORG identifier is set, the Low-Byte of DBNO
new
is
defined via DBNO and the High-Byte of DBNO
new
via ORG identifier, where
the highest Bit of the ORG-identifier is eliminated.
The following formula illustrates this:
DBNO
new
=256 x (ORG-identifier AND 7Fh) + DBNO
Transfer of blocks
with numbers
>255
 Loading...
Loading...