Programming 47
Torque Limit Operation Examples
Operation examples will be described separately for winding operation, in which the speed and motor torque are in the same
directions, and rewinding operation, in the which the speed and motor torque are in opposite directions.
Winding Operation
In a winding operation, the line (speed) and torque generated by the motor are in the same direction. For the winding operation, both
the speed limit and the torque reference input are positive. The motor will accelerate when the torque reference input is larger than the
load and will decelerate when it is smaller than the load. If the motor turns faster than the speed limit, a negative compensation value is
output from the speed limiter circuit. When the speed then drops below the speed limit, a positive compensation value is output. The
torque compensation is proportional to the ASR proportional gain. When the sum of the torque reference and the torque compensation
output by the speed limiter is the same as the actual load, the motor will stop accelerating and run at a constant speed.
Rewinding Operation
In a rewinding operation, the line (speed) and torque generated by the motor are in the opposite directions. (In this example, it
is assumed that the line speed is positive and the torque reference input is negative.) For the rewinding operation, the speed
limit is positive and the torque reference input is negative. If the motor turns faster than the speed limit, a negative
compensation value is output. If the speed is zero or is below the speed limit, a zero compensation value is output. In this way,
the output from the speed limiter is used to maintain the motor speed between zero and the speed limit. When the sum of the
torque reference and the torque compensation output by the speed limiter is the same as the actual load, the motor will stop
accelerating and run at a constant speed.
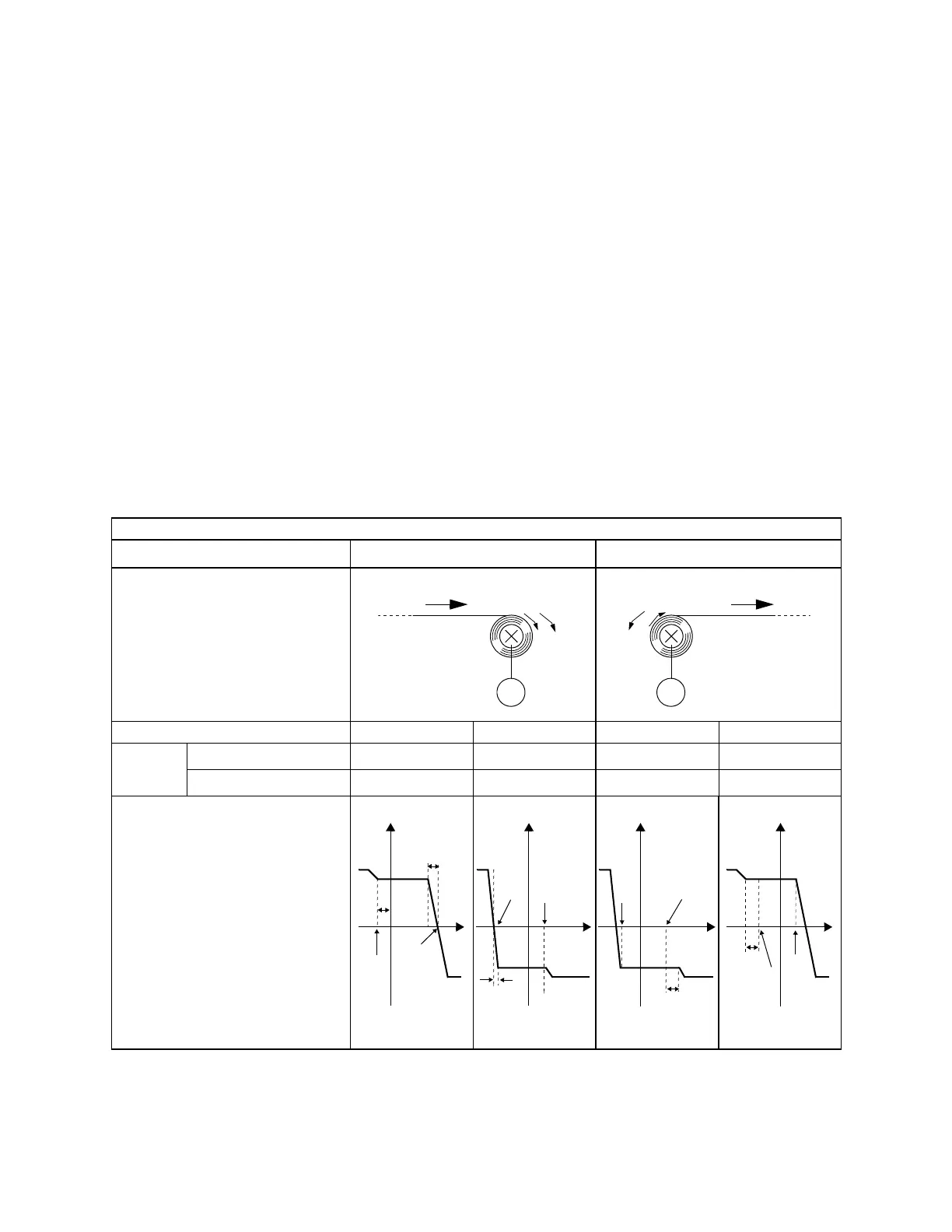
Table 7 Torque Control Example
Winding Operation Rewinding Operation
Configuration
Direction of Motor Rotation Forward Reverse Forward Reverse
Reference
Polarity
Torque Reference (TREF)
+--+
Speed Limit (NLIM)
+-+-
Torque Profile
M
Motor
Line Direction
TN
M
Motor
Line Direction
T
N
0
Speed
NLIM
TREF
Torque
Torque
Limit
Torque
Limit
DeltaN
DeltaN(%)=TREF(%)/C5-01
d5-05
Speed
d5-05
TREF
Torque
Torque
Limit
0
DeltaN(%)=TREF(%)/C5-01
NLIM
DeltaN
Speed
NLIM
Torque
Torque
Limit
0
Torque
Limit
DeltaN(%)=TREF(%)/C5-01
d5-05
DeltaN
TREF
=TREF(%)/d5-05(%)
Smaller of
0
Speed
NLIM
TREF
Torque
Torque
Limit
Torque
Limit
DeltaN(%)=TREF(%)/C5-01
=TREF(%)/d5-05(%)
Smaller of
d5-05
DeltaN

 Loading...
Loading...











