Technical data
121
• cable length, i.e. the longer the cable the weaker the fuse protection, as the long cable limits the
fault current
• cable size, i.e. the smaller the cable cross-section the weaker the fuse protection, as the small cable
size limits the fault current
• transformer size, i.e the smaller the transformer the weaker the fuse protection, as the small
transformer limits the fault current
• transformer impedance, i.e. the higher the z
k
the weaker the fuse protection as high impedance
limits the fault current.
The protection can be improved by installing a larger supply transformer and/or bigger cables, and in
most cases by selecting aR fuses instead of gG fuses. Selection of smaller fuses improves the
protection, but may also affect the fuse life time and lead to unnecessary operation of the fuses.
In case of any uncertainty regarding the drive protection, please contact your local ABB.
Cable types
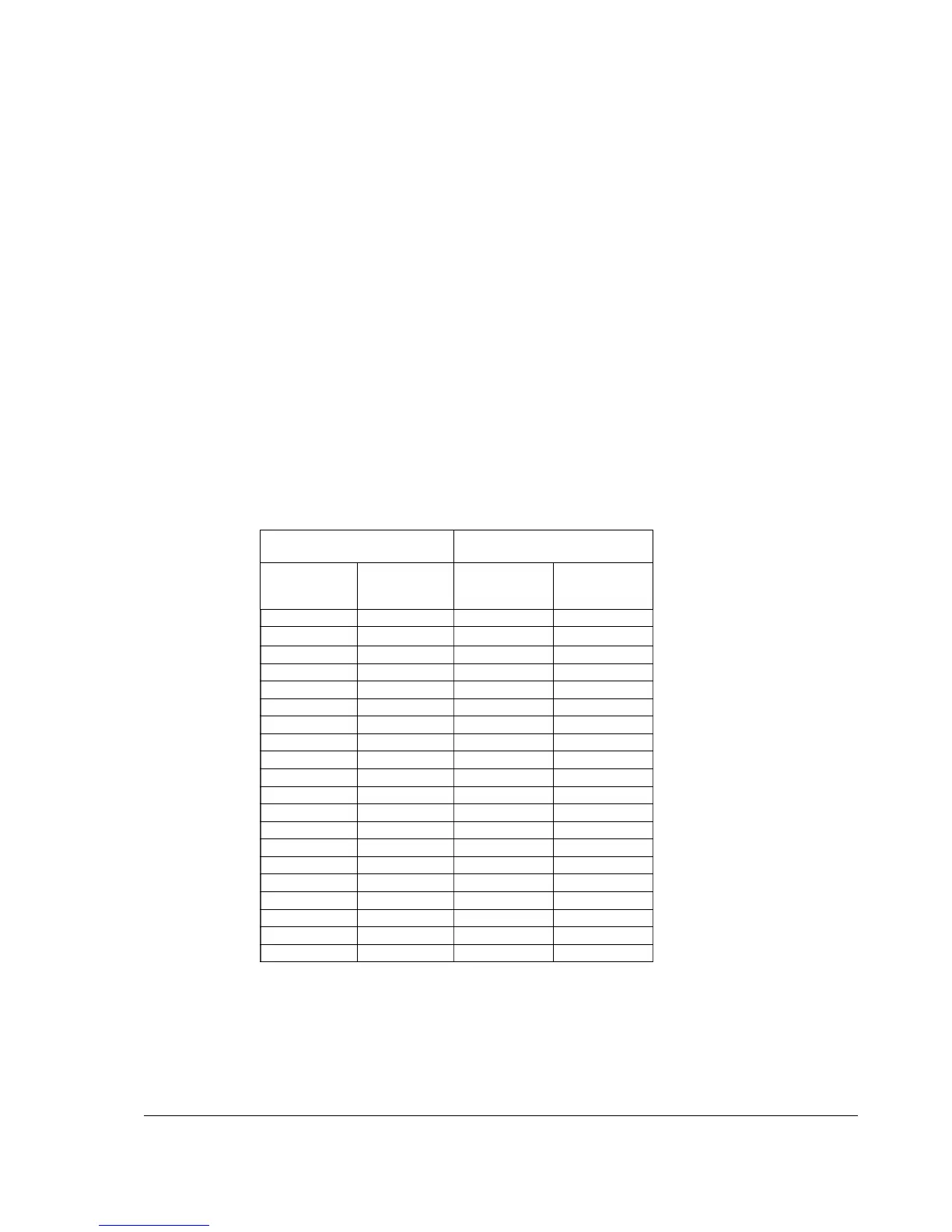
The table below gives copper and aluminium cable types for different load currents.
Cable sizing is based on max. 9 cables laid on a cable ladder side by side, three
ladder type trays one on top of the other, ambient temperature 30 °C (86 °F), PVC
insulation, surface temperature 70 °C (158 °F) (EN 60204-1 and
IEC 60364-5-52:2001). For other conditions, size the cables according to local
safety regulations, appropriate input voltage and the load current of the drive.
Copper cables with concentric
copper shield
Aluminium cables with concentric
copper shield
Max. load
current
A
Cable type
mm
2
Max. load
current
A
Cable type
mm
2
56 3×16 69 3×35
71 3×25 83 3×50
88 3×35 107 3×70
107 3×50 130 3×95
137 3×70 151 3×120
167 3×95 174 3×150
193 3×120 199 3×185
223 3×150 235 3×240
255 3×185 214 2 × (3×70)
301 3×240 260 2 × (3×95)
274 2 × (3×70) 302 2 × (3×120)
334 2 × (3×95) 348 2 × (3×150)
386 2 × (3×120) 398 2 × (3×185)
446 2 × (3×150) 470 2 × (3×240)
510 2 × (3x185) 522 3 × (3×150)
602 2 × (3×240) 597 3 × (3×185)
579 3 × (3×120) 705 3 × (3×240)
669 3 × (3×150)
765 3 × (3×185)
903 3 × (3×240)
3BFA 01051905 C
 Loading...
Loading...











