dBm The decibel (dB) is commonly used to describe RMS voltage or
power ratios between two signals. By itself, a decibel value has no
particular meaning. Decibels are a ratio or comparison unit and have no
absolute meaning without knowledge of a reference or comparison unit.
When power comparisons are made to a 1 mW reference level, the letter
m is added to give “dBm”. For power ratios such as dBm, it is common to
specify the resistance loading the voltage source. Often the system
resistance is added to the units by indicating “dBm (50
W)” for a 50W
resistance system.
dB = 10 x log
10
( P / Pref )
dBm = 10 x log
10
( P / 0.001 )
where power P = V
2
/R
For a 50
W resistance, 1 mW of power corresponds to 0.224 VRMS.
Use the following conversions to determine dBm levels when connecting
75
W or 600W load resistances.
dBm (75
W) = dBm (50 W) – 1.75
dBm (600
W) = dBm (50 W) – 10.79
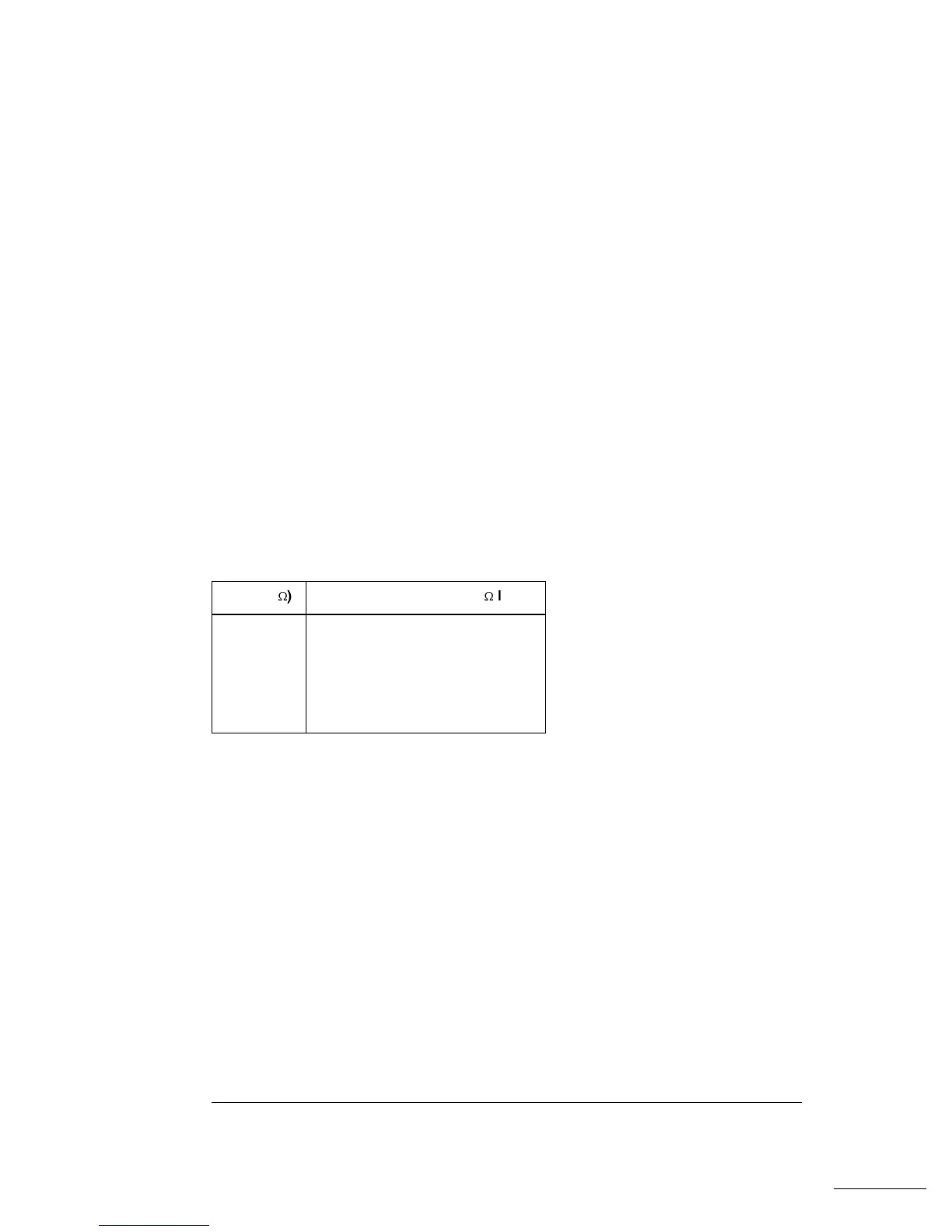
dBm (50
W
) Output Voltage Level (50
W
load)
+23.98 3.53 VRMS
+13.01 1.00 VRMS
+6.99 500 mVRMS
0.0 224 mVRMS
-6.99 100 mVRMS
-13.01 50 mVRMS
Chapter 7 Tutorial
Attributes of AC Signals
286

 Loading...
Loading...