Data Transfer File Instructions
Chapter 12
125
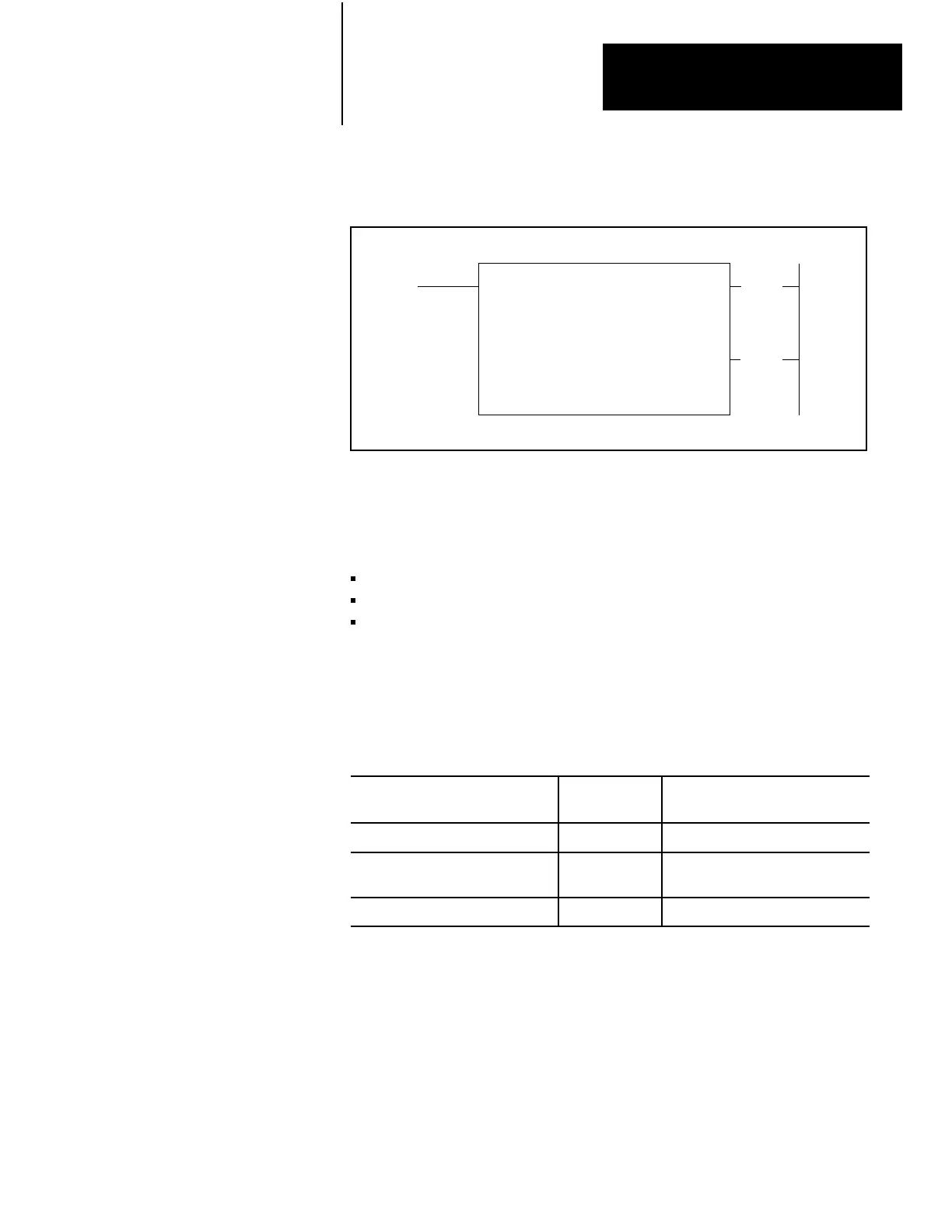
Figure 12.4
Example
of an Internally Indexed File Instruction
FILE-TO-FILE
MOVE
COUNTER ADDR:
214
POSITION: 001
FILE LENGTH: 014
FILE A: 512-527
FILE R: 562-577
RA
TE PER SCAN:
014
214
(EN)
17
214
(DN)
15
Notice that another term has been added to the instruction block: rate per
scan. It defines the number of words in the file operated upon during one
scan. Its value is user-chosen according to how the file operation is to take
place. There are three modes of operation based on rate per scan. They are:
Complete
Distributed complete
Incremental
The relationship between the rate per scan and the modes of operation are
summarized in Table 12.A.
Table 12.A
Modes
of Instruction Operation
Mode of Operation
R = Rate Per
Scan
Number of Words Operated Upon
COMPLETE R = File Length Entire file per scan
DISTRIBUTED COMPLETE 0 < R < File
Length
R words per scan
INCREMENTAL R = 0 One word per rung transition
Complete Mode
In the complete mode, the rate per scan is equal to the file length, and the
entire file is operated upon in one scan. On a false-to-true transition of the
rung condition, the instruction is enabled and the accumulated value of the
file counter is internally indexed from the first to the last word of the file.
As the accumulated value points to each word, the operation defined by the
File instruction is performed. The operation of a File instruction in the
complete mode is shown in Figure 12.5.
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...











