Rockwell Automation Publication 750-PM001N-EN-P - February 2017 439
Appendix C
Application Notes
Voltage Tolerance
Example:
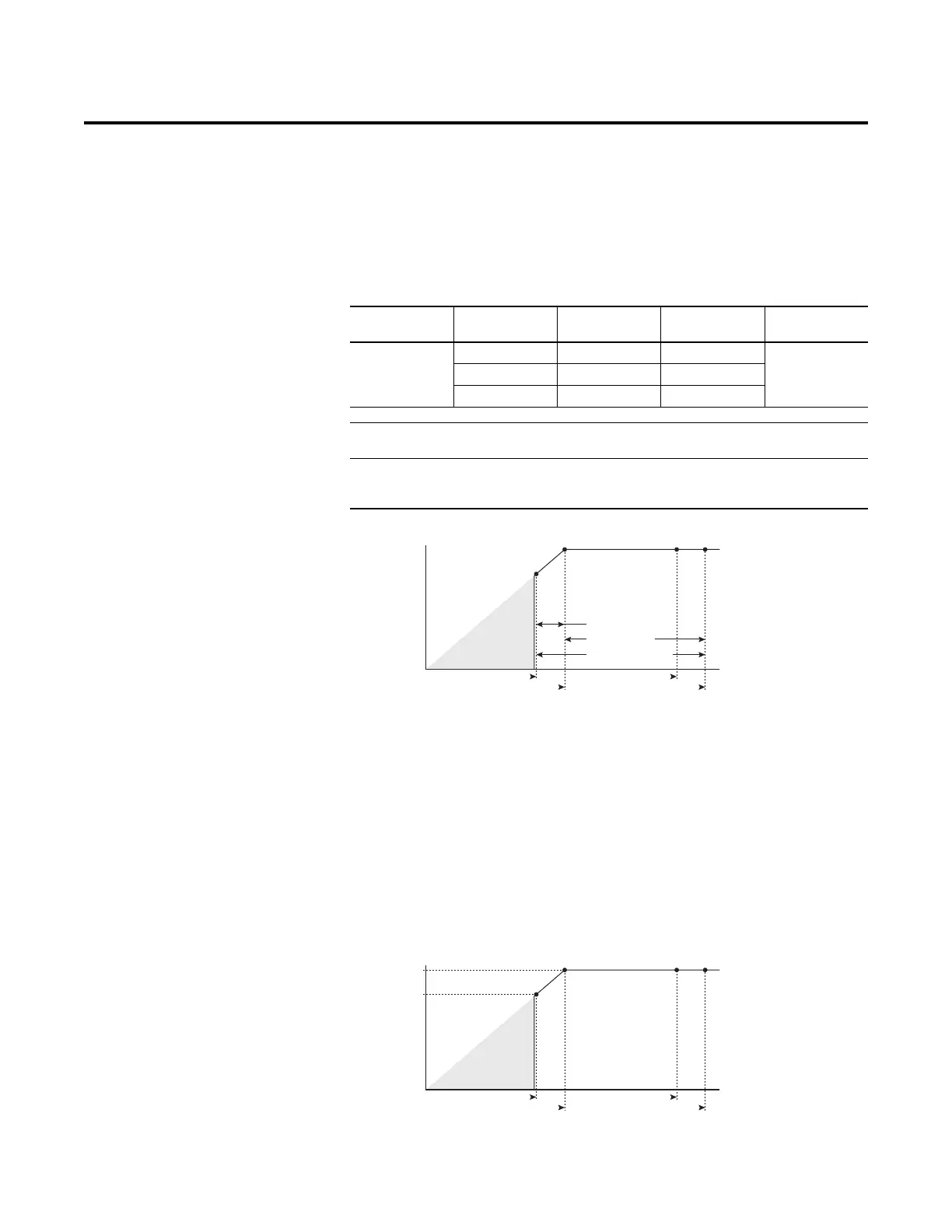
Calculate the maximum power of a 5 Hp, 460V motor that is connected to a
480V rated drive supplied with 342V Actual Line Voltage input.
• Actual Line Voltage / Nominal Motor Voltage = 74.3 %
• 74.3 % 5 Hp = 3.7 Hp
• 74.3 % 60 Hz = 44.6 Hz
At 342V Actual Line Voltage, the maximum power the 5 Hp, 460V motor can
produce is 3.7 Hp at 44.6 Hz.
Drive Rating Nominal Line
Voltage
Nominal Motor
Voltage
Drive Full Power
Range
Drive Operating
Range
380…400 380 380 380…528 342…528
400 400 400…528
480 460 460…528
Drive Full Power Range = Nominal Motor Voltage to Drive Rated Voltage 10 %.
Rated current is available across the entire Drive Full Power Range
Drive Operating Range = Lowest Nominal Motor Voltage - 10 % to Drive Rated Voltage 10 %.
Drive Output is linearly derated when Actual Line Voltage is less than the Nominal
Motor Voltage
Hp @ Motor (Drive Output)
Actual Line Voltage (Drive Input)
Full Power Range
Drive Operating Range
Nominal Motor Voltage -10%
Nominal Motor Voltage
Derated Power Range
No Drive
Output
Drive Rated Voltage
Drive Rated Voltage +10%
5 Hp
3.7 Hp
Hp @ Motor (Drive Output)
Actual Line Voltage (Drive Input)
342V
460V
No Drive
Output
480V
528V
 Loading...
Loading...











