9
The Shock Pulse Method
The BearingChecker is based on the Shock Pulse Method. Measurements with the SPM method give an
indirect measure of impact velocity, i.e. the difference in velocity between two bodies at the moment of
impact. At the point of impact, a mechanical compression wave (a shock pulse) arises instantly in each body.
The peak value of the shock pulse is determined by the impact velocity and is not influenced by the mass
or the shape of the colliding bodies. Shock pulses in rotating ball and roller bearings are caused by impacts
between raceways and rolling elements. From the points of impact the shock pulses travel through the
bearing and the bearing housing. Extensive experience proves that there is a simple relationship between
the bearing’s operating condition and the value of the shock pulses.
A transducer detects the shock pulses in the bearing. The transducer signals are processed in the bearing
detector’s microprocessor and the measured shock pulse values are shown on the display. An headphone
can be connected to the instrument for listening to the shock pulse pattern. Please note that this instru-
ment cannot be used for plain bearings.
Shock pulses are short duration pressure pulses which are generated by mechanical impacts. Mechanical
impacts occur in all rotating rolling bearings because of irregularities in the surfaces of the raceways and
the rolling elements. The magnitude of the shock pulses depends on the impact velocity.
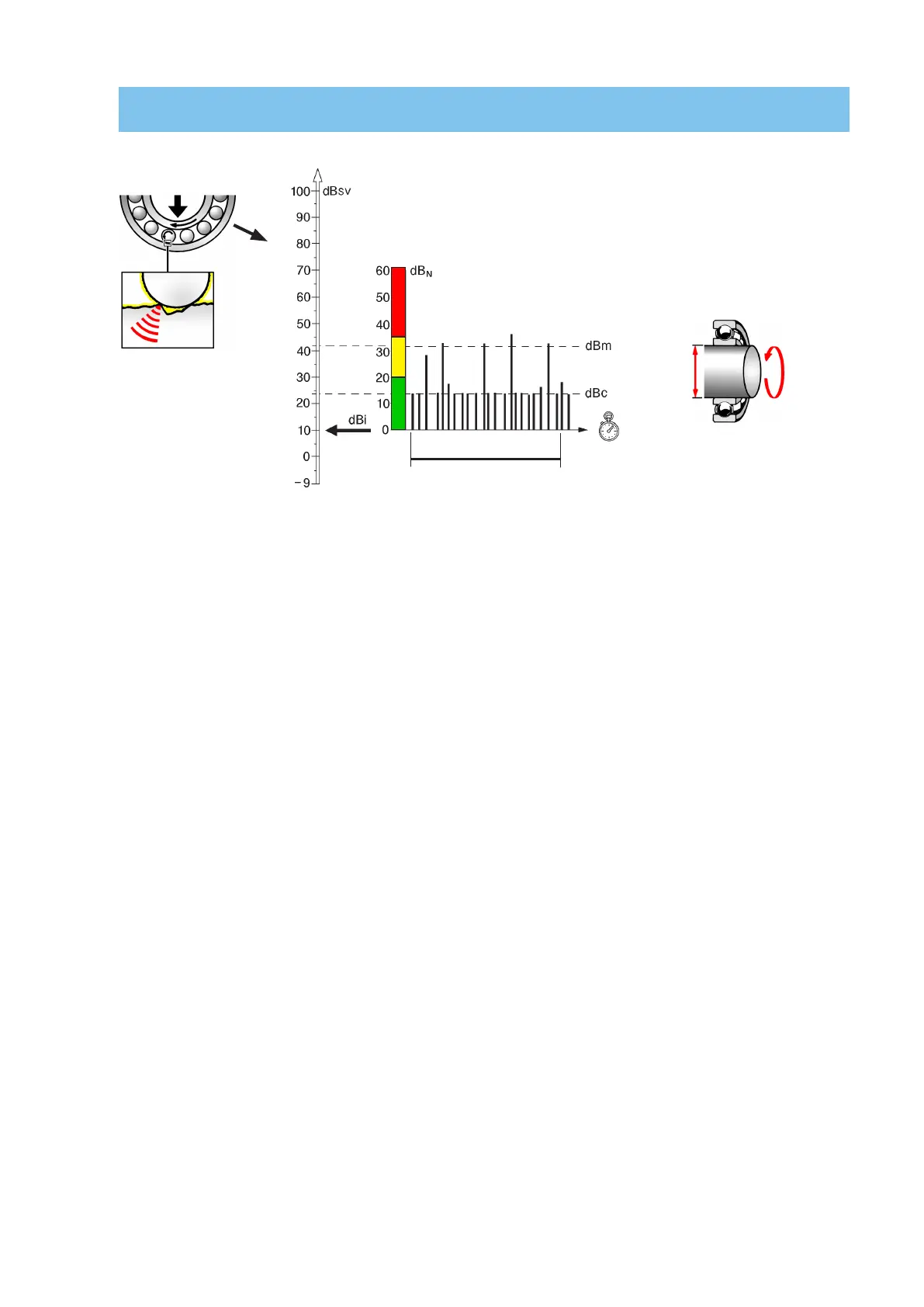
Carpet value dBc
Surface roughness (small irregularities) will cause a rapid sequence of minor shock pulses which together
constitute the shock carpet of the bearing. The magnitude of the shock carpet is expressed by the carpet
value dBc (decibel carpet value). The carpet value is affected by the oil film between rolling elements and
raceways. When the film thickness is normal, the bearing’s carpet value is low. Poor alignment and instal-
lation as well as insufficient lubrication will reduce the thickness of the oil film in the whole or parts of the
bearing. This causes the carpet value dBc to rise above normal.
Maximum value dBm
Bearing damage, i.e. relatively large irregularities in the surfaces, will cause single shock pulses with higher
magnitudes at random intervals. The highest shock pulse value measured on a bearing is called its maximum
value dBm (decibel maximum value). The maximum value dBm is used to determine the operating condition
of the bearing. The carpet value dBc helps to analyze the cause of reduced or bad operating condition.
Shock Pulse Measurement
dBi = Initial value of a bearing
dBc = Carpet value (weak pulses)
dBm = Maximum value (strong pulses)
dBn = Unit for normalized shock level
dBsv = Unit for absolute shock level
rpm
d
The initial value dBi
depends on rpm and
shaft diameter d.
2 seconds

 Loading...
Loading...