12
Example: If the value is 200 mV ( 0.2 V), the probe signal corresponds to 20 °C/%RH;
0mVd.c. corresponds to 0 ºC.
Pressure probes: In case of extreme out of range reading errors, check, first of all, if the
corresponding analogue inputs of these probes are set to accept current signal - 4÷20 mA
(see pages 8,9). Check, also, that the full-scales set in the software correspond to the probe
full scale. Measuring with a volt-meter the voltage between the terminals Bn and M, you can
calculate the current signal coming from the probe, as the analogue input has an impedance of
50 ohms (I=V/R)
The pressure value "Ps" that the probe transmits can be calculated as follows (FS=Full Scale):
Ps=(Vmis : 50 - 0,004) x (FSmax - FSmin) : 0,016 + FSmin
Example: Probe type: FSmin. -0,5 Bar/FSmax. 7 Bar; Voltage: Vmis= 0,5 Vd.c.
Therefore, the pressure value is:
Ps=(0,5:50 - 0,004) X (7 - (-0,5)) : 0,016 + (-0,5)=2,3Bar
Make sure that the capillary of the probe is not obstructed.
NTC Probes : The probe signal is an 'ohm' value depending on temperature.
The table below shows some resistance values at different temperatures. Disconnect the
probe from the interface and measure its resistance: The corresponding temperature value
can be checked by using the following table.
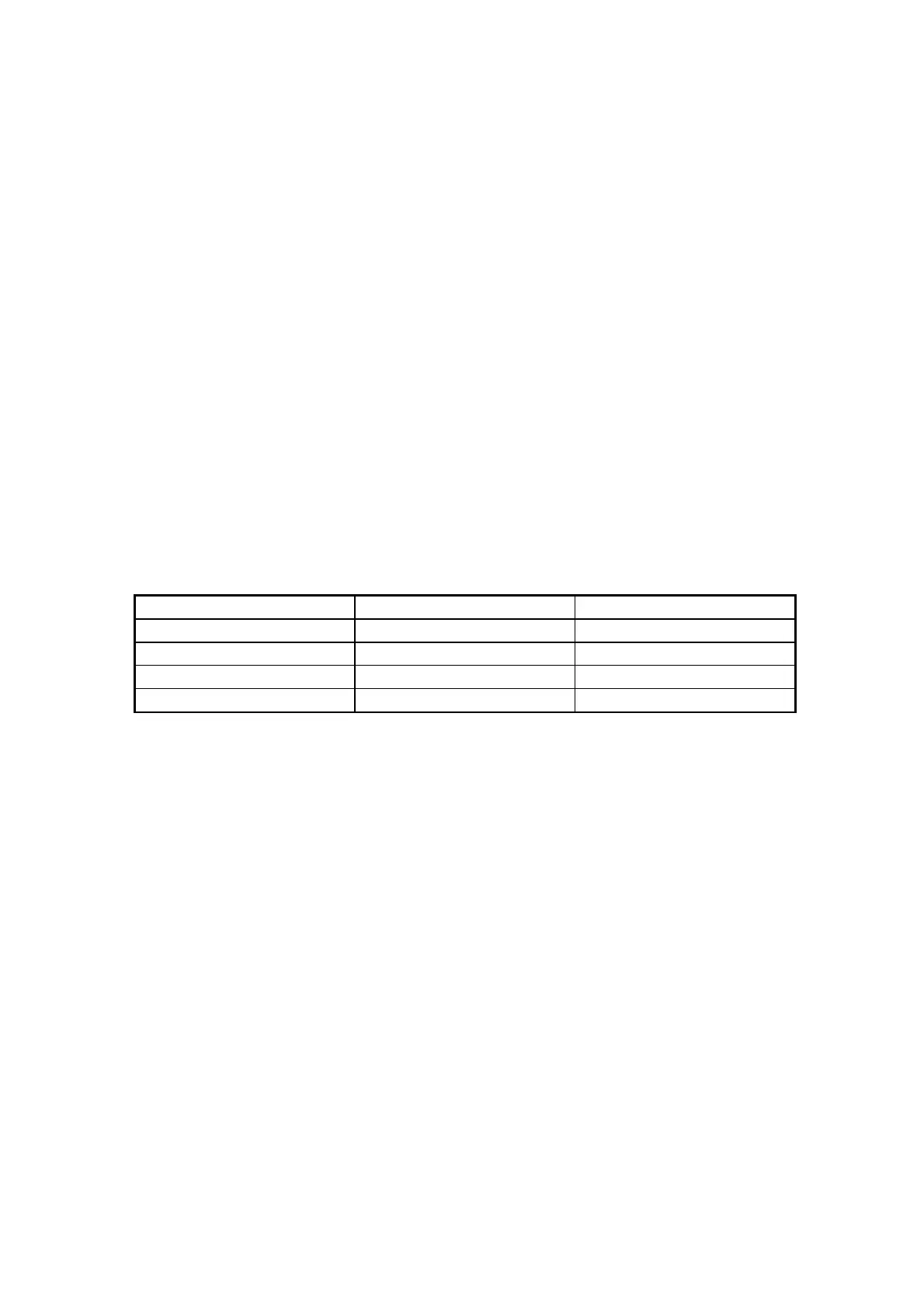
°C KOhm °C KOhm °C KOhm
-20 67,71 0 27,28 20 12,09
-15 53,39 5 22,05 25 10,00
-10 42,25 17 17,96 30 8,31
-5 33,89 15 14,68 35 6,94
Faulty eeprom alarm:
a. Contact the nearest Service Centre.
Macroplus turns on and off repeatedly (watch dog) or it activates some (digital and/or analogue)
outputs randomly.
Check
a. the connections between interfaces and controller (see pages 2 and 4);
b. power cables: It is recommended that they are sited as far from the interfaces'
microprocessor and the control board as possible;
c. the number of incompatibility errors between the physical and logical outputs of the program
(see operation guide). The software, in fact, might transmit a command that is not carried out
due to a software error or to any interference. Check the outputs to be sure of the correct
functioning of the entire system.
 Loading...
Loading...