BGX501-943-R01 Prometer 100 User Manual Page 61 of 72
Appendix E: Calculation Principles
(to be updated)
Current and Voltage
Current and voltage are first harmonic component (fundamental).
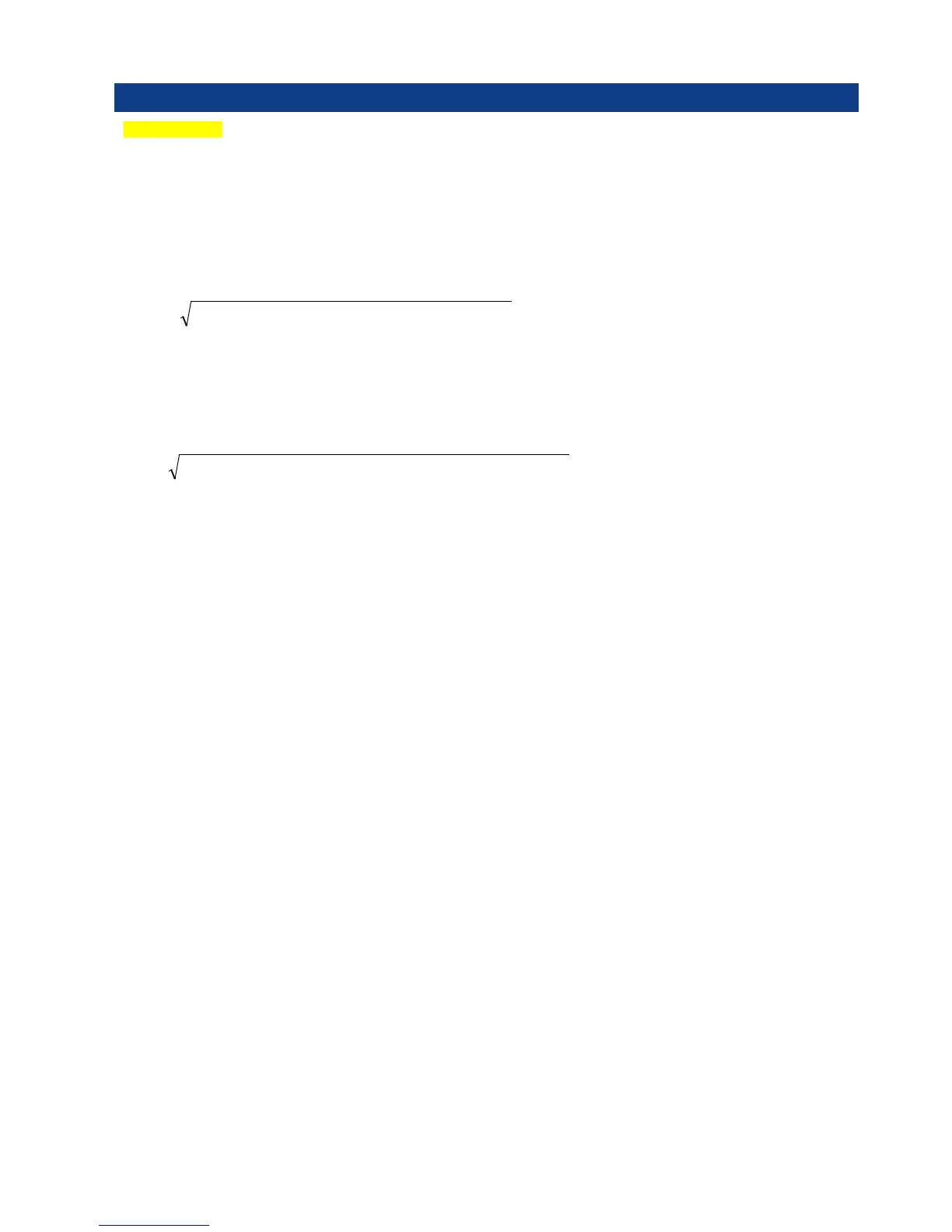
Calculated phase to phase voltage
Phase to phase voltage is calculated from the phase voltages’ fundamental vectors. This calculation is only
made in the 3-element meter; in the 2-element meter, the phase to phase voltage is measured.
)21cos(21221(12
1111
2
1
2
11
pUpUUUUUU −⋅⋅⋅−+=
Calculated I2
In the 2-element meter, I2 is not measured but is calculated for monitoring purposes. It is calculated from the
current’s fundamental vectors.
Current I2’s fundamental harmonic.
2
11
2
11111
))31sin(3())31cos(31(2 pIpIIpIpIIII −⋅+−⋅+=
Voltage unbalance
Class A
The basic measurement of voltage harmonics, for class A, is defined in IEC 61000-4-7 class I. That standard
shall be used to determine a 10/12-cycle gapless harmonic subgroup measurement, denoted U
isg,h
in IEC
61000-4-7.
Power
Harmonic component power
The calculations below are for active power, the calculations for reactive are identical except for that cos-
functions are replaced with sin-functions.
Active power in L1 is calculated for harmonic component n.
Total active power is calculated for harmonic component n.
Phase angle between harmonic component
2-element meter:
For 2-element meters, only the total power is calculated in each harmonic component.
Phase angle between harmonic component
Phase angle between harmonic component
)2cos(332)1cos(112
nnnnnnn
IUIUP
ϕϕ
⋅+⋅⋅=

 Loading...
Loading...